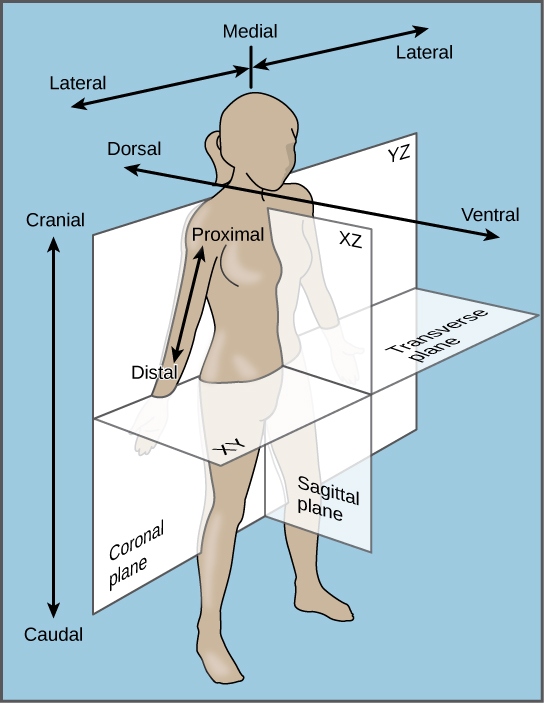
| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Animals in the phylum Echinodermata (such as sea stars, sand dollars, and sea urchins) display radial symmetry as adults, but their larval stages exhibit bilateral symmetry. This is termed secondary radial symmetry. They are believed to have evolved from bilaterally symmetrical animals; thus, they are classified as bilaterally symmetrical.
Watch this video to see a quick sketch of the different types of body symmetry.
Most animal species undergo a separation of tissues into germ layers during embryonic development. Recall that these germ layers are formed during gastrulation, and that they are predetermined to develop into the animal’s specialized tissues and organs. Animals develop either two or three embryonic germs layers ( [link] ). The animals that display radial symmetry develop two germ layers, an inner layer (endoderm) and an outer layer (ectoderm). These animals are called diploblasts . Diploblasts have a non-living layer between the endoderm and ectoderm. More complex animals (those with bilateral symmetry) develop three tissue layers: an inner layer (endoderm), an outer layer (ectoderm), and a middle layer (mesoderm). Animals with three tissue layers are called triploblasts .
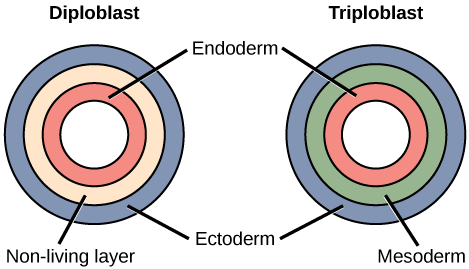
Which of the following statements about diploblasts and triploblasts is false?
Each of the three germ layers is programmed to give rise to particular body tissues and organs. The endoderm gives rise to the lining of the digestive tract (including the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas), as well as to the lining of the trachea, bronchi, and lungs of the respiratory tract, along with a few other structures. The ectoderm develops into the outer epithelial covering of the body surface, the central nervous system, and a few other structures. The mesoderm is the third germ layer; it forms between the endoderm and ectoderm in triploblasts. This germ layer gives rise to all muscle tissues (including the cardiac tissues and muscles of the intestines), connective tissues such as the skeleton and blood cells, and most other visceral organs such as the kidneys and the spleen.
Further subdivision of animals with three germ layers (triploblasts) results in the separation of animals that may develop an internal body cavity derived from mesoderm, called a coelom , and those that do not. This epithelial cell-lined coelomic cavity represents a space, usually filled with fluid, which lies between the visceral organs and the body wall. It houses many organs such as the digestive system, kidneys, reproductive organs, and heart, and contains the circulatory system. In some animals, such as mammals, the part of the coelom called the pleural cavity provides space for the lungs to expand during breathing. The evolution of the coelom is associated with many functional advantages. Primarily, the coelom provides cushioning and shock absorption for the major organ systems. Organs housed within the coelom can grow and move freely, which promotes optimal organ development and placement. The coelom also provides space for the diffusion of gases and nutrients, as well as body flexibility, promoting improved animal motility.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?