| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In humans, as well as in many other animals and some plants, the sex of the individual is determined by sex chromosomes—one pair of non-homologous chromosomes. Until now, we have only considered inheritance patterns among non-sex chromosomes, or autosomes. In addition to 22 homologous pairs of autosomes, human females have a homologous pair of X chromosomes, whereas human males have an XY chromosome pair. Although the Y chromosome contains a small region of similarity to the X chromosome so that they can pair during meiosis, the Y chromosome is much shorter and contains fewer genes. When a gene being examined is present on the X, but not the Y, chromosome, it is X-linked .
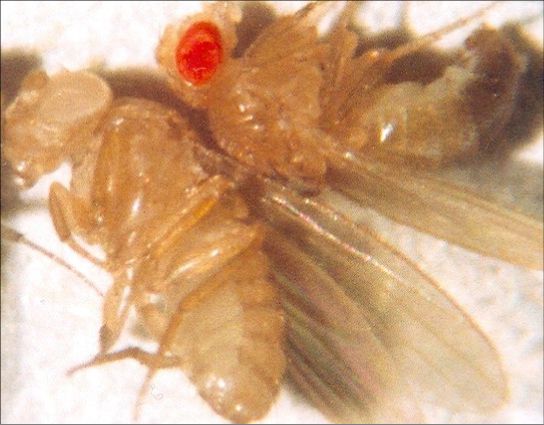
Eye color in Drosophila , the common fruit fly, was the first X-linked trait to be identified. Thomas Hunt Morgan mapped this trait to the X chromosome in 1910. Like humans, Drosophila males have an XY chromosome pair, and females are XX. In flies the wild-type eye color is red (X W ) and is dominant to white eye color (X w ) ( [link] ). Because of the location of the eye-color gene, reciprocal crosses do not produce the same offspring ratios. Males are said to be hemizygous , in that they have only one allele for any X-linked characteristic. Hemizygosity makes descriptions of dominance and recessiveness irrelevant for XY males. Drosophila males lack the white gene on the Y chromosome; that is, their genotype can only be X W Y or X w Y. In contrast, females have two allele copies of this gene and can be X W X W , X W X w , or X w X w .

In an X-linked cross, the genotypes of F 1 and F 2 offspring depend on whether the recessive trait was expressed by the male or the female in the P generation. With respect to Drosophila eye color, when the P male expresses the white-eye phenotype and the female is homozygously red-eyed, all members of the F 1 generation exhibit red eyes ( [link] ). The F 1 females are heterozygous (X W X w ), and the males are all X W Y, having received their X chromosome from the homozygous dominant P female and their Y chromosome from the P male. A subsequent cross between the X W X w female and the X W Y male would produce only red-eyed females (with X W X W or X W X w genotypes) and both red- and white-eyed males (with X W Y or X w Y genotypes). Now, consider a cross between a homozygous white-eyed female and a male with red eyes. The F 1 generation would exhibit only heterozygous red-eyed females (X W X w ) and only white-eyed males (X w Y). Half of the F 2 females would be red-eyed (X W X w ) and half would be white-eyed (X w X w ). Similarly, half of the F 2 males would be red-eyed (X W Y) and half would be white-eyed (X w Y).
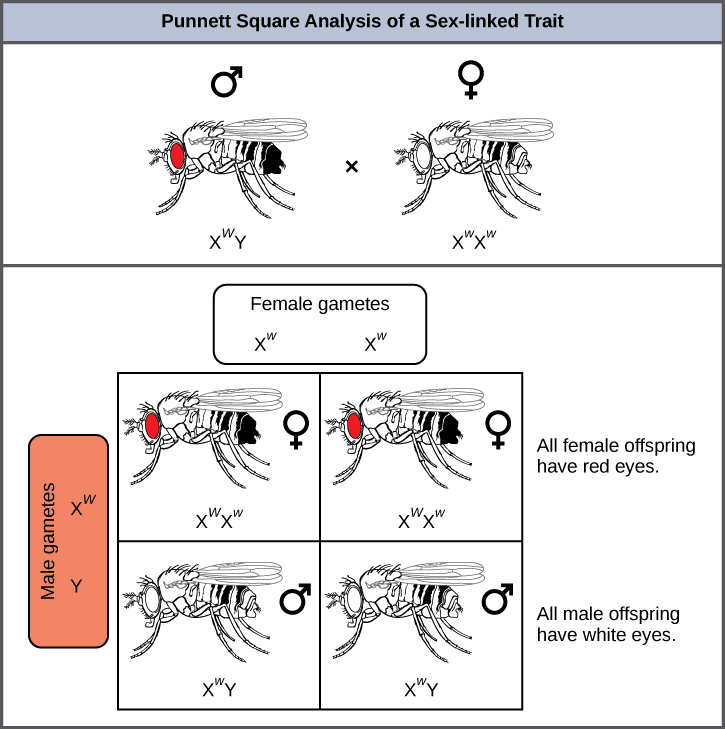
What ratio of offspring would result from a cross between a white-eyed male and a female that is heterozygous for red eye color?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?