| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Constellations on the Ecliptic | |
|---|---|
| Constellation on the Ecliptic | Dates When the Sun Crosses It |
| Capricornus | January 21–February 16 |
| Aquarius | February 16–March 11 |
| Pisces | March 11–April 18 |
| Aries | April 18–May 13 |
| Taurus | May 13–June 22 |
| Gemini | June 22–July 21 |
| Cancer | July 21–August 10 |
| Leo | August 10–September 16 |
| Virgo | September 16–October 31 |
| Libra | October 31–November 23 |
| Scorpius | November 23–November 29 |
| Ophiuchus | November 29–December 18 |
| Sagittarius | December 18–January 21 |
The ecliptic does not lie along the celestial equator but is inclined to it at an angle of about 23.5°. In other words, the Sun’s annual path in the sky is not linked with Earth’s equator. This is because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted by about 23.5° from a vertical line sticking out of the plane of the ecliptic ( [link] ). Being tilted from “straight up” is not at all unusual among celestial bodies; Uranus and Pluto are actually tilted so much that they orbit the Sun “on their side.”
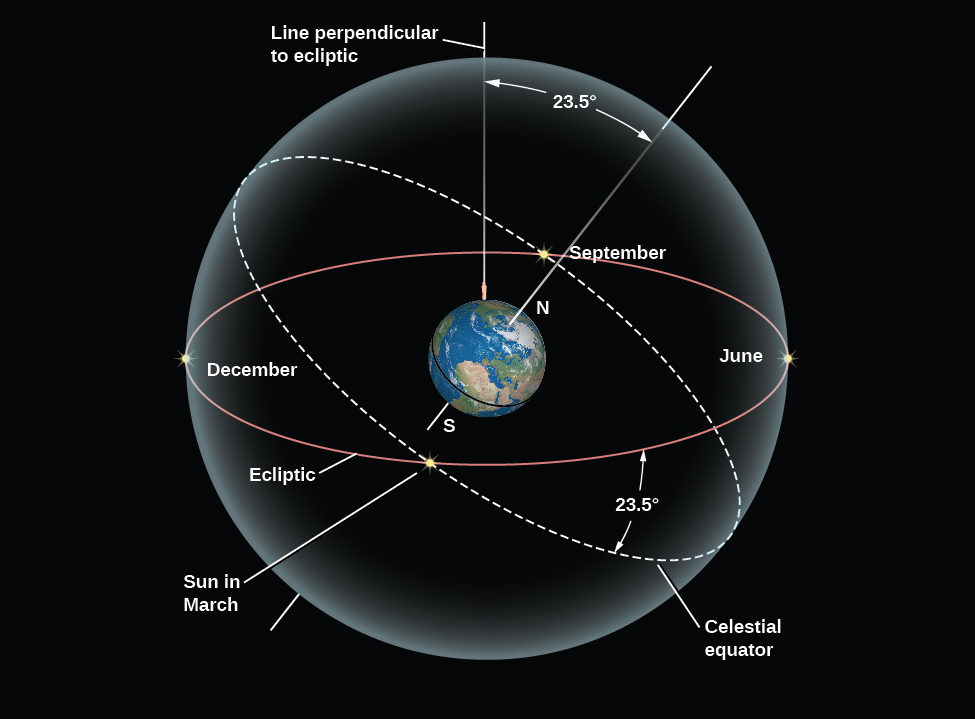
The inclination of the ecliptic is the reason the Sun moves north and south in the sky as the seasons change. In Earth, Moon, and Sky , we discuss the progression of the seasons in more detail.
The Sun is not the only object that moves among the fixed stars. The Moon and each of the planets that are visible to the unaided eye—Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus (although just barely)—also change their positions slowly from day to day. During a single day, the Moon and planets all rise and set as Earth turns, just as the Sun and stars do. But like the Sun, they have independent motions among the stars, superimposed on the daily rotation of the celestial sphere. Noticing these motions, the Greeks of 2000 years ago distinguished between what they called the fixed stars —those that maintain fixed patterns among themselves through many generations—and the wandering stars , or planets . The word “planet,” in fact, means “wanderer” in ancient Greek.
Today, we do not regard the Sun and Moon as planets, but the ancients applied the term to all seven of the moving objects in the sky. Much of ancient astronomy was devoted to observing and predicting the motions of these celestial wanderers. They even dedicated a unit of time, the week, to the seven objects that move on their own; that’s why there are 7 days in a week. The Moon, being Earth’s nearest celestial neighbor, has the fastest apparent motion; it completes a trip around the sky in about 1 month (or moonth ). To do this, the Moon moves about 12°, or 24 times its own apparent width on the sky, each day.
This is true whether the motion is measured in kilometers per hour or degrees per hour; we just need to use consistent units.
As an example, let’s say you notice the bright star Sirius due south from your observing location in the Northern Hemisphere. You note the time, and then later, you note the time that Sirius sets below the horizon. You find that Sirius has traveled an angular distance of about 75° in 5 h. About how many hours will it take for Sirius to return to its original location?
The actual time is a few minutes shorter than this, and we will explore why in a later chapter.
The speed of the moon is 0.5°/1 h. To move a full 360°, the moon needs 720 h:
Dividing
720 h by the conversion factor of 24 h/day reveals the lunar cycle is about 30 days.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?