| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Our senses suggest to us that Earth is the center of the universe—the hub around which the heavens turn. This geocentric (Earth-centered) view was what almost everyone believed until the European Renaissance. After all, it is simple, logical, and seemingly self-evident. Furthermore, the geocentric perspective reinforced those philosophical and religious systems that taught the unique role of human beings as the central focus of the cosmos. However, the geocentric view happens to be wrong. One of the great themes of our intellectual history is the overthrow of the geocentric perspective. Let us, therefore, take a look at the steps by which we reevaluated the place of our world in the cosmic order.
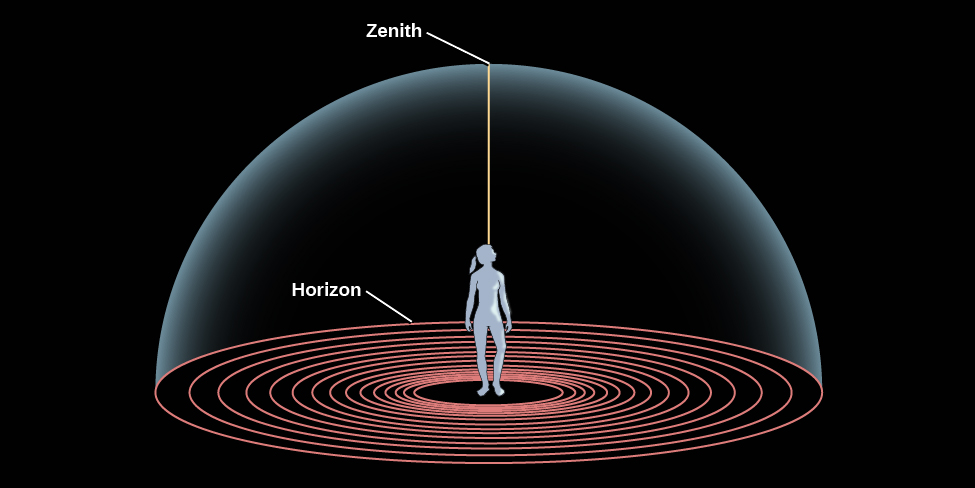
If you go on a camping trip or live far from city lights, your view of the sky on a clear night is pretty much identical to that seen by people all over the world before the invention of the telescope. Gazing up, you get the impression that the sky is a great hollow dome with you at the center ( [link] ), and all the stars are an equal distance from you on the surface of the dome. The top of that dome, the point directly above your head, is called the zenith , and where the dome meets Earth is called the horizon . From the sea or a flat prairie, it is easy to see the horizon as a circle around you, but from most places where people live today, the horizon is at least partially hidden by mountains, trees, buildings, or smog.
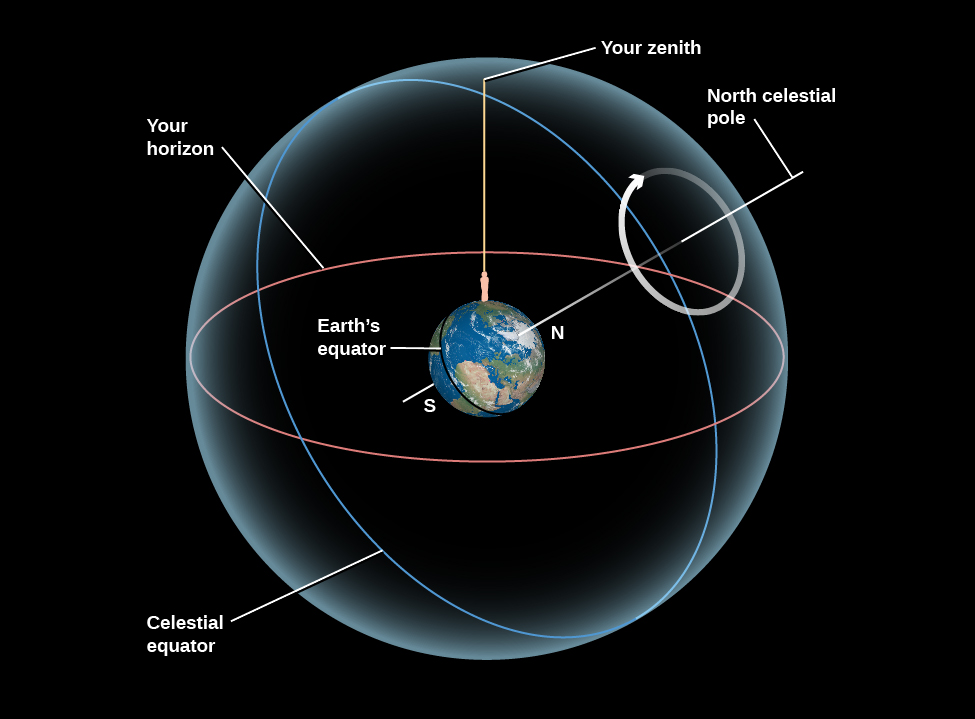
If you lie back in an open field and observe the night sky for hours, as ancient shepherds and travelers regularly did, you will see stars rising on the eastern horizon (just as the Sun and Moon do), moving across the dome of the sky in the course of the night, and setting on the western horizon. Watching the sky turn like this night after night, you might eventually get the idea that the dome of the sky is really part of a great sphere that is turning around you, bringing different stars into view as it turns. The early Greeks regarded the sky as just such a celestial sphere ( [link] ). Some thought of it as an actual sphere of transparent crystalline material, with the stars embedded in it like tiny jewels.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?