| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| The Evolution of a Star with the Sun’s Mass | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage | Time in This Stage (years) | Surface Temperature (K) | Luminosity ( L Sun ) | Diameter
(Sun = 1) |
| Main sequence | 11 billion | 6000 | 1 | 1 |
| Becomes red giant | 1.3 billion | 3100 at minimum | 2300 at maximum | 165 |
| Helium fusion | 100 million | 4800 | 50 | 10 |
| Giant again | 20 million | 3100 | 5200 | 180 |
When stars swell up to become red giants, they have very large radii and therefore a low escape velocity. Recall that the force of gravity depends not only on the mass doing the pulling, but also on our distance from the center of gravity. As a red giant star gets a lot bigger, a point on the surface of the star is now farther from the center, and thus has less gravity. That’s why the speed needed to escape the star goes down. Radiation pressure, stellar pulsations, and violent events like the helium flash can all drive atoms in the outer atmosphere away from the star, and cause it to lose a substantial fraction of its mass into space. Astronomers estimate that by the time a star like the Sun reaches the point of the helium flash, for example, it will have lost as much as 25% of its mass. And it can lose still more mass when it ascends the red-giant branch for the second time. As a result, aging stars are surrounded by one or more expanding shells of gas, each containing as much as 10–20% of the Sun’s mass (or 0.1–0.2 M Sun ).
When nuclear energy generation in the carbon-oxygen core ceases, the star’s core begins to shrink again and to heat up as it gets more and more compressed. (Remember that this compression will not be halted by another type of fusion in these low-mass stars.) The whole star follows along, shrinking and also becoming very hot—reaching surface temperatures as high as 100,000 K. Such hot stars are very strong sources of stellar winds and ultraviolet radiation, which sweep outward into the shells of material ejected when the star was a red giant. The winds and the ultraviolet radiation heat the shells, ionize them, and set them aglow (just as ultraviolet radiation from hot, young stars produces H II regions; see Between the Stars: Gas and Dust in Space ).
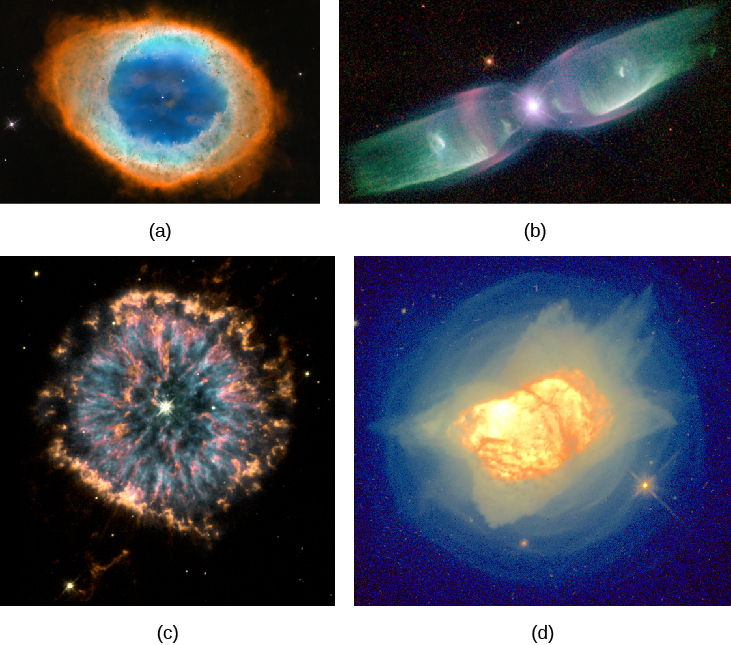
The result is the creation of some of the most beautiful objects in the cosmos (see the gallery in [link] and [link] ). These objects were given an extremely misleading name when first found in the eighteenth century: planetary nebulae . The name is derived from the fact that a few planetary nebulae, when viewed through a small telescope, have a round shape bearing a superficial resemblance to planets. Actually, they have nothing to do with planets, but once names are put into regular use in astronomy, it is extremely difficult to change them. There are tens of thousands of planetary nebulae in our own Galaxy, although many are hidden from view because their light is absorbed by interstellar dust.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?