| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
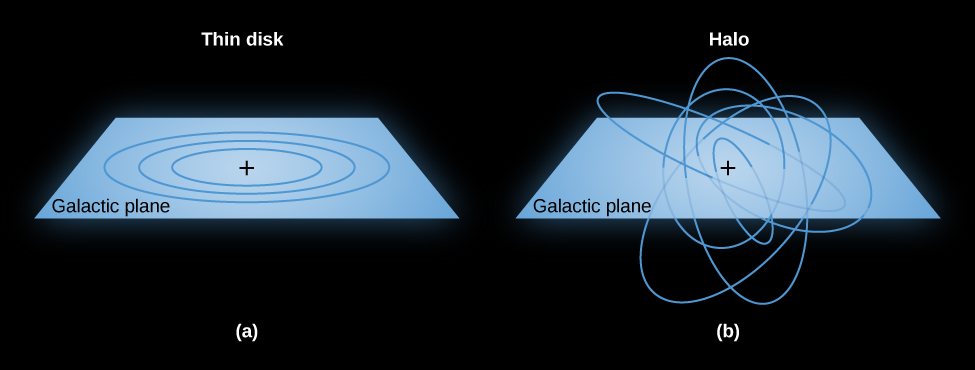
In the first section of his chapter, we described the thin disk, thick disk, and stellar halo. Look back at [link] and note some of the patterns. Young stars lie in the thin disk, are rich in metals, and orbit the Galaxy’s center at high speed. The stars in the halo are old, have low abundances of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, and have highly elliptical orbits randomly oriented in direction (see [link] ). Halo stars can plunge through the disk and central bulge, but they spend most of their time far above or below the plane of the Galaxy. The stars in the thick disk are intermediate between these two extremes. Let’s first see why age and heavier-element abundance are correlated and then see what these correlations tell us about the origin of our Galaxy.
The discovery that there are two different kinds of stars was first made by Walter Baade during World War II. As a German national, Baade was not allowed to do war research as many other U.S.-based scientists were doing, so he was able to make regular use of the Mount Wilson telescopes in southern California. His observations were aided by the darker skies that resulted from the wartime blackout of Los Angeles.
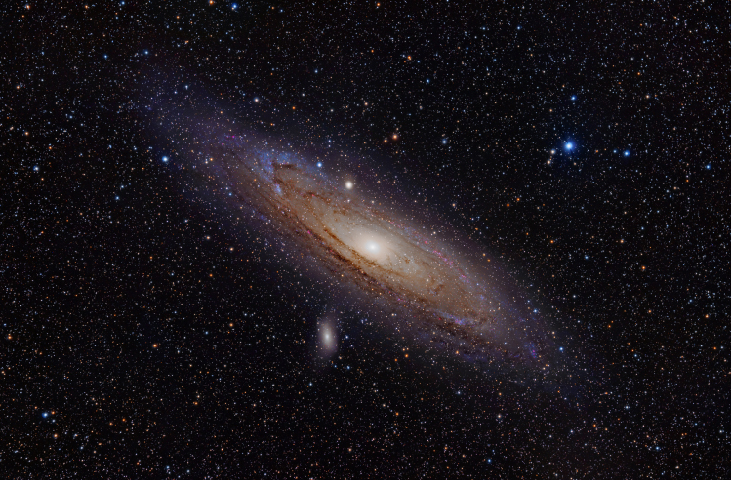
Among the things a large telescope and dark skies enabled Baade to examine carefully were other galaxies—neighbors of our Milky Way Galaxy. We will discuss other galaxies in the next chapter ( Galaxies ), but for now we will just mention that the nearest Galaxy that resembles our own (with a similar disk and spiral structure) is often called the Andromeda galaxy , after the constellation in which we find it.
Baade was impressed by the similarity of the mainly reddish stars in the Andromeda galaxy’s nuclear bulge to those in our Galaxy’s globular clusters and the halo. He also noted the difference in color between all these and the bluer stars found in the spiral arms near the Sun ( [link] ). On this basis, he called the bright blue stars in the spiral arms population I and all the stars in the halo and globular clusters population II .

We now know that the populations differ not only in their locations in the Galaxy, but also in their chemical composition, age, and orbital motions around the center of the Galaxy. Population I stars are found only in the disk and follow nearly circular orbits around the galactic center. Examples are bright supergiant stars, main-sequence stars of high luminosity (spectral classes O and B), which are concentrated in the spiral arms, and members of young open star clusters. Interstellar matter and molecular clouds are found in the same places as population I stars.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?