| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
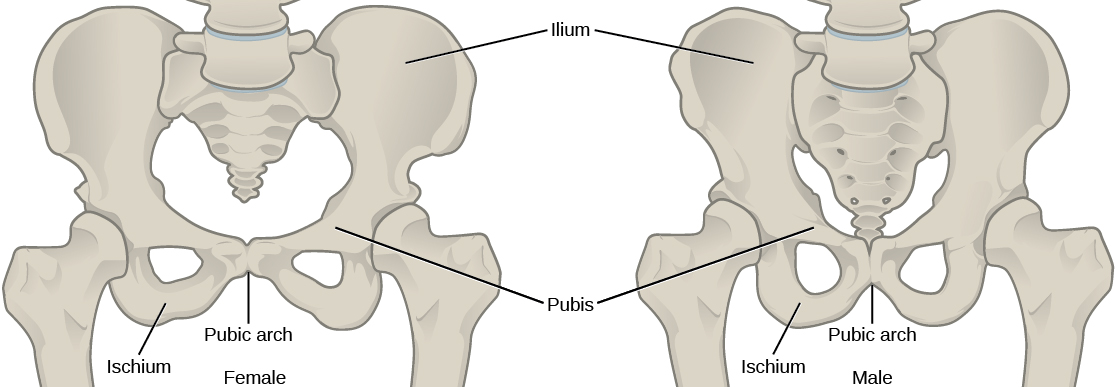
The pelvic girdle attaches to the lower limbs of the axial skeleton. Because it is responsible for bearing the weight of the body and for locomotion, the pelvic girdle is securely attached to the axial skeleton by strong ligaments. It also has deep sockets with robust ligaments to securely attach the femur to the body. The pelvic girdle is further strengthened by two large hip bones. In adults, the hip bones, or coxal bones , are formed by the fusion of three pairs of bones: the ilium, ischium, and pubis. The pelvis joins together in the anterior of the body at a joint called the pubic symphysis and with the bones of the sacrum at the posterior of the body.
The female pelvis is slightly different from the male pelvis. Over generations of evolution, females with a wider pubic angle and larger diameter pelvic canal reproduced more successfully. Therefore, their offspring also had pelvic anatomy that enabled successful childbirth ( [link] ).
The lower limb consists of the thigh, the leg, and the foot. The bones of the lower limb are the femur (thigh bone), patella (kneecap), tibia and fibula (bones of the leg), tarsals (bones of the ankle), and metatarsals and phalanges (bones of the foot) ( [link] ). The bones of the lower limbs are thicker and stronger than the bones of the upper limbs because of the need to support the entire weight of the body and the resulting forces from locomotion. In addition to evolutionary fitness, the bones of an individual will respond to forces exerted upon them.
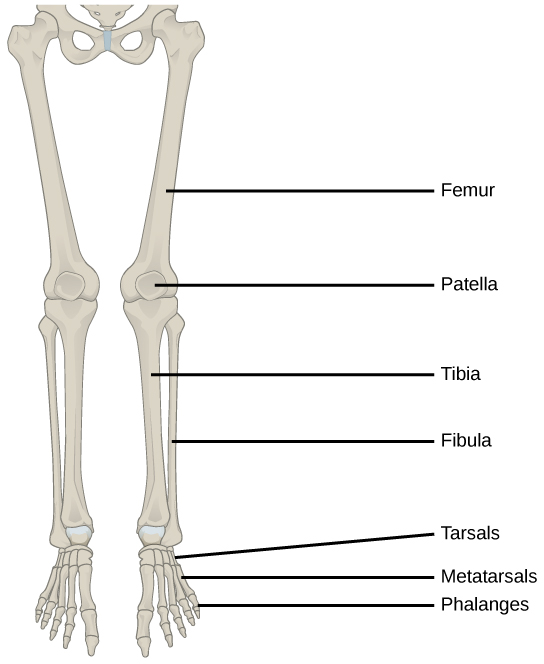
The femur , or thighbone, is the longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in the body. The femur and pelvis form the hip joint at the proximal end. At the distal end, the femur, tibia, and patella form the knee joint. The patella , or kneecap, is a triangular bone that lies anterior to the knee joint. The patella is embedded in the tendon of the femoral extensors (quadriceps). It improves knee extension by reducing friction. The tibia , or shinbone, is a large bone of the leg that is located directly below the knee. The tibia articulates with the femur at its proximal end, with the fibula and the tarsal bones at its distal end. It is the second largest bone in the human body and is responsible for transmitting the weight of the body from the femur to the foot. The fibula , or calf bone, parallels and articulates with the tibia. It does not articulate with the femur and does not bear weight. The fibula acts as a site for muscle attachment and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.
The tarsals are the seven bones of the ankle. The ankle transmits the weight of the body from the tibia and the fibula to the foot. The metatarsals are the five bones of the foot. The phalanges are the 14 bones of the toes. Each toe consists of three phalanges, except for the big toe that has only two ( [link] ). Variations exist in other species; for example, the horse’s metacarpals and metatarsals are oriented vertically and do not make contact with the substrate.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?