| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
All mammals have lungs that are the main organs for breathing. Lung capacity has evolved to support the animal’s activities. During inhalation, the lungs expand with air, and oxygen diffuses across the lung’s surface and enters the bloodstream. During exhalation, the lungs expel air and lung volume decreases. In the next few sections, the process of human breathing will be explained.
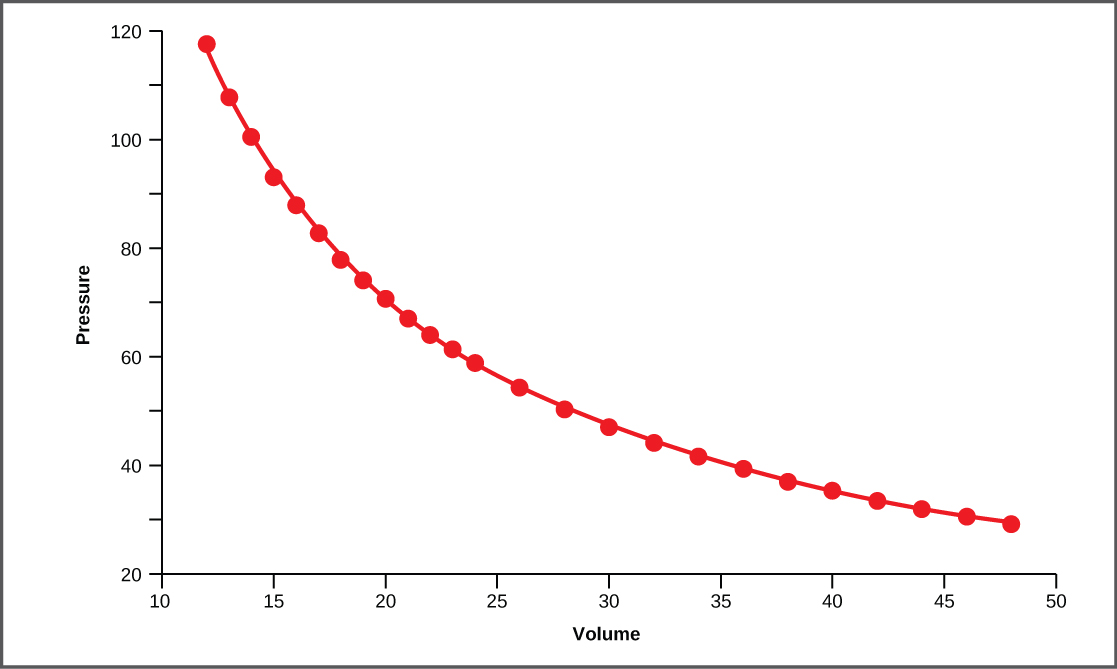
Boyle’s Law is the gas law that states that in a closed space, pressure and volume are inversely related. As volume decreases, pressure increases and vice versa ( [link] ). The relationship between gas pressure and volume helps to explain the mechanics of breathing.
There is always a slightly negative pressure within the thoracic cavity, which aids in keeping the airways of the lungs open. During inhalation, volume increases as a result of contraction of the diaphragm, and pressure decreases (according to Boyle’s Law). This decrease of pressure in the thoracic cavity relative to the environment makes the cavity less than the atmosphere ( [link] a ). Because of this drop in pressure, air rushes into the respiratory passages. To increase the volume of the lungs, the chest wall expands. This results from the contraction of the intercostal muscles , the muscles that are connected to the rib cage. Lung volume expands because the diaphragm contracts and the intercostals muscles contract, thus expanding the thoracic cavity. This increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity lowers pressure compared to the atmosphere, so air rushes into the lungs, thus increasing its volume. The resulting increase in volume is largely attributed to an increase in alveolar space, because the bronchioles and bronchi are stiff structures that do not change in size.
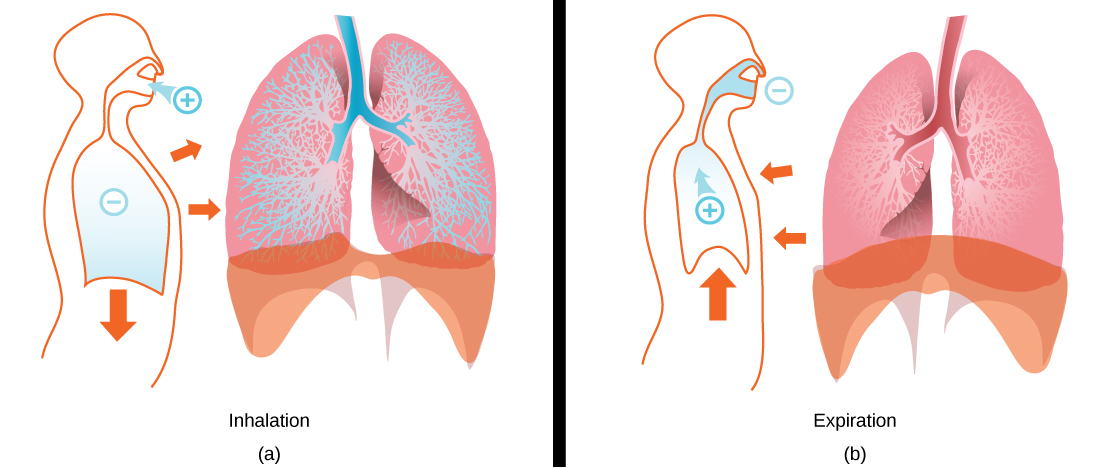
The chest wall expands out and away from the lungs. The lungs are elastic; therefore, when air fills the lungs, the elastic recoil within the tissues of the lung exerts pressure back toward the interior of the lungs. These outward and inward forces compete to inflate and deflate the lung with every breath. Upon exhalation, the lungs recoil to force the air out of the lungs, and the intercostal muscles relax, returning the chest wall back to its original position ( [link] b ). The diaphragm also relaxes and moves higher into the thoracic cavity. This increases the pressure within the thoracic cavity relative to the environment, and air rushes out of the lungs. The movement of air out of the lungs is a passive event. No muscles are contracting to expel the air.
Each lung is surrounded by an invaginated sac. The layer of tissue that covers the lung and dips into spaces is called the visceral pleura . A second layer of parietal pleura lines the interior of the thorax ( [link] ). The space between these layers, the intrapleural space , contains a small amount of fluid that protects the tissue and reduces the friction generated from rubbing the tissue layers together as the lungs contract and relax. Pleurisy results when these layers of tissue become inflamed; it is painful because the inflammation increases the pressure within the thoracic cavity and reduces the volume of the lung.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?