| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
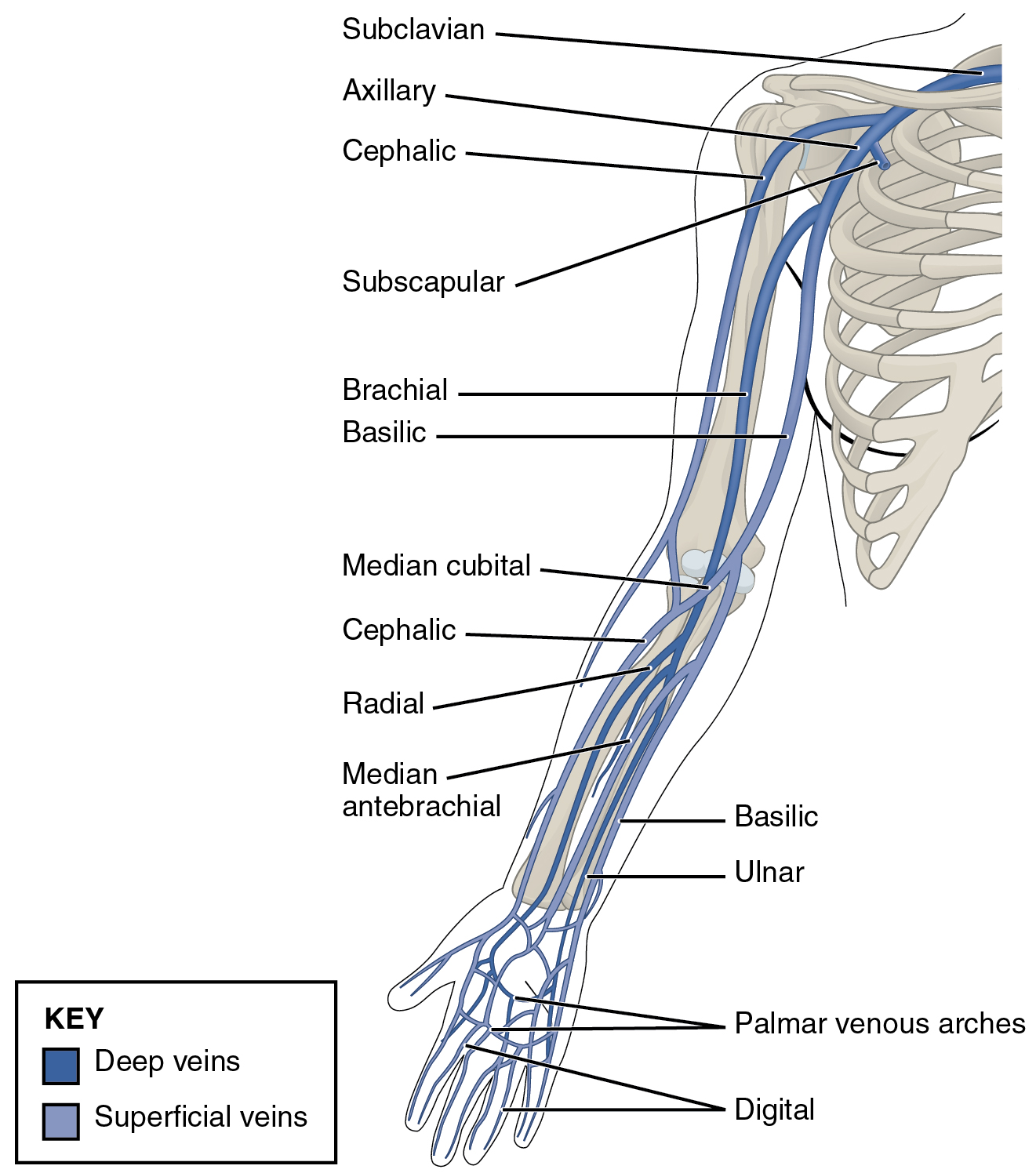
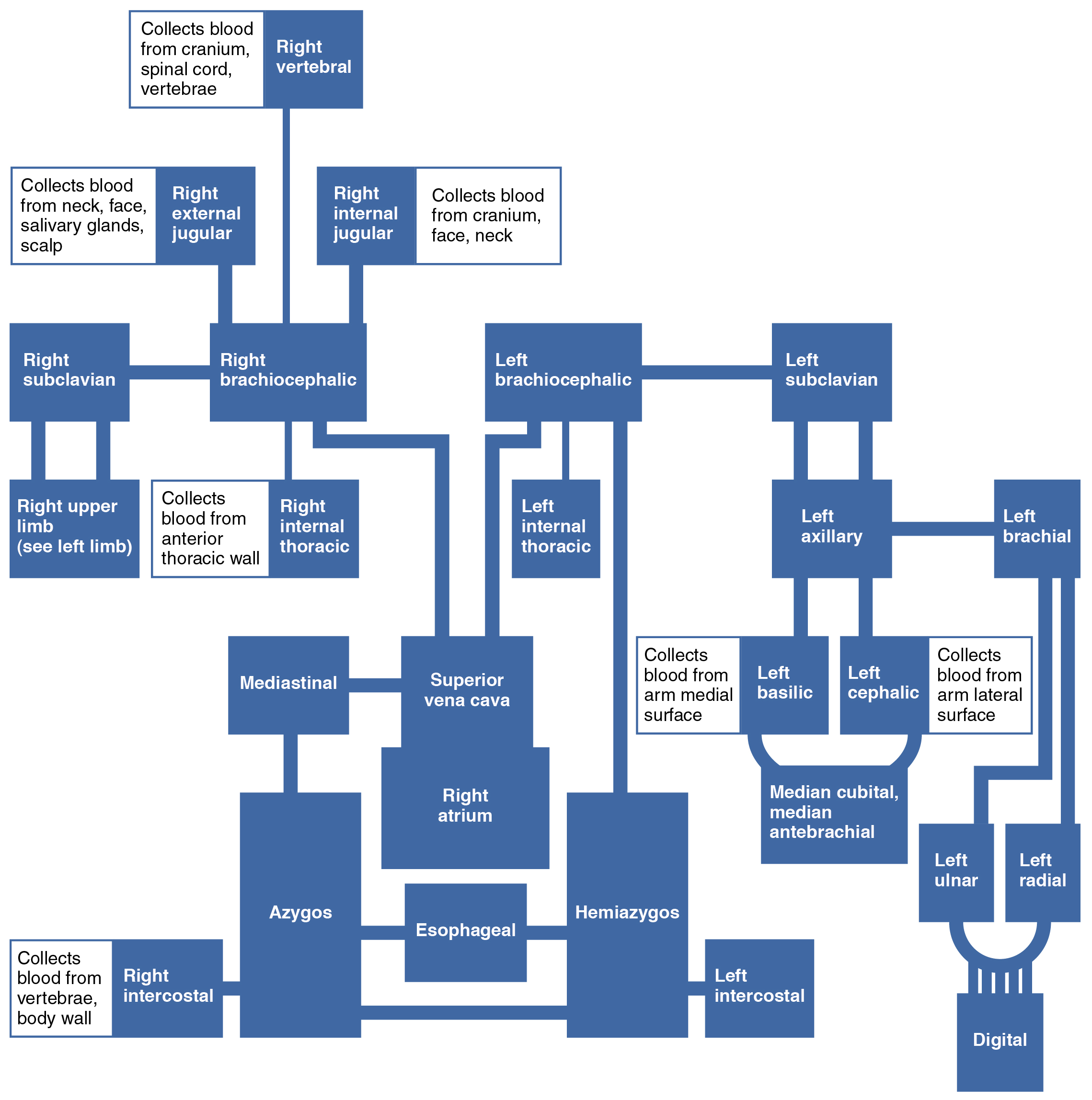
| Veins of the Upper Limbs | |
|---|---|
| Vessel | Description |
| Digital veins | Drain the digits and lead to the palmar arches of the hand and dorsal venous arch of the foot |
| Palmar venous arches | Drain the hand and digits, and lead to the radial vein, ulnar veins, and the median antebrachial vein |
| Radial vein | Vein that parallels the radius and radial artery; arises from the palmar venous arches and leads to the brachial vein |
| Ulnar vein | Vein that parallels the ulna and ulnar artery; arises from the palmar venous arches and leads to the brachial vein |
| Brachial vein | Deeper vein of the arm that forms from the radial and ulnar veins in the lower arm; leads to the axillary vein |
| Median antebrachial vein | Vein that parallels the ulnar vein but is more medial in location; intertwines with the palmar venous arches; leads to the basilic vein |
| Basilic vein | Superficial vein of the arm that arises from the median antebrachial vein, intersects with the median cubital vein, parallels the ulnar vein, and continues into the upper arm; along with the brachial vein, it leads to the axillary vein |
| Median cubital vein | Superficial vessel located in the antecubital region that links the cephalic vein to the basilic vein in the form of a v; a frequent site from which to draw blood |
| Cephalic vein | Superficial vessel in the upper arm; leads to the axillary vein |
| Subscapular vein | Drains blood from the subscapular region and leads to the axillary vein |
| Axillary vein | The major vein in the axillary region; drains the upper limb and becomes the subclavian vein |
Other than the small amount of blood drained by the azygos and hemiazygos veins, most of the blood inferior to the diaphragm drains into the inferior vena cava before it is returned to the heart (see [link] ). Lying just beneath the parietal peritoneum in the abdominal cavity, the inferior vena cava parallels the abdominal aorta, where it can receive blood from abdominal veins. The lumbar portions of the abdominal wall and spinal cord are drained by a series of lumbar veins , usually four on each side. The ascending lumbar veins drain into either the azygos vein on the right or the hemiazygos vein on the left, and return to the superior vena cava. The remaining lumbar veins drain directly into the inferior vena cava.
Blood supply from the kidneys flows into each renal vein , normally the largest veins entering the inferior vena cava. A number of other, smaller veins empty into the left renal vein. Each adrenal vein drains the adrenal or suprarenal glands located immediately superior to the kidneys. The right adrenal vein enters the inferior vena cava directly, whereas the left adrenal vein enters the left renal vein.
From the male reproductive organs, each testicular vein flows from the scrotum, forming a portion of the spermatic cord. Each ovarian vein drains an ovary in females. Each of these veins is generically called a gonadal vein . The right gonadal vein empties directly into the inferior vena cava, and the left gonadal vein empties into the left renal vein.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?