| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Before the invention of the telescope, the Sun was thought to be an unchanging and perfect sphere. We now know that the Sun is in a perpetual state of change: its surface is a seething, bubbling cauldron of hot gas. Areas that are darker and cooler than the rest of the surface come and go. Vast plumes of gas erupt into the chromosphere and corona. Occasionally, there are even giant explosions on the Sun that send enormous streamers of charged particles and energy hurtling toward Earth. When they arrive, these can cause power outages and other serious effects on our planet.
The first evidence that the Sun changes came from studies of sunspots , which are large, dark features seen on the surface of the Sun caused by increased magnetic activity. They look darker because the spots are typically at a temperature of about 3800 K, whereas the bright regions that surround them are at about 5800 K ( [link] ). Occasionally, these spots are large enough to be visible to the unaided eye, and we have records going back over a thousand years from observers who noticed them when haze or mist reduced the Sun’s intensity. (We emphasize what your parents have surely told you: looking at the Sun for even a brief time can cause permanent eye damage. This is the one area of astronomy where we don’t encourage you to do your own observing without getting careful instructions or filters from your instructor.)
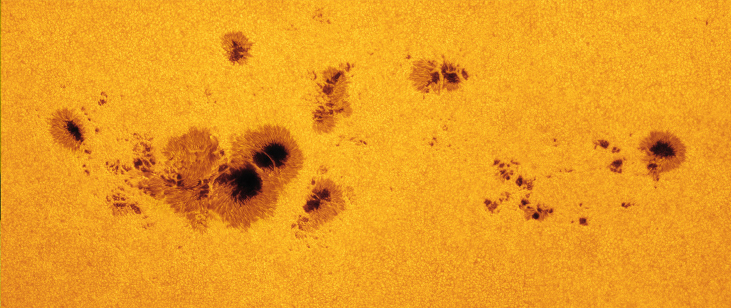
While we understand that sunspots look darker because they are cooler, they are nevertheless hotter than the surfaces of many stars. If they could be removed from the Sun, they would shine brightly. They appear dark only in contrast with the hotter, brighter photosphere around them.
Individual sunspots come and go, with lifetimes that range from a few hours to a few months. If a spot lasts and develops, it usually consists of two parts: an inner darker core, the umbra , and a surrounding less dark region, the penumbra . Many spots become much larger than Earth, and a few, like the largest one shown in [link] , have reached diameters over 140,000 kilometers. Frequently, spots occur in groups of 2 to 20 or more. The largest groups are very complex and may have over 100 spots. Like storms on Earth, sunspots are not fixed in position, but they drift slowly compared with the Sun’s rotation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?