| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Visit this link interactive lab to see more information about neurogenesis, including an interactive laboratory simulation and a video that explains how BrdU labels new cells.
While glial cells are often thought of as the supporting cast of the nervous system, the number of glial cells in the brain actually outnumbers the number of neurons by a factor of 10. Neurons would be unable to function without the vital roles that are fulfilled by these glial cells. Glia guide developing neurons to their destinations, buffer ions and chemicals that would otherwise harm neurons, and provide myelin sheaths around axons. When glia do not function properly, the result can be disastrous—most brain tumors are caused by mutations in glia.
All functions performed by the nervous system—from a simple motor reflex to more advanced functions like making a memory or a decision—require neurons to communicate with one another. Neurons communicate between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites, and sometimes the cell body, of another neuron across the gap between them, known as the synaptic cleft . When an action potential reaches the end of an axon it stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft between the synaptic knob of the axon and the post-synaptic membrane of the dendrite or soma of the next cell. The neurotransmitter is released through exocytosis of vesicles containing the neurotransmitter molecules. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors in the post-synaptic membrane. These receptor molecules are chemically regulated ion channels and will open, allowing sodium to enter the cell. If sufficient neurotransmitter has been released an action potential may be initiated in the next cell, but this is not guaranteed. If insufficient neurotransmitter is released the nerve signal will die at this point. There are a number of different neurotransmitters that are specific to neuron types that have specific functions.
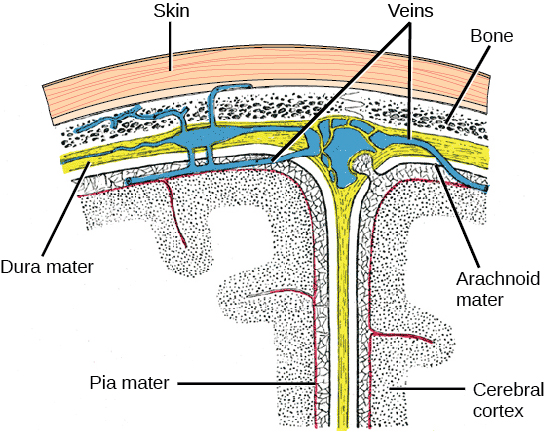
The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain and spinal cord and is covered with three layers of protective coverings called meninges (“meninges” is derived from the Greek and means “membranes”) ( [link] ). The outermost layer is the dura mater, the middle layer is the web-like arachnoid mater, and the inner layer is the pia mater, which directly contacts and covers the brain and spinal cord. The space between the arachnoid and pia maters is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) . The brain floats in CSF, which acts as a cushion and shock absorber.
The brain is the part of the central nervous system that is contained in the cranial cavity of the skull. It includes the cerebral cortex, limbic system, basal ganglia, thalamus, hypothalamus, cerebellum, brainstem, and retinas. The outermost part of the brain is a thick piece of nervous system tissue called the cerebral cortex . The cerebral cortex, limbic system, and basal ganglia make up the two cerebral hemispheres. A thick fiber bundle called the corpus callosum (corpus = “body”; callosum = “tough”) connects the two hemispheres. Although there are some brain functions that are localized more to one hemisphere than the other, the functions of the two hemispheres are largely redundant. In fact, sometimes (very rarely) an entire hemisphere is removed to treat severe epilepsy. While patients do suffer some deficits following the surgery, they can have surprisingly few problems, especially when the surgery is performed on children who have very immature nervous systems.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?