| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
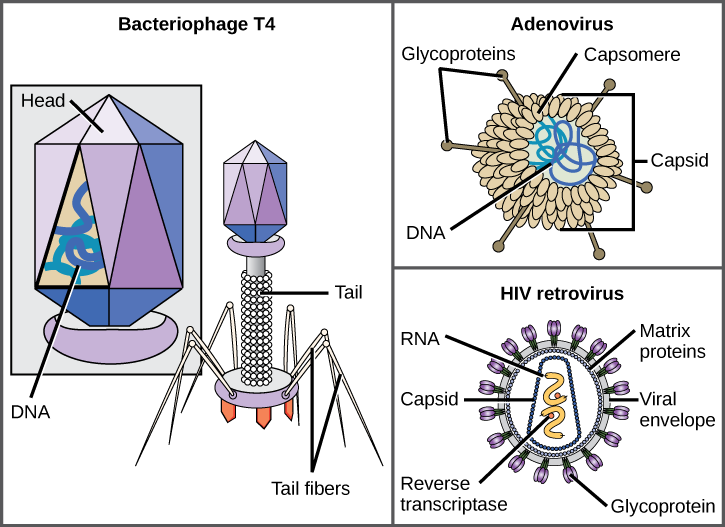
Which of the following statements about virus structure is true?
Unlike nearly all living organisms that use DNA as their genetic material, viruses may use either DNA or RNA as theirs. The virus core contains the genome or total genetic content of the virus. Viral genomes tend to be small, containing only those genes that encode proteins that the virus cannot get from the host cell. This genetic material may be single- or double-stranded. It may also be linear or circular. While most viruses contain a single nucleic acid, others have genomes that have several, which are called segments.
In DNA viruses, the viral DNA directs the host cell’s replication proteins to synthesize new copies of the viral genome and to transcribe and translate that genome into viral proteins. DNA viruses cause human diseases, such as chickenpox, hepatitis B, and some venereal diseases, like herpes and genital warts.
RNA viruses contain only RNA as their genetic material. To replicate their genomes in the host cell, the RNA viruses encode enzymes that can replicate RNA into DNA, which cannot be done by the host cell. These RNA polymerase enzymes are more likely to make copying errors than DNA polymerases, and therefore often make mistakes during transcription. For this reason, mutations in RNA viruses occur more frequently than in DNA viruses. This causes them to change and adapt more rapidly to their host. Human diseases caused by RNA viruses include hepatitis C, measles, and rabies.
To understand the features shared among different groups of viruses, a classification scheme is necessary. As most viruses are not thought to have evolved from a common ancestor, however, the methods that scientists use to classify living things are not very useful. Biologists have used several classification systems in the past, based on the morphology and genetics of the different viruses. However, these earlier classification methods grouped viruses differently, based on which features of the virus they were using to classify them. The most commonly used classification method today is called the Baltimore classification scheme and is based on how messenger RNA (mRNA) is generated in each particular type of virus.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?