| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
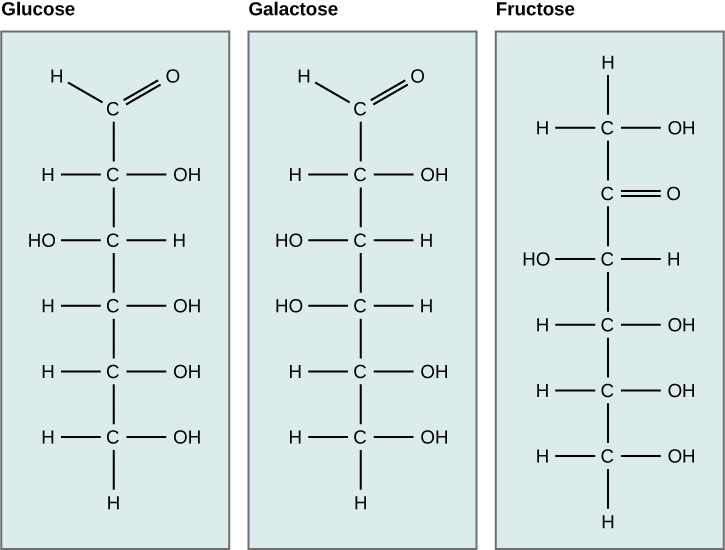
What kind of sugars are these, aldose or ketose?
Glucose, galactose, and fructose are isomeric monosaccharides (hexoses), meaning they have the same chemical formula but have slightly different structures. Glucose and galactose are aldoses, and fructose is a ketose.
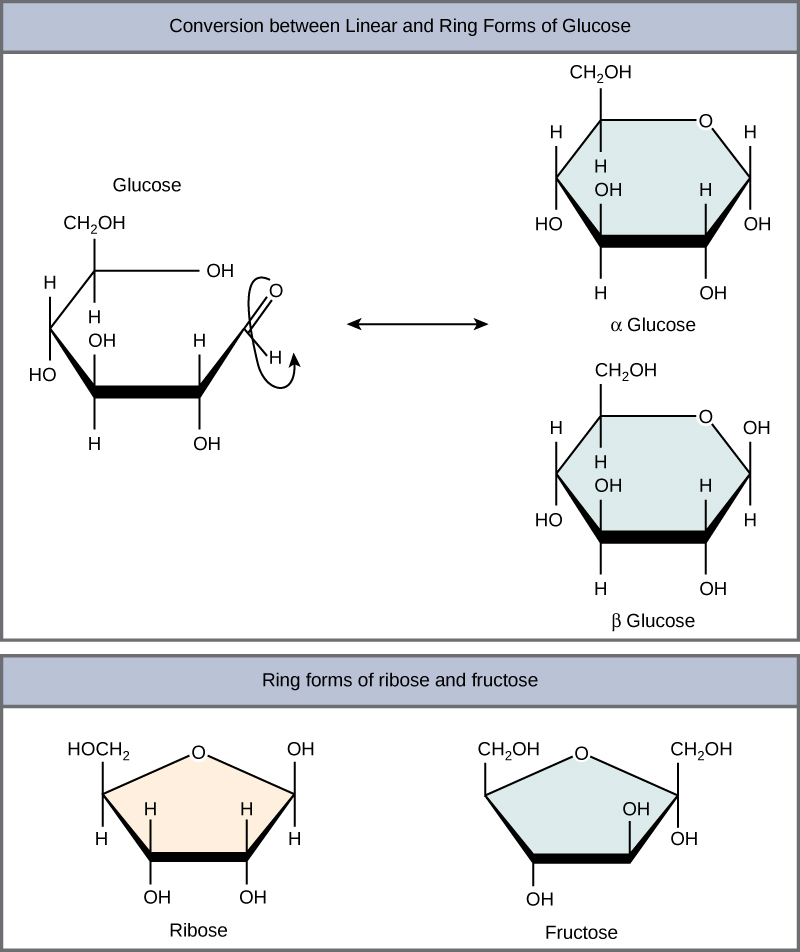
Monosaccharides can exist as a linear chain or as ring-shaped molecules; in aqueous solutions they are usually found in ring forms ( [link] ). Glucose in a ring form can have two different arrangements of the hydroxyl group (OH) around the anomeric carbon (carbon 1 that becomes asymmetric in the process of ring formation). If the hydroxyl group is below carbon number 1 in the sugar, it is said to be in the alpha ( α ) position, and if it is above the plane, it is said to be in the beta ( β ) position.
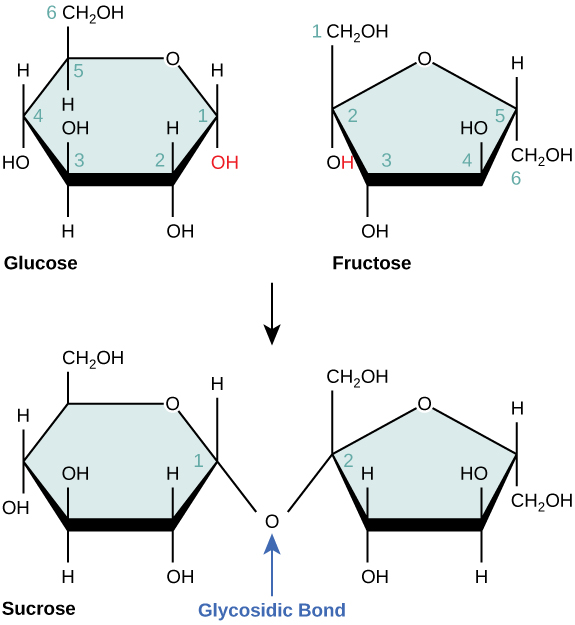
Disaccharides (di- = “two”) form when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction (also known as a condensation reaction or dehydration synthesis). During this process, the hydroxyl group of one monosaccharide combines with the hydrogen of another monosaccharide, releasing a molecule of water and forming a covalent bond. A covalent bond formed between a carbohydrate molecule and another molecule (in this case, between two monosaccharides) is known as a glycosidic bond ( [link] ). Glycosidic bonds (also called glycosidic linkages) can be of the alpha or the beta type.
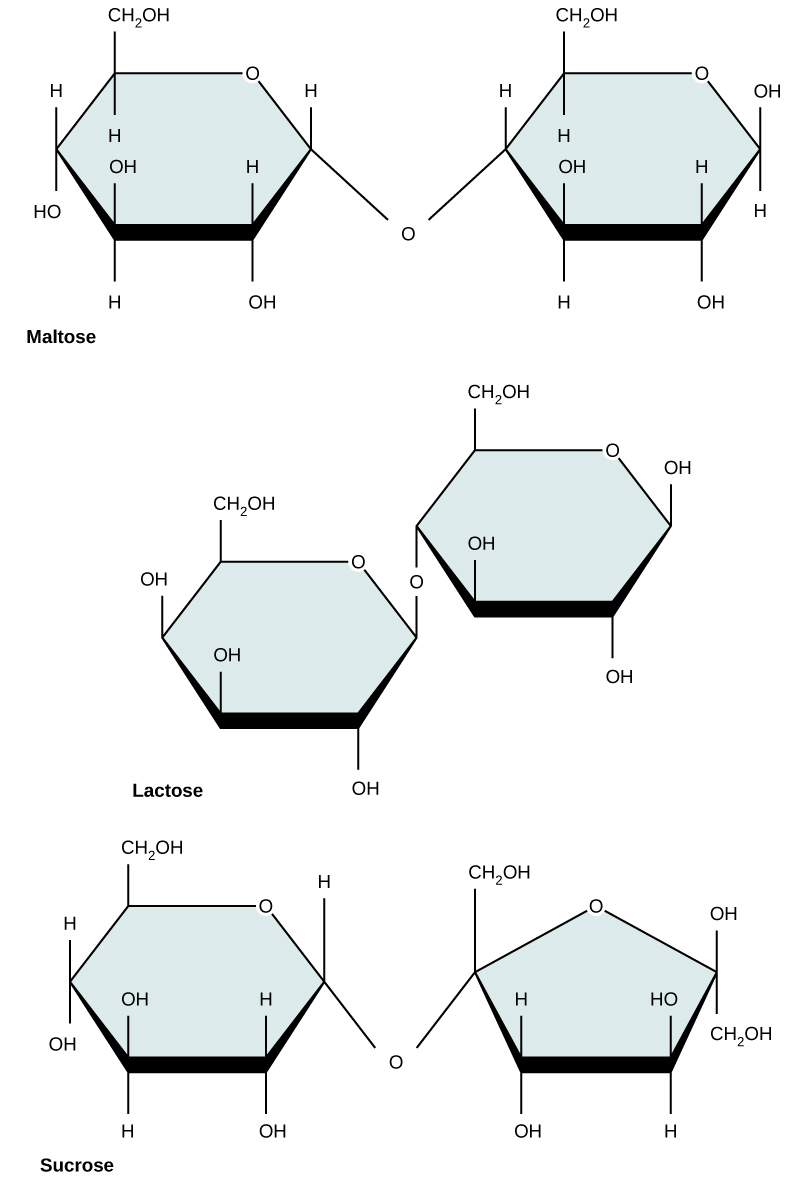
Common disaccharides include lactose, maltose, and sucrose ( [link] ). Lactose is a disaccharide consisting of the monomers glucose and galactose. It is found naturally in milk. Maltose, or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed by a dehydration reaction between two glucose molecules. The most common disaccharide is sucrose, or table sugar, which is composed of the monomers glucose and fructose.
A long chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds is known as a polysaccharide (poly- = “many”). The chain may be branched or unbranched, and it may contain different types of monosaccharides. The molecular weight may be 100,000 daltons or more depending on the number of monomers joined. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?