| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We can classify acids by the number of protons per molecule that they can give up in a reaction. Acids such as HCl, HNO 3 , and HCN that contain one ionizable hydrogen atom in each molecule are called monoprotic acids . Their reactions with water are:
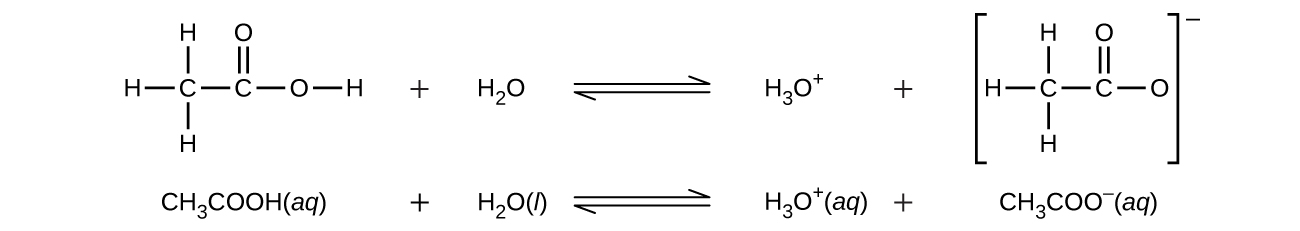
Even though it contains four hydrogen atoms, acetic acid, CH 3 CO 2 H, is also monoprotic because only the hydrogen atom from the carboxyl group (COOH) reacts with bases:
Similarly, monoprotic bases are bases that will accept a single proton.
Diprotic acids contain two ionizable hydrogen atoms per molecule; ionization of such acids occurs in two steps. The first ionization always takes place to a greater extent than the second ionization. For example, sulfuric acid, a strong acid, ionizes as follows:
This stepwise ionization process occurs for all polyprotic acids. When we make a solution of a weak diprotic acid, we get a solution that contains a mixture of acids. Carbonic acid, H 2 CO 3 , is an example of a weak diprotic acid. The first ionization of carbonic acid yields hydronium ions and bicarbonate ions in small amounts.
The bicarbonate ion can also act as an acid. It ionizes and forms hydronium ions and carbonate ions in even smaller quantities.
is larger than by a factor of 10 4 , so H 2 CO 3 is the dominant producer of hydronium ion in the solution. This means that little of the formed by the ionization of H 2 CO 3 ionizes to give hydronium ions (and carbonate ions), and the concentrations of H 3 O + and are practically equal in a pure aqueous solution of H 2 CO 3 .
If the first ionization constant of a weak diprotic acid is larger than the second by a factor of at least 20, it is appropriate to treat the first ionization separately and calculate concentrations resulting from it before calculating concentrations of species resulting from subsequent ionization. This can simplify our work considerably because we can determine the concentration of H 3 O + and the conjugate base from the first ionization, then determine the concentration of the conjugate base of the second ionization in a solution with concentrations determined by the first ionization.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?