| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Business Fundamentals was developed by the Global Text Project, which is working to create open-content electronictextbooks that are freely available on the website http://globaltext.terry.uga.edu. Distribution is also possible viapaper, CD, DVD, and via this collaboration, through Connexions. The goal is to make textbooks available to the manywho cannot afford them. For more information on getting involved with the Global Text Project or Connexions email us atdrexel@uga.edu and dcwill@cnx.org.
Editor: John Maynard (The University of Georgia, USA)
Contributors: Suzanne Barnett, Lydia Jones, Carol McDonell, Bernie Meineke, Tammy Segura (Georgia Small Business Development Center, USA)
Reviewer: Dr Gideon Markman (The University of Georgia, USA)
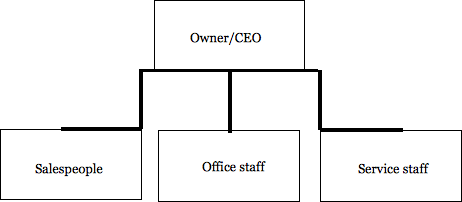
By definition, a small business is typically a flat, centralized organization. The founder/owner is the boss and makes all the critical decisions. However, as the personnel count grows, the firm’s structure typically expands either horizontally (flat) or vertically (tall). Again, various factors including the owner’s management style, might affect what type of structure a business assumes.
Flat organizations follow the decentralized approach, or organic system. There are fewer levels of management which creates an environment for faster growth and response between all levels. Organizations that follow this type of structure have wider spans of supervisory control and have more horizontal communication. This type of structure promotes task interdependence with less attention to formal procedures.
More decisions are made at the middle levels of the organization. They are less bureaucratic and less structured. Externally, the organization as a whole becomes more adaptable to its market and can quickly react to changes. Internally, the organization as a whole encourages more participation between all levels of the organization. As a result, all levels have the potential of working more closely together which enhances a closer working environment with better communication and creativity.
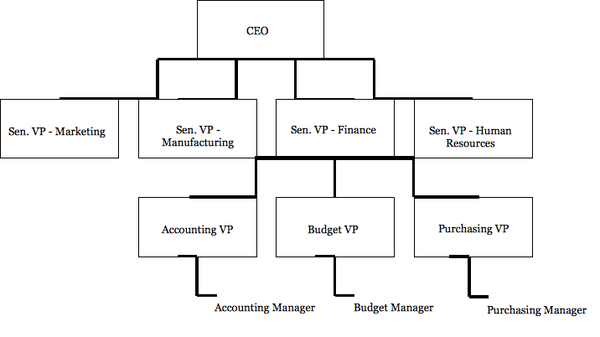
A tall structure is a more formal, bureaucratic organization or mechanistic system. In this environment, multiple levels of management control decision making processes and employees within the organization. When numerous levels become involved in daily operations, decision-making tends to be more impersonal. Since this type of structure has more levels, the division of labor is much more specialized. Departments can become more compartmentalized, which increases the communication within them, but does not lend itself to communication with other departments.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Business fundamentals' conversation and receive update notifications?