| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Biodiversity is not evenly distributed on Earth. Lake Victoria contained almost 500 species of cichlids alone, ignoring the other fish families present in the lake. All of these species were found only in Lake Victoria; therefore, the 500 species of cichlids were endemic. Endemic species are found in only one location. Endemics with highly restricted distributions are particularly vulnerable to extinction. Higher taxonomic levels, such as genera and families, can also be endemic. Lake Huron contains about 79 species of fish, all of which are found in many other lakes in North America. What accounts for the difference in fish diversity in these two lakes? Lake Victoria is a tropical lake, while Lake Huron is a temperate lake. Lake Huron in its present form is only about 7,000 years old, while Lake Victoria in its present form is about 15,000 years old. Biogeographers have suggested these two factors, latitude and age, are two of several hypotheses to explain biodiversity patterns on the planet.
There are three main fields of study under the heading of biogeography: ecological biogeography, historical biogeography (called paleobiogeography), and conservation biogeography. Ecological biogeography studies the current factors affecting the distribution of plants and animals. Historical biogeography, as the name implies, studies the past distribution of species. Conservation biogeography, on the other hand, is focused on the protection and restoration of species based upon known historical and current ecological information. Each of these fields considers both zoogeography and phytogeography—the past and present distribution of animals and plants.
One of the oldest observed patterns in ecology is that species biodiversity in almost every taxonomic group increases as latitude declines. In other words, biodiversity increases closer to the equator ( [link] ).
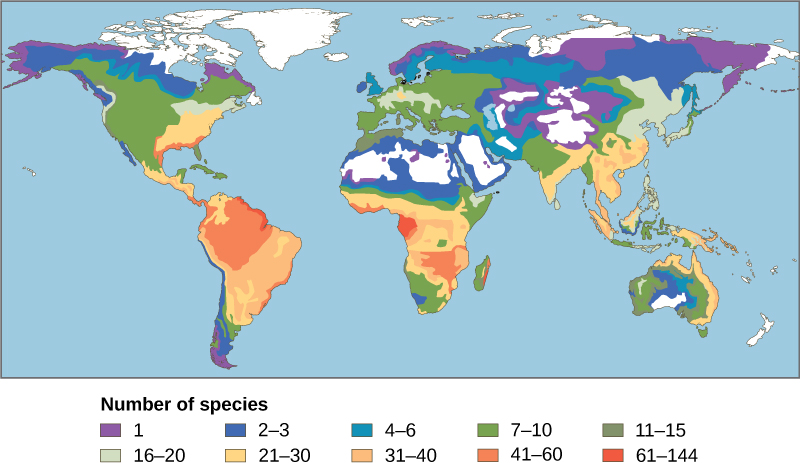
It is not yet clear why biodiversity increases closer to the equator, but hypotheses include the greater age of the ecosystems in the tropics versus temperate regions that were largely devoid of life or drastically impoverished during the last glaciation. The idea is that greater age provides more time for speciation. Another possible explanation is the increased energy the tropics receive from the sun versus the decreased energy that temperate and polar regions receive. It is not entirely clear how greater energy input could translate into more species. The complexity of tropical ecosystems may promote speciation by increasing the heterogeneity , or number of ecological niches, in the tropics relative to higher latitudes. The greater heterogeneity provides more opportunities for coevolution, specialization, and perhaps greater selection pressures leading to population differentiation. However, this hypothesis suffers from some circularity—ecosystems with more species encourage speciation, but how did they get more species to begin with? The tropics have been perceived as being more stable than temperate regions, which have a pronounced climate and day-length seasonality. The tropics have their own forms of seasonality, such as rainfall, but they are generally assumed to be more stable environments and this stability might promote speciation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?