| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The RQ is used to calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveolar spaces within the lung, the alveolar Above, the partial pressure of oxygen in the lungs was calculated to be 150 mm Hg. However, lungs never fully deflate with an exhalation; therefore, the inspired air mixes with this residual air and lowers the partial pressure of oxygen within the alveoli. This means that there is a lower concentration of oxygen in the lungs than is found in the air outside the body. Knowing the RQ, the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli can be calculated:
With an RQ of 0.8 and a in the alveoli of 40 mm Hg, the alveolar is equal to:
Notice that this pressure is less than the external air. Therefore, the oxygen will flow from the inspired air in the lung ( = 150 mm Hg) into the bloodstream ( = 100 mm Hg) ( [link] ).
In the lungs, oxygen diffuses out of the alveoli and into the capillaries surrounding the alveoli. Oxygen (about 98 percent) binds reversibly to the respiratory pigment hemoglobin found in red blood cells (RBCs). RBCs carry oxygen to the tissues where oxygen dissociates from the hemoglobin and diffuses into the cells of the tissues. More specifically, alveolar is higher in the alveoli ( = 100 mm Hg) than blood (40 mm Hg) in the capillaries. Because this pressure gradient exists, oxygen diffuses down its pressure gradient, moving out of the alveoli and entering the blood of the capillaries where O 2 binds to hemoglobin. At the same time, alveolar is lower = 40 mm Hg than blood = (45 mm Hg). CO 2 diffuses down its pressure gradient, moving out of the capillaries and entering the alveoli.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide move independently of each other; they diffuse down their own pressure gradients. As blood leaves the lungs through the pulmonary veins, the venous = 100 mm Hg, whereas the venous = 40 mm Hg. As blood enters the systemic capillaries, the blood will lose oxygen and gain carbon dioxide because of the pressure difference of the tissues and blood. In systemic capillaries, = 100 mm Hg, but in the tissue cells, = 40 mm Hg. This pressure gradient drives the diffusion of oxygen out of the capillaries and into the tissue cells. At the same time, blood = 40 mm Hg and systemic tissue = 45 mm Hg. The pressure gradient drives CO 2 out of tissue cells and into the capillaries. The blood returning to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries has a venous = 40 mm Hg and a = 45 mm Hg. The blood enters the lung capillaries where the process of exchanging gases between the capillaries and alveoli begins again ( [link] ).
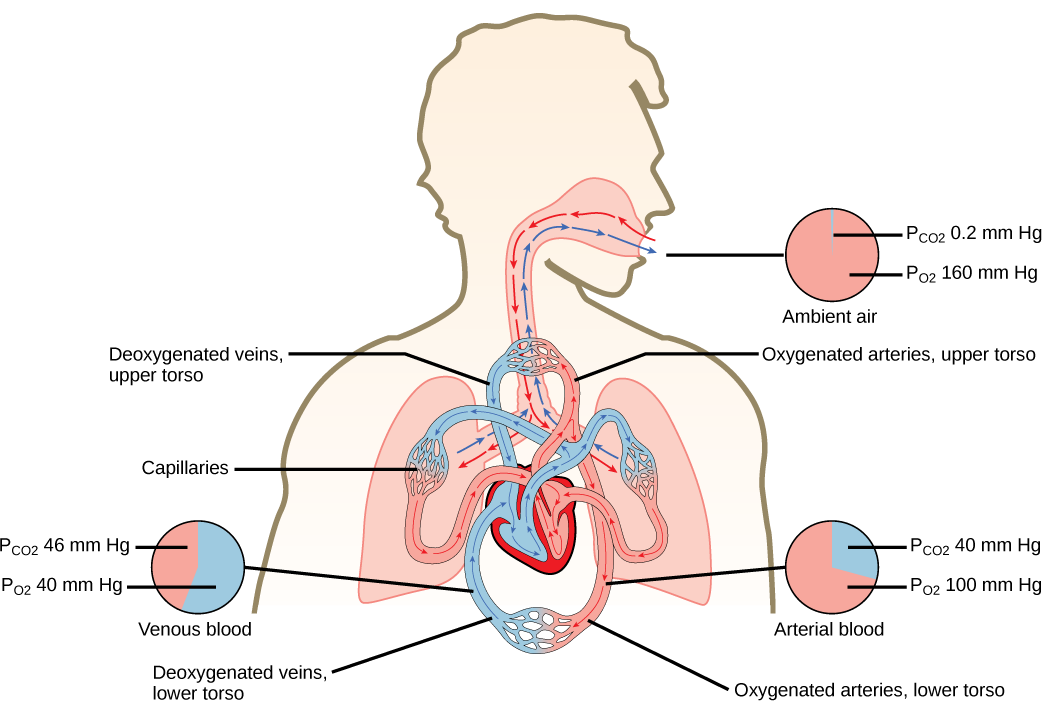
Which of the following statements is false?
In short, the change in partial pressure from the alveoli to the capillaries drives the oxygen into the tissues and the carbon dioxide into the blood from the tissues. The blood is then transported to the lungs where differences in pressure in the alveoli result in the movement of carbon dioxide out of the blood into the lungs, and oxygen into the blood.
Watch this video to learn how to carry out spirometry.
The lungs can hold a large volume of air, but they are not usually filled to maximal capacity. Lung volume measurements include tidal volume, expiratory reserve volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and residual volume. The sum of these equals the total lung capacity. Gas movement into or out of the lungs is dependent on the pressure of the gas. Air is a mixture of gases; therefore, the partial pressure of each gas can be calculated to determine how the gas will flow in the lung. The difference between the partial pressure of the gas in the air drives oxygen into the tissues and carbon dioxide out of the body.
[link] Which of the following statements is false?
[link] C

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?