| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
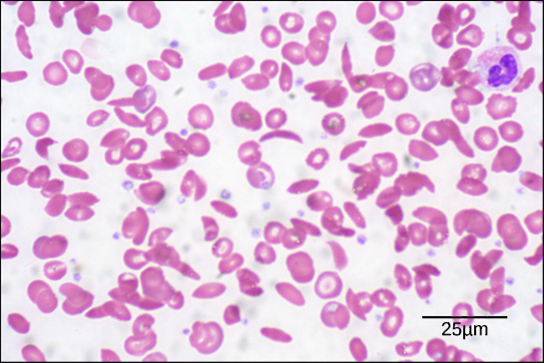
Diseases like sickle cell anemia and thalassemia decrease the blood’s ability to deliver oxygen to tissues and its oxygen-carrying capacity. In sickle cell anemia , the shape of the red blood cell is crescent-shaped, elongated, and stiffened, reducing its ability to deliver oxygen ( [link] ). In this form, red blood cells cannot pass through the capillaries. This is painful when it occurs. Thalassemia is a rare genetic disease caused by a defect in either the alpha or the beta subunit of Hb. Patients with thalassemia produce a high number of red blood cells, but these cells have lower-than-normal levels of hemoglobin. Therefore, the oxygen-carrying capacity is diminished.
Carbon dioxide molecules are transported in the blood from body tissues to the lungs by one of three methods: dissolution directly into the blood, binding to hemoglobin, or carried as a bicarbonate ion. Several properties of carbon dioxide in the blood affect its transport. First, carbon dioxide is more soluble in blood than oxygen. About 5 to 7 percent of all carbon dioxide is dissolved in the plasma. Second, carbon dioxide can bind to plasma proteins or can enter red blood cells and bind to hemoglobin. This form transports about 10 percent of the carbon dioxide. When carbon dioxide binds to hemoglobin, a molecule called carbaminohemoglobin is formed. Binding of carbon dioxide to hemoglobin is reversible. Therefore, when it reaches the lungs, the carbon dioxide can freely dissociate from the hemoglobin and be expelled from the body.
Third, the majority of carbon dioxide molecules (85 percent) are carried as part of the bicarbonate buffer system . In this system, carbon dioxide diffuses into the red blood cells. Carbonic anhydrase (CA) within the red blood cells quickly converts the carbon dioxide into carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3 ). Carbonic acid is an unstable intermediate molecule that immediately dissociates into bicarbonate ions and hydrogen (H + ) ions. Since carbon dioxide is quickly converted into bicarbonate ions, this reaction allows for the continued uptake of carbon dioxide into the blood down its concentration gradient. It also results in the production of H + ions. If too much H + is produced, it can alter blood pH. However, hemoglobin binds to the free H + ions and thus limits shifts in pH. The newly synthesized bicarbonate ion is transported out of the red blood cell into the liquid component of the blood in exchange for a chloride ion (Cl - ); this is called the chloride shift . When the blood reaches the lungs, the bicarbonate ion is transported back into the red blood cell in exchange for the chloride ion. The H + ion dissociates from the hemoglobin and binds to the bicarbonate ion. This produces the carbonic acid intermediate, which is converted back into carbon dioxide through the enzymatic action of CA. The carbon dioxide produced is expelled through the lungs during exhalation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?