| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The post-anal tail is a posterior elongation of the body extending beyond the anus. The tail contains skeletal elements and muscles, which provide a source of locomotion in aquatic species, such as fishes. In some terrestrial vertebrates, the tail may also function in balance, locomotion, courting, and signaling when danger is near. In many species, the tail is absent or reduced; for example, in apes, including humans, it is present in the embryo, but reduced in size and nonfunctional in adults.
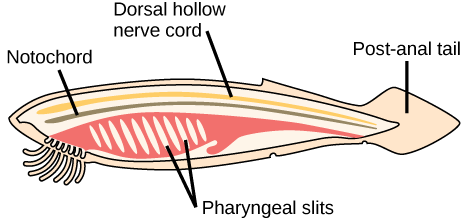
Which of the following statements about common features of chordates is true?
In addition to the vertebrates, the phylum Chordata contains two clades of invertebrates: Urochordata (tunicates) and Cephalochordata (lancelets). Members of these groups possess the four distinctive features of chordates at some point during their development.
The tunicates ( [link] ) are also called sea squirts. The name tunicate derives from the cellulose-like carbohydrate material, called the tunic, which covers the outer body. Although tunicates are classified as chordates, the adult forms are much modified in body plan and do not have a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, or a post-anal tail, although they do have pharyngeal slits. The larval form possesses all four structures. Most tunicates are hermaphrodites. Tunicate larvae hatch from eggs inside the adult tunicate’s body. After hatching, a tunicate larva swims for a few days until it finds a suitable surface on which it can attach, usually in a dark or shaded location. It then attaches by the head to the substrate and undergoes metamorphosis into the adult form, at which point the notochord, nerve cord, and tail disappear.
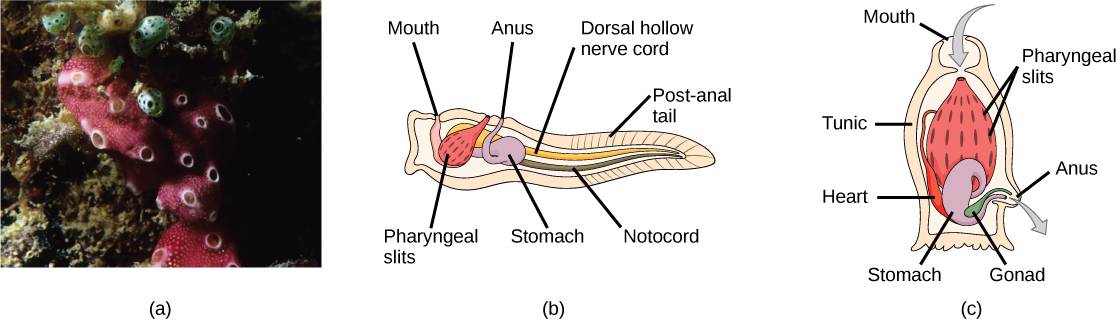
Most tunicates live a sessile existence in shallow ocean waters and are suspension feeders. The primary foods of tunicates are plankton and detritus. Seawater enters the tunicate’s body through its incurrent siphon. Suspended material is filtered out of this water by a mucus net (pharyngeal slits) and is passed into the intestine through the action of cilia. The anus empties into the excurrent siphon, which expels wastes and water.
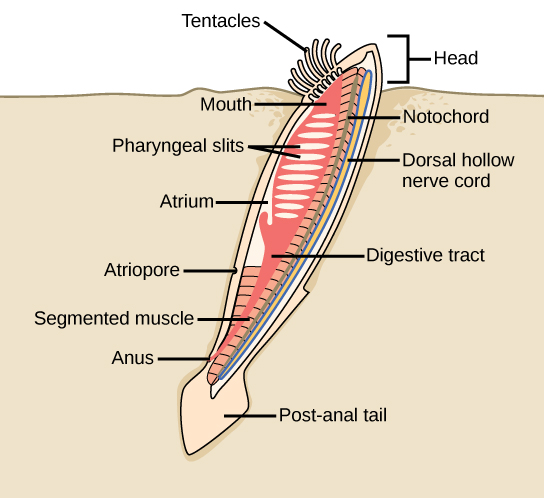
Lancelets possess a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail in the adult stage ( [link] ). The notochord extends into the head, which gives the subphylum its name (Cephalochordata). Extinct fossils of this subphylum date to the middle of the Cambrian period (540–488 mya).The living forms, the lancelets, are named for their blade-like shape. Lancelets are only a few centimeters long and are usually found buried in sand at the bottom of warm temperate and tropical seas. Like tunicates, they are suspension feeders.
Echinoderms are deuterostome marine organisms. This phylum of animals bear a calcareous endoskeleton composed of ossicles covered by a spiny skin. Echinoderms possess a water-based circulatory system. The madreporite is the point of entry and exit for water for the water vascular system.
The characteristic features of Chordata are a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. Chordata contains two clades of invertebrates: Urochordata (tunicates) and Cephalochordata (lancelets), together with the vertebrates. Most tunicates live on the ocean floor and are suspension feeders. Lancelets are suspension feeders that feed on phytoplankton and other microorganisms.
[link] Which of the following statements about common features of chordates is true?
[link] A

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?