| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Devastating pathogen-borne diseases and plagues, both viral and bacterial in nature, have affected humans since the beginning of human history. The true cause of these diseases was not understood at the time, and some people thought that diseases were a spiritual punishment. Over time, people came to realize that staying apart from afflicted persons, and disposing of the corpses and personal belongings of victims of illness, reduced their own chances of getting sick.
Epidemiologists study how diseases affect a population. An epidemic is a disease that occurs in an unusually high number of individuals in a population at the same time. A pandemic is a widespread, usually worldwide, epidemic. An endemic disease is a disease that is constantly present, usually at low incidence, in a population.
There are records about infectious diseases as far back as 3000 B.C. A number of significant pandemics caused by bacteria have been documented over several hundred years. Some of the most memorable pandemics led to the decline of cities and nations.
In the 21 st century, infectious diseases remain among the leading causes of death worldwide, despite advances made in medical research and treatments in recent decades. A disease spreads when the pathogen that causes it is passed from one person to another. For a pathogen to cause disease, it must be able to reproduce in the host’s body and damage the host in some way.
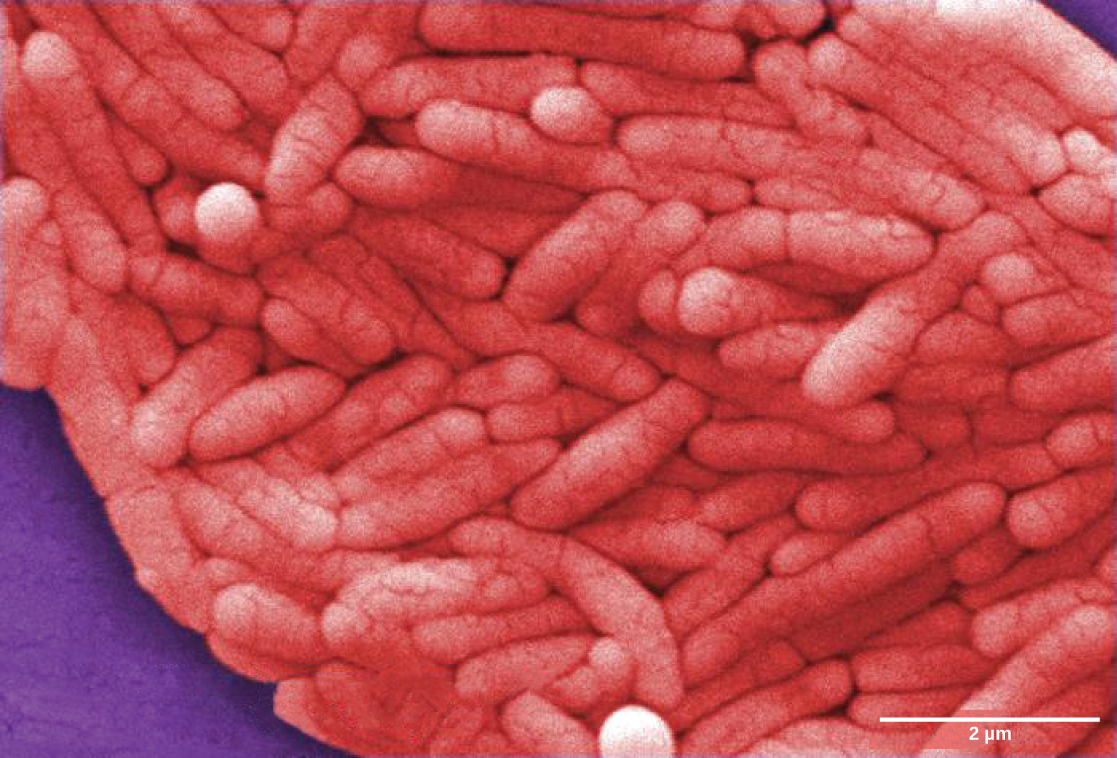
In 430 B.C., the Plague of Athens killed one-quarter of the Athenian troops that were fighting in the great Peloponnesian War and weakened Athens’ dominance and power. The plague impacted people living in overcrowded Athens as well as troops aboard ships that had to return to Athens. The source of the plague may have been identified recently when researchers from the University of Athens were able to use DNA from teeth recovered from a mass grave. The scientists identified nucleotide sequences from a pathogenic bacterium, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi ( [link] ), which causes typhoid fever. Papagrigorakis MJ , Synodinos PN , and Yapijakis C . Ancient typhoid epidemic reveals possible ancestral strain of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Infect Genet Evol 7 (2007): 126–7, Epub 2006 Jun. This disease is commonly seen in overcrowded areas and has caused epidemics throughout recorded history.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?