| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A tight junction is a watertight seal between two adjacent animal cells ( [link] ). The cells are held tightly against each other by proteins (predominantly two proteins called claudins and occludins).
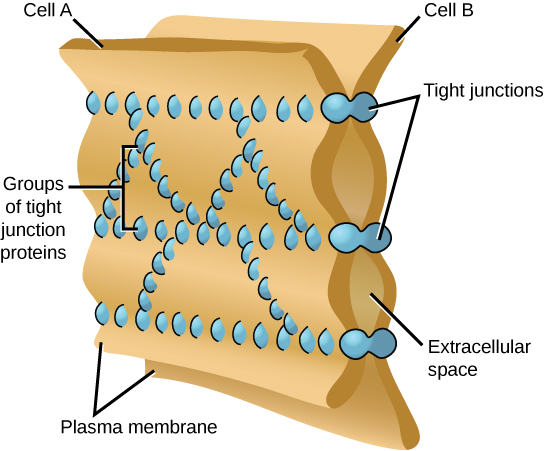
This tight adherence prevents materials from leaking between the cells; tight junctions are typically found in epithelial tissues that line internal organs and cavities, and comprise most of the skin. For example, the tight junctions of the epithelial cells lining your urinary bladder prevent urine from leaking out into the extracellular space.
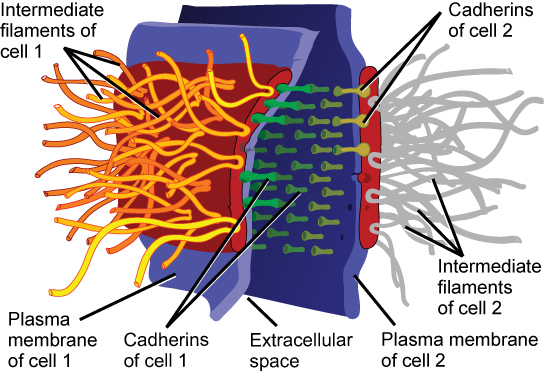
Also found only in animal cells are desmosomes , which act like spot welds between adjacent epithelial cells ( [link] ). Short proteins called cadherins in the plasma membrane connect to intermediate filaments to create desmosomes. The cadherins join two adjacent cells together and maintain the cells in a sheet-like formation in organs and tissues that stretch, like the skin, heart, and muscles.
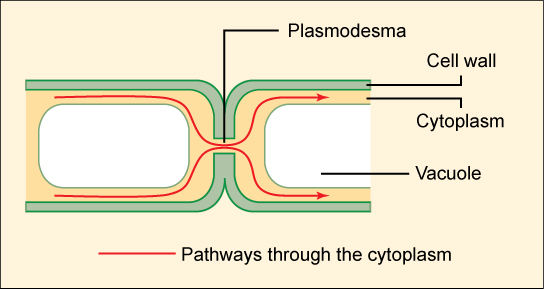
Gap junctions in animal cells are like plasmodesmata in plant cells in that they are channels between adjacent cells that allow for the transport of ions, nutrients, and other substances that enable cells to communicate ( [link] ). Structurally, however, gap junctions and plasmodesmata differ.
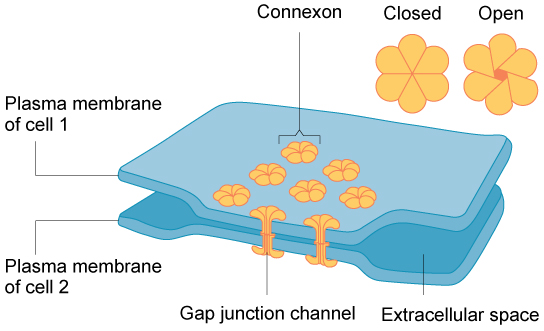
Gap junctions develop when a set of six proteins (called connexins) in the plasma membrane arrange themselves in an elongated donut-like configuration called a connexon. When the pores (“doughnut holes”) of connexons in adjacent animal cells align, a channel between the two cells forms. Gap junctions are particularly important in cardiac muscle: The electrical signal for the muscle to contract is passed efficiently through gap junctions, allowing the heart muscle cells to contract in tandem.
To conduct a virtual microscopy lab and review the parts of a cell, work through the steps of this interactive assignment .
Animal cells communicate via their extracellular matrices and are connected to each other via tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions. Plant cells are connected and communicate with each other via plasmodesmata.
When protein receptors on the surface of the plasma membrane of an animal cell bind to a substance in the extracellular matrix, a chain of reactions begins that changes activities taking place within the cell. Plasmodesmata are channels between adjacent plant cells, while gap junctions are channels between adjacent animal cells. However, their structures are quite different. A tight junction is a watertight seal between two adjacent cells, while a desmosome acts like a spot weld.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?