| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
the area of a 1-m telescope is
and the area of a 4-m telescope is
Therefore, with 16 times the area, a 4-m telescope collects 16 times the light of a 1-m telescope.
After the telescope forms an image, we need some way to detect and record it so that we can measure, reproduce, and analyze the image in various ways. Before the nineteenth century, astronomers simply viewed images with their eyes and wrote descriptions of what they saw. This was very inefficient and did not lead to a very reliable long-term record; you know from crime shows on television that eyewitness accounts are often inaccurate.
In the nineteenth century, the use of photography became widespread. In those days, photographs were a chemical record of an image on a specially treated glass plate. Today, the image is generally detected with sensors similar to those in digital cameras, recorded electronically, and stored in computers. This permanent record can then be used for detailed and quantitative studies. Professional astronomers rarely look through the large telescopes that they use for their research.
Whether or not you wear glasses, you see the world through lenses; they are key elements of your eyes. A lens is a transparent piece of material that bends the rays of light passing through it. If the light rays are parallel as they enter, the lens brings them together in one place to form an image ( [link] ). If the curvatures of the lens surfaces are just right, all parallel rays of light (say, from a star) are bent, or refracted , in such a way that they converge toward a point, called the focus of the lens. At the focus, an image of the light source appears. In the case of parallel light rays, the distance from the lens to the location where the light rays focus, or image, behind the lens is called the focal length of the lens.
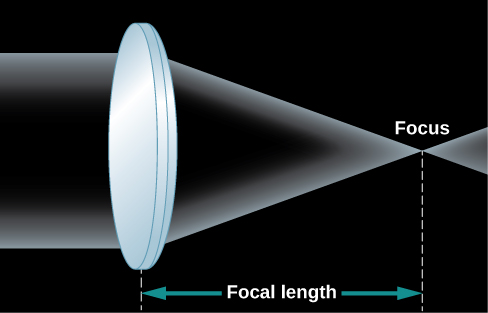
As you look at [link] , you may ask why two rays of light from the same star would be parallel to each other. After all, if you draw a picture of star shining in all directions, the rays of light coming from the star don’t look parallel at all. But remember that the stars (and other astronomical objects) are all extremely far away. By the time the few rays of light pointed toward us actually arrive at Earth, they are, for all practical purposes, parallel to each other. Put another way, any rays that were not parallel to the ones pointed at Earth are now heading in some very different direction in the universe.
To view the image formed by the lens in a telescope, we use an additional lens called an eyepiece . The eyepiece focuses the image at a distance that is either directly viewable by a human or at a convenient place for a detector. Using different eyepieces, we can change the magnification (or size) of the image and also redirect the light to a more accessible location. Stars look like points of light, and magnifying them makes little difference, but the image of a planet or a galaxy, which has structure, can often benefit from being magnified.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?