| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An infected cell (or a tumor cell) is usually incapable of synthesizing and displaying MHC I molecules appropriately. The metabolic resources of cells infected by some viruses produce proteins that interfere with MHC I processing and/or trafficking to the cell surface. The reduced MHC I on host cells varies from virus to virus and results from active inhibitors being produced by the viruses. This process can deplete host MHC I molecules on the cell surface, which NK cells detect as “unhealthy” or “abnormal” while searching for cellular MHC I molecules. Similarly, the dramatically altered gene expression of tumor cells leads to expression of extremely deformed or absent MHC I molecules that also signal “unhealthy” or “abnormal.”
NK cells are always active; an interaction with normal, intact MHC I molecules on a healthy cell disables the killing sequence, and the NK cell moves on. After the NK cell detects an infected or tumor cell, its cytoplasm secretes granules comprised of perforin , a destructive protein that creates a pore in the target cell. Granzymes are released along with the perforin in the immunological synapse. A granzyme is a protease that digests cellular proteins and induces the target cell to undergo programmed cell death, or apoptosis. Phagocytic cells then digest the cell debris left behind. NK cells are constantly patrolling the body and are an effective mechanism for controlling potential infections and preventing cancer progression.
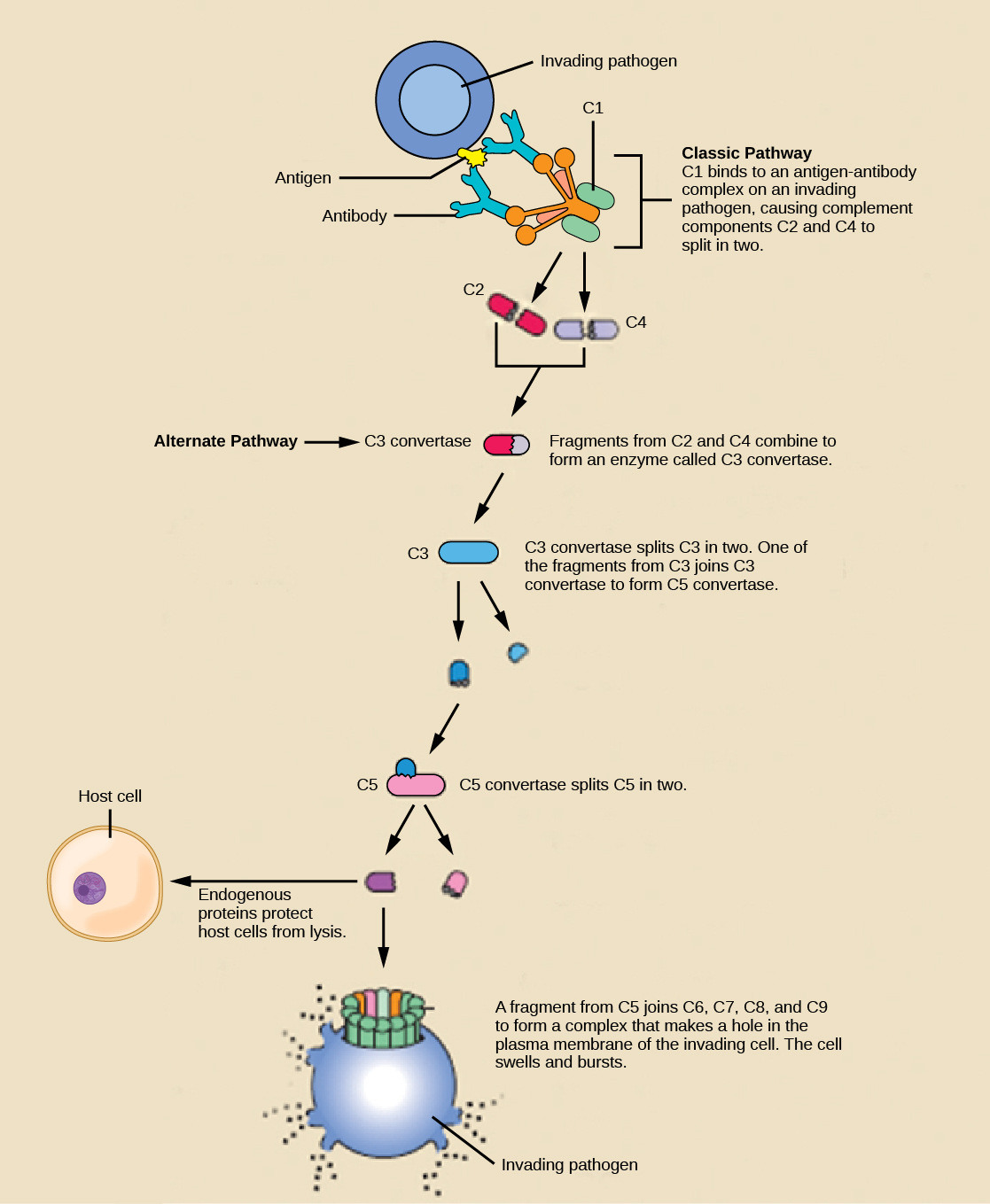
An array of approximately 20 types of soluble proteins, called a complement system , functions to destroy extracellular pathogens. Cells of the liver and macrophages synthesize complement proteins continuously; these proteins are abundant in the blood serum and are capable of responding immediately to infecting microorganisms. The complement system is so named because it is complementary to the antibody response of the adaptive immune system. Complement proteins bind to the surfaces of microorganisms and are particularly attracted to pathogens that are already bound by antibodies. Binding of complement proteins occurs in a specific and highly regulated sequence, with each successive protein being activated by cleavage and/or structural changes induced upon binding of the preceding protein(s). After the first few complement proteins bind, a cascade of sequential binding events follows in which the pathogen rapidly becomes coated in complement proteins.
Complement proteins perform several functions. The proteins serve as a marker to indicate the presence of a pathogen to phagocytic cells, such as macrophages and B cells, and enhance engulfment; this process is called opsonization . Certain complement proteins can combine to form attack complexes that open pores in microbial cell membranes. These structures destroy pathogens by causing their contents to leak, as illustrated in [link] .
The innate immune system serves as a first responder to pathogenic threats that bypass natural physical and chemical barriers of the body. Using a combination of cellular and molecular attacks, the innate immune system identifies the nature of a pathogen and responds with inflammation, phagocytosis, cytokine release, destruction by NK cells, and/or a complement system. When innate mechanisms are insufficient to clear an infection, the adaptive immune response is informed and mobilized.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?