| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A balanced equation for a chemical reaction indicates what is reacting and what is produced, but it reveals nothing about how the reaction actually takes place. The reaction mechanism (or reaction path) is the process, or pathway, by which a reaction occurs.
A chemical reaction usually occurs in steps, although it may not always be obvious to an observer. The decomposition of ozone, for example, appears to follow a mechanism with two steps:
We call each step in a reaction mechanism an elementary reaction . Elementary reactions occur exactly as they are written and cannot be broken down into simpler steps. Elementary reactions add up to the overall reaction, which, for the decomposition, is:
Notice that the oxygen atom produced in the first step of this mechanism is consumed in the second step and therefore does not appear as a product in the overall reaction. Species that are produced in one step and consumed in a subsequent step are called intermediates .
While the overall reaction equation for the decomposition of ozone indicates that two molecules of ozone react to give three molecules of oxygen, the mechanism of the reaction does not involve the collision and reaction of two ozone molecules. Rather, it involves a molecule of ozone decomposing to an oxygen molecule and an intermediate oxygen atom; the oxygen atom then reacts with a second ozone molecule to give two oxygen molecules. These two elementary reactions occur exactly as they are shown in the reaction mechanism.
The molecularity of an elementary reaction is the number of reactant species (atoms, molecules, or ions). For example, a unimolecular reaction involves the rearrangement of a single reactant species to produce one or more molecules of product:
The rate equation for a unimolecular reaction is:
A unimolecular reaction may be one of several elementary reactions in a complex mechanism. For example, the reaction:
illustrates a unimolecular elementary reaction that occurs as one part of a two-step reaction mechanism. However, some unimolecular reactions may have only a single reaction in the reaction mechanism. (In other words, an elementary reaction can also be an overall reaction in some cases.) For example, the gas-phase decomposition of cyclobutane, C 4 H 8 , to ethylene, C 2 H 4 , occurs via a unimolecular, single-step mechanism:
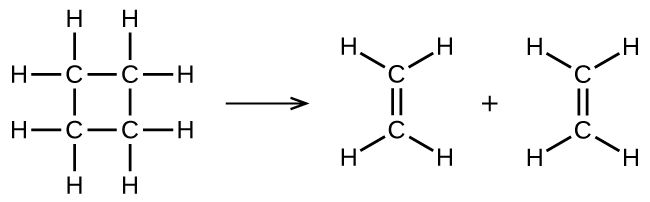
For these unimolecular reactions to occur, all that is required is the separation of parts of single reactant molecules into products.
Chemical bonds do not simply fall apart during chemical reactions. Energy is required to break chemical bonds. The activation energy for the decomposition of C 4 H 8 , for example, is 261 kJ per mole. This means that it requires 261 kilojoules to distort one mole of these molecules into activated complexes that decompose into products:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?