| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The measurement of time is based on the rotation of Earth. Throughout most of human history, time has been reckoned by positions of the Sun and stars in the sky. Only recently have mechanical and electronic clocks taken over this function in regulating our lives.
The most fundamental astronomical unit of time is the day, measured in terms of the rotation of Earth. There is, however, more than one way to define the day. Usually, we think of it as the rotation period of Earth with respect to the Sun, called the solar day . After all, for most people sunrise is more important than the rising time of Arcturus or some other star, so we set our clocks to some version of Sun-time. However, astronomers also use a sidereal day , which is defined in terms of the rotation period of Earth with respect to the stars.
A solar day is slightly longer than a sidereal day because (as you can see from [link] ) Earth not only turns but also moves along its path around the Sun in a day. Suppose we start when Earth’s orbital position is at day 1, with both the Sun and some distant star (located in the direction indicated by the long white arrow pointing left), directly in line with the zenith for the observer on Earth. When Earth has completed one rotation with respect to the distant star and is at day 2, the long arrow again points to the same distant star. However, notice that because of the movement of Earth along its orbit from day 1 to 2, the Sun has not yet reached a position above the observer. To complete a solar day, Earth must rotate an additional amount, equal to 1/365 of a full turn. The time required for this extra rotation is 1/365 of a day, or about 4 minutes. So the solar day is about 4 minutes longer than the sidereal day.
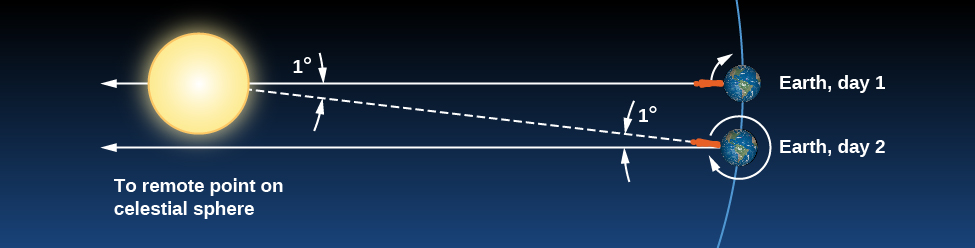
Because our ordinary clocks are set to solar time, stars rise 4 minutes earlier each day. Astronomers prefer sidereal time for planning their observations because in that system, a star rises at the same time every day.
It will rise at about 1:00 p.m. and be high in the sky at around sunset instead of midnight. Sirius is the brightest star in the constellation of Canis Major (the big dog). So, some other constellation will be prominently visible high in the sky at this later date.
In two months, the star will rise:
This means it will rise at 4:30 p.m.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?