| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
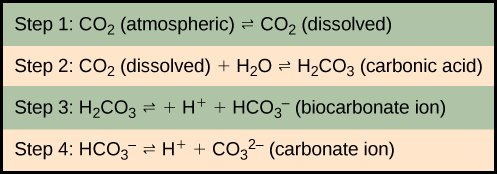
The equilibrium coefficients are such that more than 90 percent of the carbon in the ocean is found as bicarbonate ions. Some of these ions combine with seawater calcium to form calcium carbonate (CaCO 3 ), a major component of marine organism shells. These organisms eventually form sediments on the ocean floor. Over geologic time, the calcium carbonate forms limestone, which comprises the largest carbon reservoir on Earth.
On land, carbon is stored in soil as a result of the decomposition of living organisms (by decomposers) or from weathering of terrestrial rock and minerals. This carbon can be leached into the water reservoirs by surface runoff. Deeper underground, on land and at sea, are fossil fuels: the anaerobically decomposed remains of plants that take millions of years to form. Fossil fuels are considered a non-renewable resource because their use far exceeds their rate of formation. A non-renewable resource , such as fossil fuel, is either regenerated very slowly or not at all. Another way for carbon to enter the atmosphere is from land (including land beneath the surface of the ocean) by the eruption of volcanoes and other geothermal systems. Carbon sediments from the ocean floor are taken deep within the Earth by the process of subduction : the movement of one tectonic plate beneath another. Carbon is released as carbon dioxide when a volcano erupts or from volcanic hydrothermal vents.
Carbon dioxide is also added to the atmosphere by the animal husbandry practices of humans. The large numbers of land animals raised to feed the Earth’s growing population results in increased carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere due to farming practices and the respiration and methane production. This is another example of how human activity indirectly affects biogeochemical cycles in a significant way. Although much of the debate about the future effects of increasing atmospheric carbon on climate change focuses on fossils fuels, scientists take natural processes, such as volcanoes and respiration, into account as they model and predict the future impact of this increase.
Getting nitrogen into the living world is difficult. Plants and phytoplankton are not equipped to incorporate nitrogen from the atmosphere (which exists as tightly bonded, triple covalent N 2 ) even though this molecule comprises approximately 78 percent of the atmosphere. Nitrogen enters the living world via free-living and symbiotic bacteria, which incorporate nitrogen into their macromolecules through nitrogen fixation (conversion of N 2 ). Cyanobacteria live in most aquatic ecosystems where sunlight is present; they play a key role in nitrogen fixation. Cyanobacteria are able to use inorganic sources of nitrogen to “fix” nitrogen. Rhizobium bacteria live symbiotically in the root nodules of legumes (such as peas, beans, and peanuts) and provide them with the organic nitrogen they need. Free-living bacteria, such as Azotobacter , are also important nitrogen fixers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?