| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Let’s briefly review the key reasons that measuring distances to the stars is such a struggle. As discussed in The Brightness of Stars , our problem is that stars come in a bewildering variety of intrinsic luminosities. (If stars were light bulbs, we’d say they come in a wide range of wattages.) Suppose, instead, that all stars had the same “wattage” or luminosity. In that case, the more distant ones would always look dimmer, and we could tell how far away a star is simply by how dim it appeared. In the real universe, however, when we look at a star in our sky (with eye or telescope) and measure its apparent brightness, we cannot know whether it looks dim because it’s a low-wattage bulb or because it is far away, or perhaps some of each.
Astronomers need to discover something else about the star that allows us to “read off” its intrinsic luminosity—in effect, to know what the star’s true wattage is. With this information, we can then attribute how dim it looks from Earth to its distance. Recall that the apparent brightness of an object decreases with the square of the distance to that object. If two objects have the same luminosity but one is three times farther than the other, the more distant one will look nine times fainter. Therefore, if we know the luminosity of a star and its apparent brightness, we can calculate how far away it is. Astronomers have long searched for techniques that would somehow allow us to determine the luminosity of a star—and it is to these techniques that we turn next.
The breakthrough in measuring distances to remote parts of our Galaxy, and to other galaxies as well, came from the study of variable star s. Most stars are constant in their luminosity, at least to within a percent or two. Like the Sun, they generate a steady flow of energy from their interiors. However, some stars are seen to vary in brightness and, for this reason, are called variable stars . Many such stars vary on a regular cycle, like the flashing bulbs that decorate stores and homes during the winter holidays.
Let’s define some tools to help us keep track of how a star varies. A graph that shows how the brightness of a variable star changes with time is called a light curve ( [link] ). The maximum is the point of the light curve where the star has its greatest brightness; the minimum is the point where it is faintest. If the light variations repeat themselves periodically, the interval between the two maxima is called the period of the star. (If this kind of graph looks familiar, it is because we introduced it in Diameters of Stars .)
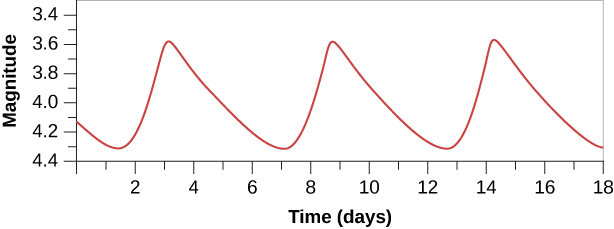
There are two special types of variable stars for which—as we will see—measurements of the light curve give us accurate distances. These are called cepheid and RR Lyrae variables, both of which are pulsating variable stars . Such a star actually changes its diameter with time—periodically expanding and contracting, as your chest does when you breathe. We now understand that these stars are going through a brief unstable stage late in their lives.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?