| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As a child, you may have made suspensions such as mixtures of mud and water, flour and water, or a suspension of solid pigments in water, known as tempera paint. These suspensions are heterogeneous mixtures composed of relatively large particles that are visible (or that can be seen with a magnifying glass). They are cloudy, and the suspended particles settle out after mixing. On the other hand, when we make a solution, we prepare a homogeneous mixture in which no settling occurs and in which the dissolved species are molecules or ions. Solutions exhibit completely different behavior from suspensions. A solution may be colored, but it is transparent, the molecules or ions are invisible, and they do not settle out on standing. A group of mixtures called colloids (or colloidal dispersions ) exhibit properties intermediate between those of suspensions and solutions ( [link] ). The particles in a colloid are larger than most simple molecules; however, colloidal particles are small enough that they do not settle out upon standing.
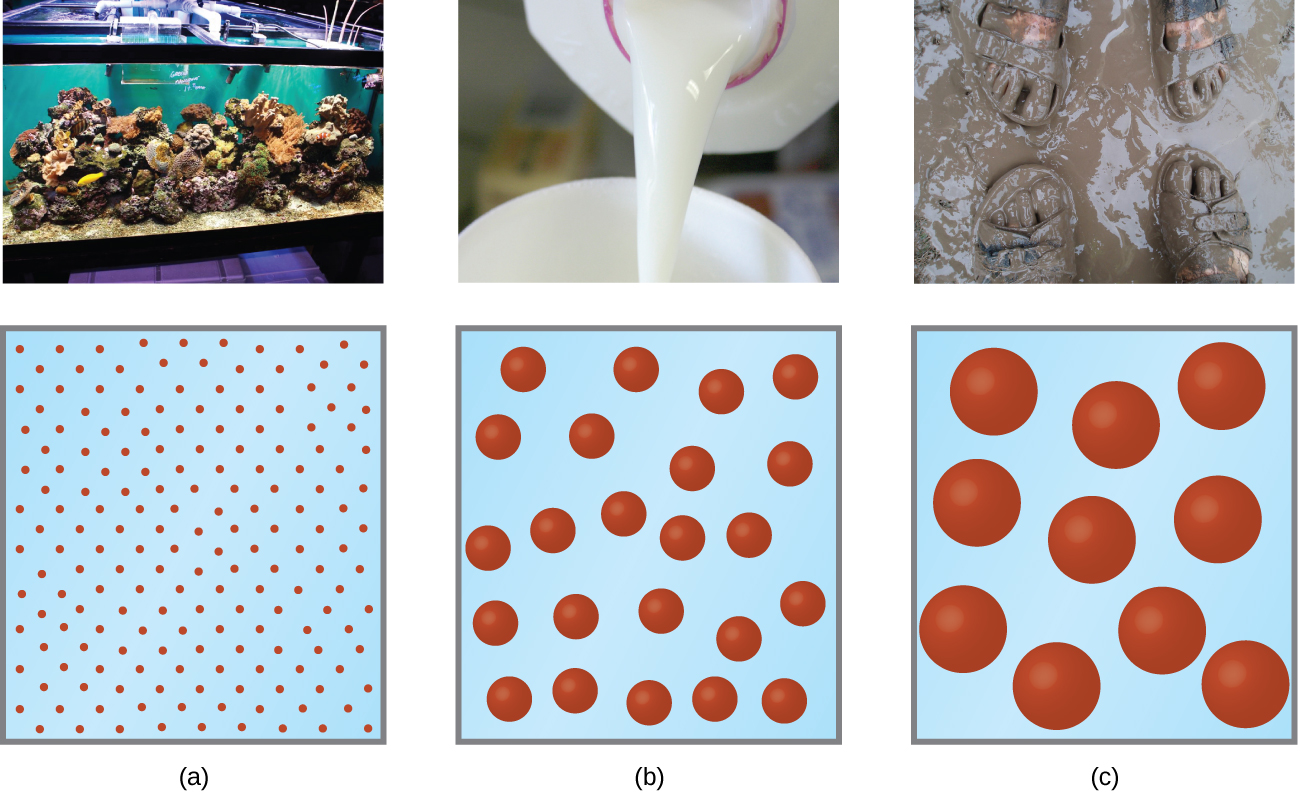
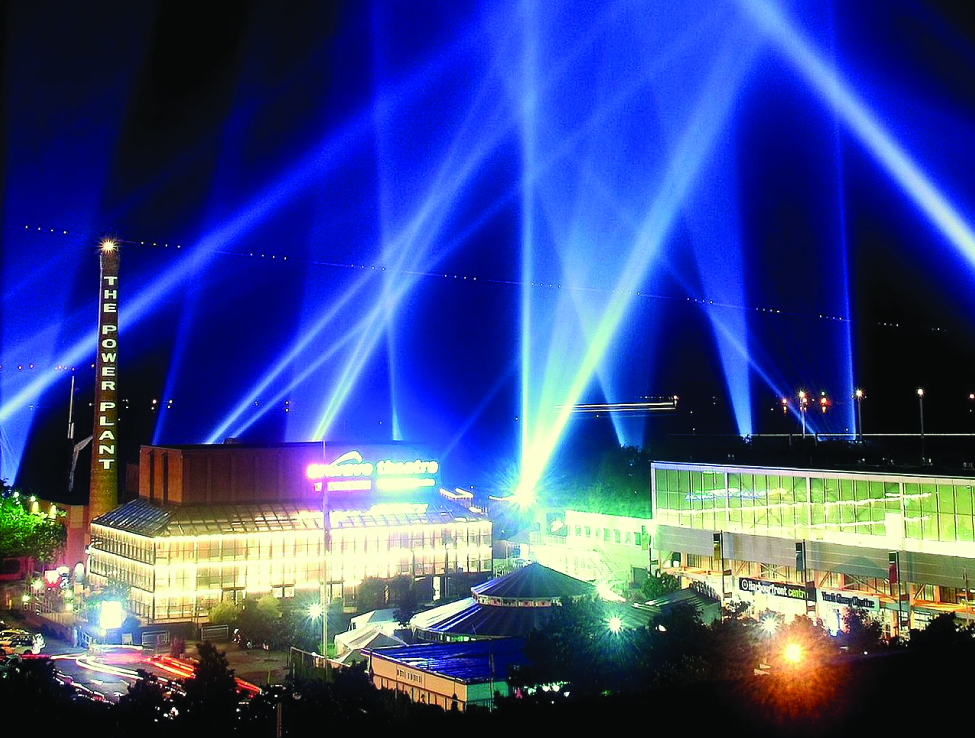
The particles in a colloid are large enough to scatter light, a phenomenon called the Tyndall effect . This can make colloidal mixtures appear cloudy or opaque, such as the searchlight beams shown in [link] . Clouds are colloidal mixtures. They are composed of water droplets that are much larger than molecules, but that are small enough that they do not settle out.

The term “colloid”—from the Greek words kolla , meaning “glue,” and eidos , meaning “like”—was first used in 1861 by Thomas Graham to classify mixtures such as starch in water and gelatin. Many colloidal particles are aggregates of hundreds or thousands of molecules, but others (such as proteins and polymer molecules) consist of a single extremely large molecule. The protein and synthetic polymer molecules that form colloids may have molecular masses ranging from a few thousand to many million atomic mass units.
Analogous to the identification of solution components as “solute” and “solvent,” the components of a colloid are likewise classified according to their relative amounts. The particulate component typically present in a relatively minor amount is called the dispersed phase and the substance or solution throughout which the particulate is dispersed is called the dispersion medium . Colloids may involve virtually any combination of physical states (gas in liquid, liquid in solid, solid in gas, etc.), as illustrated by the examples of colloidal systems given in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?