| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
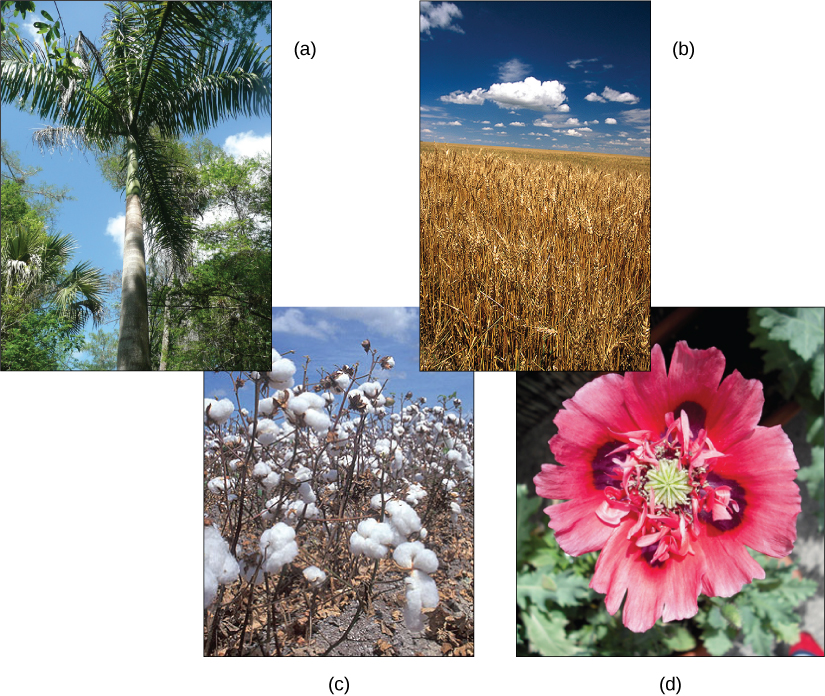
Plants play an integral role in all aspects of life on the planet, shaping the physical terrain, influencing the climate, and maintaining life as we know it. For millennia, human societies have depended on plants for nutrition and medicinal compounds, and for many industrial by-products, such as timber, paper, dyes, and textiles. Palms provide materials including rattans, oils, and dates. Wheat is grown to feed both human and animal populations. The cotton boll flower is harvested and its fibers transformed into clothing or pulp for paper. The showy opium poppy is valued both as an ornamental flower and as a source of potent opiate compounds.
Current evolutionary thought holds that all plants are monophyletic: that is, descendants of a single common ancestor. The evolutionary transition from water to land imposed severe constraints on the ancestors of contemporary plants. Plants had to evolve strategies to avoid drying out, to disperse reproductive cells in air, for structural support, and to filter sunlight. While seed plants developed adaptations that allowed them to populate even the most arid habitats on Earth, full independence from water did not happen in all plants, and most seedless plants still require a moist environment.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?