| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
In the previous section, we indicated that that open clusters are younger than globular clusters, and associations are typically even younger. In this section, we will show how we determine the ages of these star clusters. The key observation is that the stars in these different types of clusters are found in different places in the H–R diagram, and we can use their locations in the diagram in combination with theoretical calculations to estimate how long they have lived.
What does theory predict for the H–R diagram of a cluster whose stars have recently condensed from an interstellar cloud? Remember that at every stage of evolution, massive stars evolve more quickly than their lower-mass counterparts. After a few million years (“recently” for astronomers), the most massive stars should have completed their contraction phase and be on the main sequence, while the less massive ones should be off to the right, still on their way to the main sequence. These ideas are illustrated in [link] , which shows the H–R diagram calculated by R. Kippenhahn and his associates at Munich University for a hypothetical cluster with an age of 3 million years.
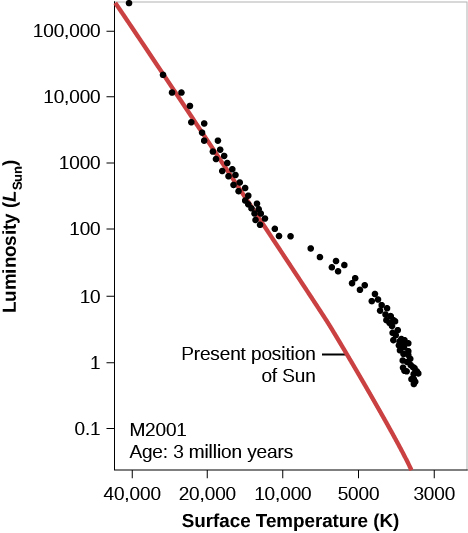
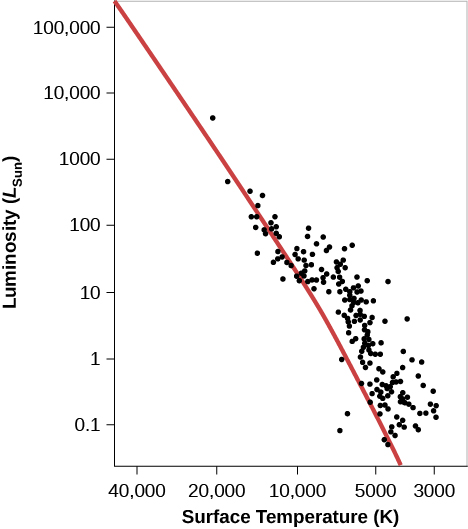
There are real star clusters that fit this description. The first to be studied (in about 1950) was NGC 2264, which is still associated with the region of gas and dust from which it was born ( [link] ).
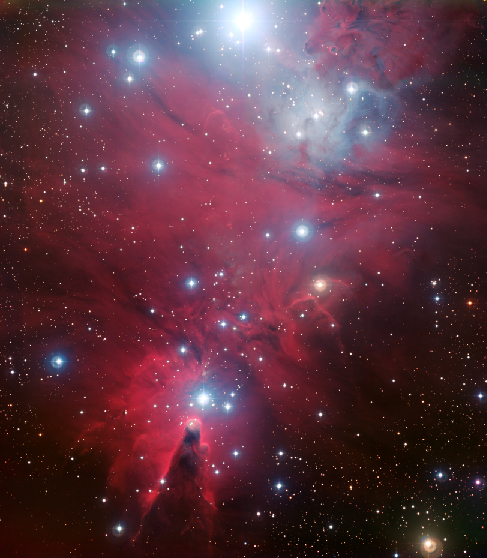

The NGC 2264 cluster’s H–R diagram is shown in [link] . The cluster in the middle of the Orion Nebula (shown in [link] and [link] ) is in a similar stage of evolution.
As clusters get older, their H–R diagrams begin to change. After a short time (less than a million years after they reach the main sequence), the most massive stars use up the hydrogen in their cores and evolve off the main sequence to become red giants and supergiants. As more time passes, stars of lower mass begin to leave the main sequence and make their way to the upper right of the H–R diagram.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?