| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
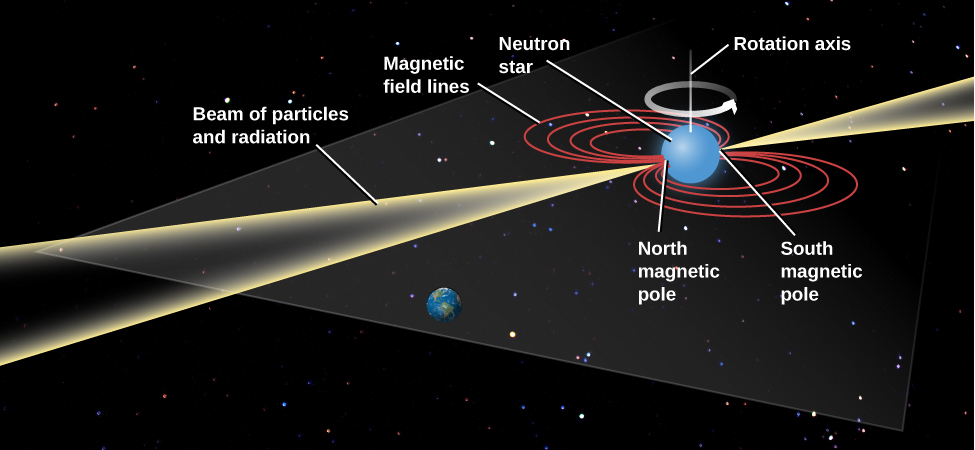
Note that in a neutron star, the magnetic north and south poles do not have to be anywhere close to the north and south poles defined by the star’s rotation. In the same way, we discussed in the chapter on The Giant Planets that the magnetic poles on the planets Uranus and Neptune are not lined up with the poles of the planet’s spin. [link] shows the poles of the magnetic field perpendicular to the poles of rotation, but the two kinds of poles could make any angle.
In fact, the misalignment of the rotational axis with the magnetic axis plays a crucial role in the generation of the observed pulses in this model. At the two magnetic poles, the particles from the neutron star are focused into a narrow beam and come streaming out of the whirling magnetic region at enormous speeds. They emit energy over a broad range of the electromagnetic spectrum. The radiation itself is also confined to a narrow beam, which explains why the pulsar acts like a lighthouse. As the rotation carries first one and then the other magnetic pole of the star into our view, we see a pulse of radiation each time.
This explanation of pulsars in terms of beams of radiation from highly magnetic and rapidly spinning neutron stars is a very clever idea. But what evidence do we have that it is the correct model? First, we can measure the masses of some pulsars, and they do turn out be in the range of 1.4 to 1.8 times that of the Sun—just what theorists predict for neutron stars. The masses are found using Kepler’s law for those few pulsars that are members of binary star systems.
But there is an even-better confirming argument, which brings us back to the Crab Nebula and its vast energy output. When the high-energy charged particles from the neutron star pulsar hit the slower-moving material from the supernova, they energize this material and cause it to “glow” at many different wavelengths—just what we observe from the Crab Nebula. The pulsar beams are a power source that “light up” the nebula long after the initial explosion of the star that made it.
Who “pays the bills” for all the energy we see coming out of a remnant like the Crab Nebula? After all, when energy emerges from one place, it must be depleted in another. The ultimate energy source in our model is the rotation of the neutron star, which propels charged particles outward and spins its magnetic field at enormous speeds. As its rotational energy is used to excite the Crab Nebula year after year, the pulsar inside the nebula slows down. As it slows, the pulses come a little less often; more time elapses before the slower neutron star brings its beam back around.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?