| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
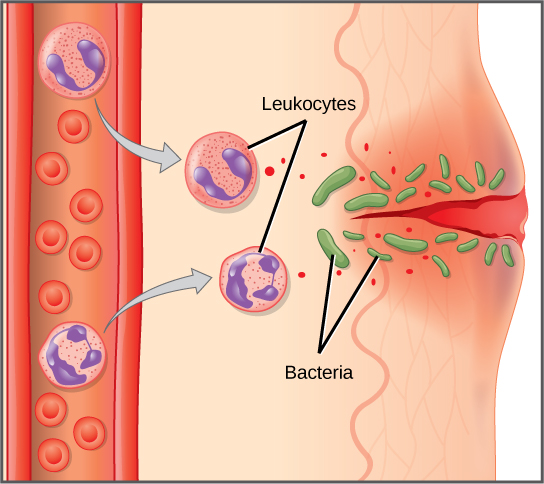
Neutrophils and eosinophils are particularly important leukocytes that engulf large pathogens, such as bacteria and fungi. A mast cell is a leukocyte that produces inflammatory molecules, such as histamine, in response to large pathogens. A basophil is a leukocyte that, like a neutrophil, releases chemicals to stimulate the inflammatory response as illustrated in [link] . Basophils are also involved in allergy and hypersensitivity responses and induce specific types of inflammatory responses. Eosinophils and basophils produce additional inflammatory mediators to recruit more leukocytes. A hypersensitive immune response to harmless antigens, such as in pollen, often involves the release of histamine by basophils and mast cells.
Cytokines also send feedback to cells of the nervous system to bring about the overall symptoms of feeling sick, which include lethargy, muscle pain, and nausea. These effects may have evolved because the symptoms encourage the individual to rest and prevent them from spreading the infection to others. Cytokines also increase the core body temperature, causing a fever, which causes the liver to withhold iron from the blood. Without iron, certain pathogens, such as some bacteria, are unable to replicate; this is called nutritional immunity.
Watch this 23-second stop-motion video showing a neutrophil that searches for and engulfs fungus spores during an elapsed time of about 79 minutes.
Lymphocytes are leukocytes that are histologically identifiable by their large, darkly staining nuclei; they are small cells with very little cytoplasm, as shown in [link] . Infected cells are identified and destroyed by natural killer (NK) cells , lymphocytes that can kill cells infected with viruses or tumor cells (abnormal cells that uncontrollably divide and invade other tissue). T cells and B cells of the adaptive immune system also are classified as lymphocytes. T cells are lymphocytes that mature in the thymus gland, and B cells are lymphocytes that mature in the bone marrow. NK cells identify intracellular infections, especially from viruses, by the altered expression of major histocompatibility class (MHC) I molecules on the surface of infected cells. MHC I molecules are proteins on the surfaces of all nucleated cells, thus they are scarce on red blood cells and platelets which are non-nucleated. The function of MHC I molecules is to display fragments of proteins from the infectious agents within the cell to T-cells; healthy cells will be ignored, while “non-self” or foreign proteins will be attacked by the immune system. MHC II molecules are found mainly on cells containing antigens (“non-self proteins”) and on lymphocytes. MHC II molecules interact with helper T-cells to trigger the appropriate immune response, which may include the inflammatory response.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?