| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The masses of molecular clouds range from a thousand times the mass of the Sun to about 3 million solar masses. Molecular clouds have a complex filamentary structure, similar to cirrus clouds in Earth’s atmosphere, but much less dense. The molecular cloud filaments can be up to 1000 light-years long. Within the clouds are cold, dense regions with typical masses of 50 to 500 times the mass of the Sun; we give these regions the highly technical name clumps . Within these clumps, there are even denser, smaller regions called cores. The cores are the embryos of stars. The conditions in these cores—low temperature and high density—are just what is required to make stars. Remember that the essence of the life story of any star is the ongoing competition between two forces: gravity and pressure . The force of gravity, pulling inward, tries to make a star collapse. Internal pressure produced by the motions of the gas atoms, pushing outward, tries to force the star to expand. When a star is first forming, low temperature (and hence, low pressure) and high density (hence, greater gravitational attraction) both work to give gravity the advantage. In order to form a star—that is, a dense, hot ball of matter capable of starting nuclear reactions deep within—we need a typical core of interstellar atoms and molecules to shrink in radius and increase in density by a factor of nearly 10 20 . It is the force of gravity that produces this drastic collapse.
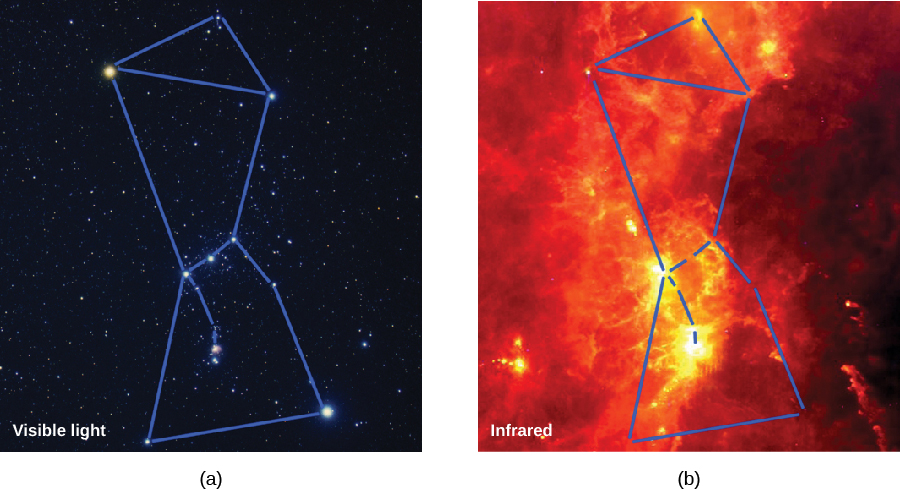
Let’s discuss what happens in regions of star formation by considering a nearby site where stars are forming right now. One of the best-studied stellar nurseries is in the constellation of Orion, The Hunter, about 1500 light-years away ( [link] ). The pattern of the hunter is easy to recognize by the conspicuous “belt” of three stars that mark his waist. The Orion molecular cloud is much larger than the star pattern and is truly an impressive structure. In its long dimension, it stretches over a distance of about 100 light-years. The total quantity of molecular gas is about 200,000 times the mass of the Sun. Most of the cloud does not glow with visible light but betrays its presence by the radiation that the dusty gas gives off at infrared and radio wavelengths.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?