| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The pharynx (throat) is involved in both digestion and respiration. It receives food and air from the mouth, and air from the nasal cavities. When food enters the pharynx, involuntary muscle contractions close off the air passageways.
A short tube of skeletal muscle lined with a mucous membrane, the pharynx runs from the posterior oral and nasal cavities to the opening of the esophagus and larynx. It has three subdivisions. The most superior, the nasopharynx, is involved only in breathing and speech. The other two subdivisions, the oropharynx and the laryngopharynx , are used for both breathing and digestion. The oropharynx begins inferior to the nasopharynx and is continuous below with the laryngopharynx ( [link] ). The inferior border of the laryngopharynx connects to the esophagus, whereas the anterior portion connects to the larynx, allowing air to flow into the bronchial tree.
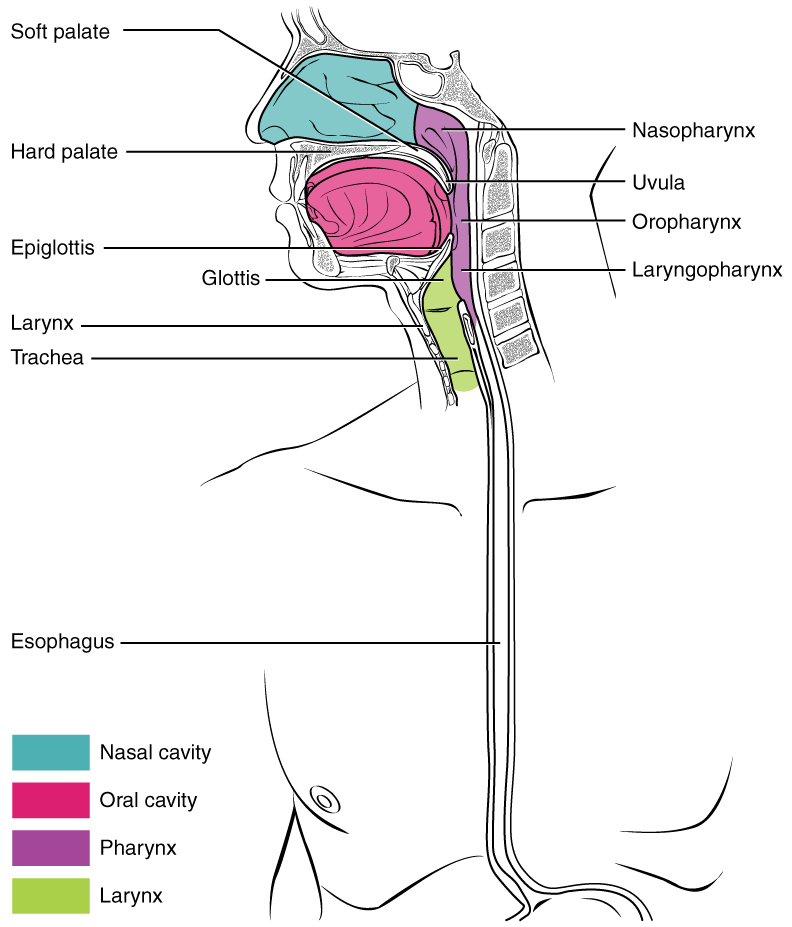
Histologically, the wall of the oropharynx is similar to that of the oral cavity. The mucosa includes a stratified squamous epithelium that is endowed with mucus-producing glands. During swallowing, the elevator skeletal muscles of the pharynx contract, raising and expanding the pharynx to receive the bolus of food. Once received, these muscles relax and the constrictor muscles of the pharynx contract, forcing the bolus into the esophagus and initiating peristalsis.
Usually during swallowing, the soft palate and uvula rise reflexively to close off the entrance to the nasopharynx. At the same time, the larynx is pulled superiorly and the cartilaginous epiglottis, its most superior structure, folds inferiorly, covering the glottis (the opening to the larynx); this process effectively blocks access to the trachea and bronchi. When the food “goes down the wrong way,” it goes into the trachea. When food enters the trachea, the reaction is to cough, which usually forces the food up and out of the trachea, and back into the pharynx.
The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach. It is approximately 25.4 cm (10 in) in length, located posterior to the trachea, and remains in a collapsed form when not engaged in swallowing. As you can see in [link] , the esophagus runs a mainly straight route through the mediastinum of the thorax. To enter the abdomen, the esophagus penetrates the diaphragm through an opening called the esophageal hiatus.
The upper esophageal sphincter , which is continuous with the inferior pharyngeal constrictor, controls the movement of food from the pharynx into the esophagus. The upper two-thirds of the esophagus consists of both smooth and skeletal muscle fibers, with the latter fading out in the bottom third of the esophagus. Rhythmic waves of peristalsis, which begin in the upper esophagus, propel the bolus of food toward the stomach. Meanwhile, secretions from the esophageal mucosa lubricate the esophagus and food. Food passes from the esophagus into the stomach at the lower esophageal sphincter (also called the gastroesophageal or cardiac sphincter). Recall that sphincters are muscles that surround tubes and serve as valves, closing the tube when the sphincters contract and opening it when they relax. The lower esophageal sphincter relaxes to let food pass into the stomach, and then contracts to prevent stomach acids from backing up into the esophagus. Surrounding this sphincter is the muscular diaphragm, which helps close off the sphincter when no food is being swallowed. When the lower esophageal sphincter does not completely close, the stomach’s contents can reflux (that is, back up into the esophagus), causing heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?