| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
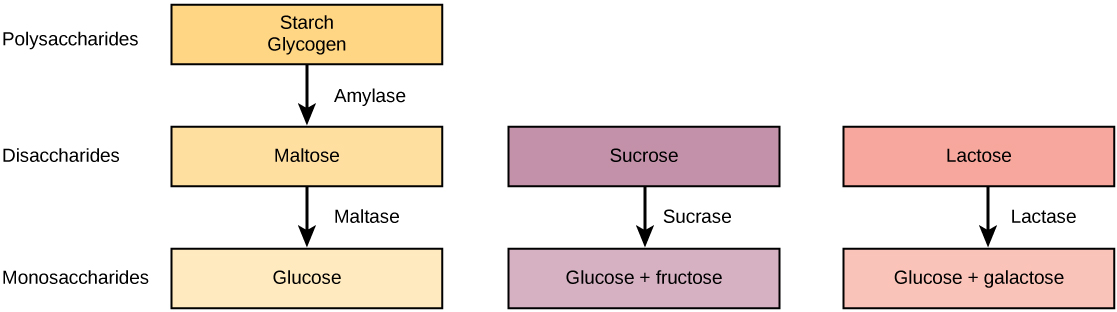
| Digestion of Carbohydrates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme | Produced By | Site of Action | Substrate Acting On | End Products |
| Salivary amylase | Salivary glands | Mouth | Polysaccharides (Starch) | Disaccharides (maltose), oligosaccharides |
| Pancreatic amylase | Pancreas | Small intestine | Polysaccharides (starch) | Disaccharides (maltose), monosaccharides |
| Oligosaccharidases | Lining of the intestine; brush border membrane | Small intestine | Disaccharides | Monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, fructose, galactose) |
A large part of protein digestion takes place in the stomach. The enzyme pepsin plays an important role in the digestion of proteins by breaking down the intact protein to peptides, which are short chains of four to nine amino acids. In the duodenum, other enzymes— trypsin , elastase , and chymotrypsin —act on the peptides reducing them to smaller peptides. Trypsin elastase, carboxypeptidase, and chymotrypsin are produced by the pancreas and released into the duodenum where they act on the chyme. Further breakdown of peptides to single amino acids is aided by enzymes called peptidases (those that break down peptides). Specifically, carboxypeptidase , dipeptidase , and aminopeptidase play important roles in reducing the peptides to free amino acids. The amino acids are absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestines. The steps in protein digestion are summarized in [link] and [link] .
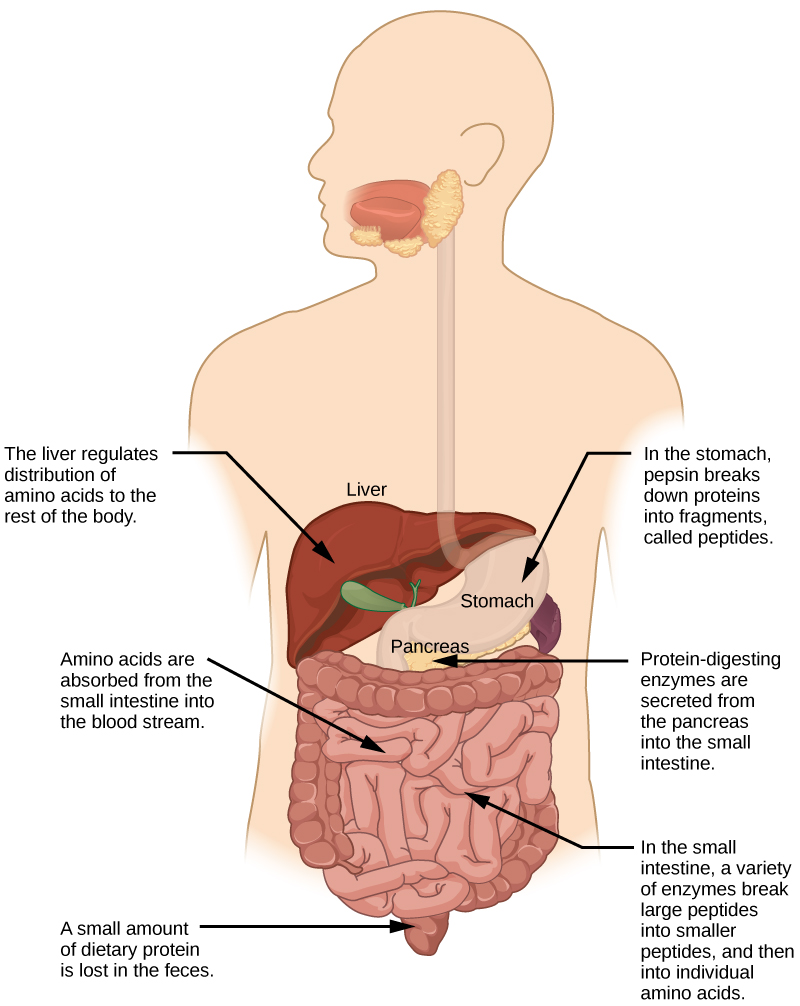
| Digestion of Protein | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme | Produced By | Site of Action | Substrate Acting On | End Products |
| Pepsin | Stomach chief cells | Stomach | Proteins | Peptides |
|
Pancreas | Small intestine | Proteins | Peptides |
| Carboxypeptidase | Pancreas | Small intestine | Peptides | Amino acids and peptides |
|
Lining of intestine | Small intestine | Peptides | Amino acids |
Lipid digestion begins in the stomach with the aid of lingual lipase and gastric lipase. However, the bulk of lipid digestion occurs in the small intestine due to pancreatic lipase. When chyme enters the duodenum, the hormonal responses trigger the release of bile, which is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile aids in the digestion of lipids, primarily triglycerides by emulsification. Emulsification is a process in which large lipid globules are broken down into several small lipid globules. These small globules are more widely distributed in the chyme rather than forming large aggregates. Lipids are hydrophobic substances: in the presence of water, they will aggregate to form globules to minimize exposure to water. Bile contains bile salts, which are amphipathic, meaning they contain hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts. Thus, the bile salts hydrophilic side can interface with water on one side and the hydrophobic side interfaces with lipids on the other. By doing so, bile salts emulsify large lipid globules into small lipid globules.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?