| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
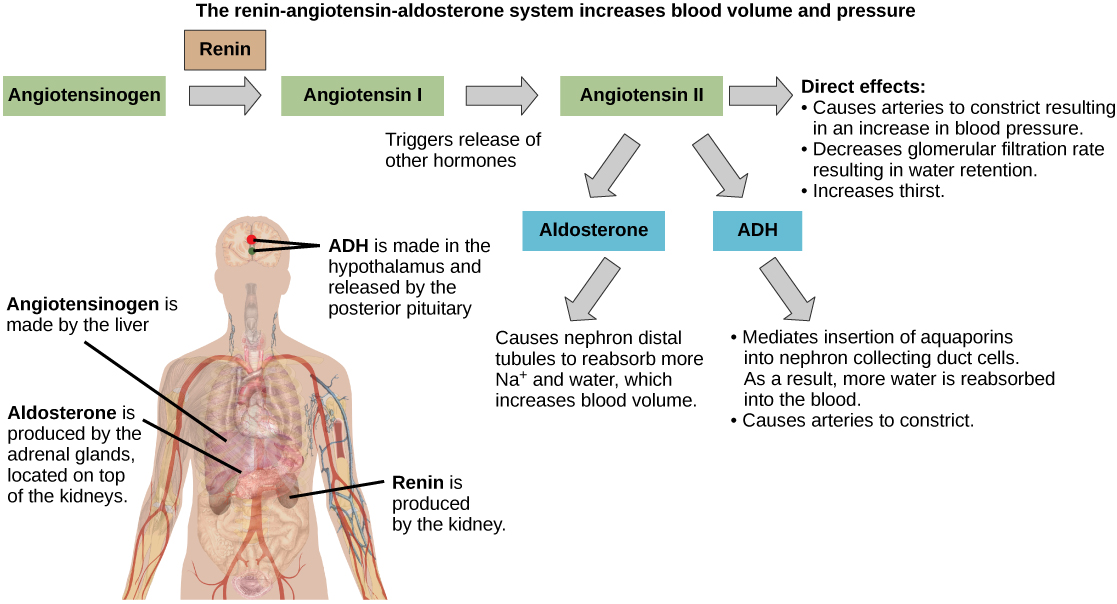
Another hormone responsible for maintaining electrolyte concentrations in extracellular fluids is aldosterone , a steroid hormone that is produced by the adrenal cortex. In contrast to ADH, which promotes the reabsorption of water to maintain proper water balance, aldosterone maintains proper water balance by enhancing Na + reabsorption and K + secretion from extracellular fluid of the cells in kidney tubules. Because it is produced in the cortex of the adrenal gland and affects the concentrations of minerals Na + and K + , aldosterone is referred to as a mineralocorticoid , a corticosteroid that affects ion and water balance. Aldosterone release is stimulated by a decrease in blood sodium levels, blood volume, or blood pressure, or an increase in blood potassium levels. It also prevents the loss of Na + from sweat, saliva, and gastric juice. The reabsorption of Na + also results in the osmotic reabsorption of water, which alters blood volume and blood pressure.
Aldosterone production can be stimulated by low blood pressure, which triggers a sequence of chemical release, as illustrated in [link] . When blood pressure drops, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is activated. Cells in the juxtaglomerular apparatus, which regulates the functions of the nephrons of the kidney, detect this and release renin . Renin, an enzyme, circulates in the blood and reacts with a plasma protein produced by the liver called angiotensinogen. When angiotensinogen is cleaved by renin, it produces angiotensin I, which is then converted into angiotensin II in the lungs. Angiotensin II functions as a hormone and then causes the release of the hormone aldosterone by the adrenal cortex, resulting in increased Na + reabsorption, water retention, and an increase in blood pressure. Angiotensin II in addition to being a potent vasoconstrictor also causes an increase in ADH and increased thirst, both of which help to raise blood pressure.
Regulation of the reproductive system is a process that requires the action of hormones from the pituitary gland, the adrenal cortex, and the gonads. During puberty in both males and females, the hypothalamus produces gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the production and release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. These hormones regulate the gonads (testes in males and ovaries in females) and therefore are called gonadotropins . In both males and females, FSH stimulates gamete production and LH stimulates production of hormones by the gonads. An increase in gonad hormone levels inhibits GnRH production through a negative feedback loop.
In males, FSH stimulates the maturation of sperm cells. FSH production is inhibited by the hormone inhibin, which is released by the testes. LH stimulates production of the sex hormones ( androgens ) by the interstitial cells of the testes and therefore is also called interstitial cell-stimulating hormone.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?