| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
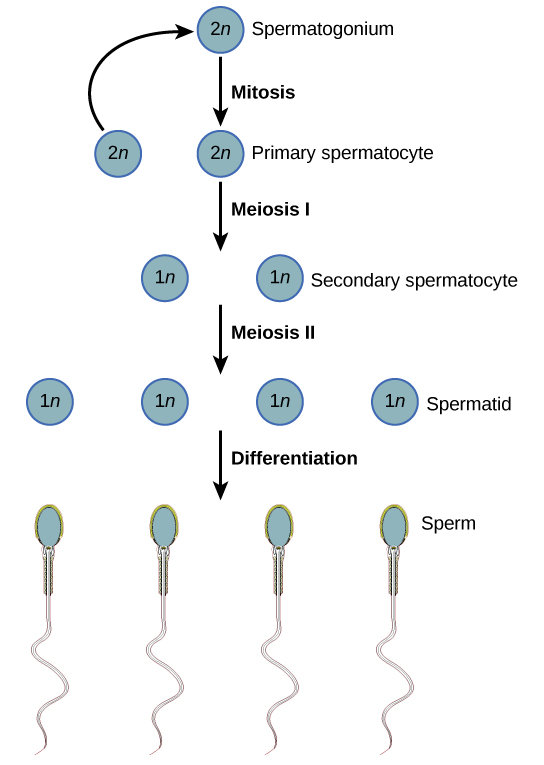
Visit this site to see the process of spermatogenesis.
The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with hormones from reproductive tissues and organs. In both sexes, the hypothalamus monitors and causes the release of hormones from the anterior pituitary gland. When the reproductive hormone is required, the hypothalamus sends a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) to the anterior pituitary. This causes the release of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary into the blood. Although these hormones are named after their functions in female reproduction, they are produced in both sexes and play important roles in controlling reproduction. Other hormones have specific functions in the male and female reproductive systems.
At the onset of puberty, the hypothalamus causes the release of FSH and LH into the male system for the first time. FSH enters the testes and stimulates the Sertoli cells located in the walls of the seminiferous tubules to begin promoting spermatogenesis ( [link] ). LH also enters the testes and stimulates the interstitial cells of Leydig, located in between the walls of the seminiferous tubules, to make and release testosterone into the testes and the blood.
Testosterone stimulates spermatogenesis. This hormone is also responsible for the secondary sexual characteristics that develop in the male during adolescence. The secondary sex characteristics in males include a deepening of the voice, the growth of facial, axillary, and pubic hair, an increase in muscle bulk, and the beginnings of the sex drive.
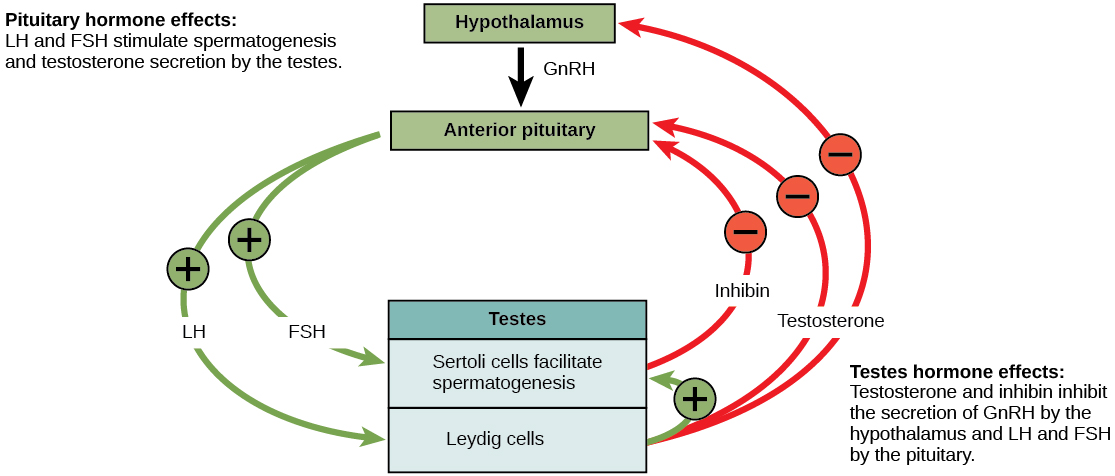
A negative feedback system occurs in the male with rising levels of testosterone acting on the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary to inhibit the release of GnRH, FSH, and LH. In addition, the Sertoli cells produce the hormone inhibin , which is released into the blood when the sperm count is too high. This inhibits the release of GnRH and FSH, which will cause spermatogenesis to slow down. If the sperm count reaches a low of 20 million/mL, the Sertoli cells cease the release of inhibin, and the sperm count increases.
The reproductive structures that evolved in land animals allow males and females to mate, fertilize internally, and support the growth and development of offspring. Gametogenesis, the production of sperm in the male (spermatogenesis), takes place through the process of meiosis.
The male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by hormones released from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary and hormones from reproductive tissues and organs. The hypothalamus monitors the need for FSH and LH production and release from the anterior pituitary. FSH and LH affect reproductive structures to cause the formation of sperm and the preparation of eggs for release and possible fertilization. In the male, FSH and LH stimulate Sertoli cells and interstitial cells of Leydig in the testes to facilitate sperm production. The Leydig cells produce testosterone, which also is responsible for the secondary sexual characteristics of males. In females, FSH and LH cause estrogen and progesterone to be produced. They regulate the female reproductive cycle, which is divided into the ovarian cycle and the menstrual cycle.
[link] Which of the following statements about the male reproductive system is false?
[link] D

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?