| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Microglia are, as the name implies, smaller than most of the other glial cells. Ongoing research into these cells, although not entirely conclusive, suggests that they may originate as white blood cells, called macrophages, that become part of the CNS during early development. While their origin is not conclusively determined, their function is related to what macrophages do in the rest of the body. When macrophages encounter diseased or damaged cells in the rest of the body, they ingest and digest those cells or the pathogens that cause disease. Microglia are the cells in the CNS that can do this in normal, healthy tissue, and they are therefore also referred to as CNS-resident macrophages.
The ependymal cell is a glial cell that filters blood to make cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) , the fluid that circulates through the CNS. Because of the privileged blood supply inherent in the BBB, the extracellular space in nervous tissue does not easily exchange components with the blood. Ependymal cells line each ventricle , one of four central cavities that are remnants of the hollow center of the neural tube formed during the embryonic development of the brain. The choroid plexus is a specialized structure in the ventricles where ependymal cells come in contact with blood vessels and filter and absorb components of the blood to produce cerebrospinal fluid. Because of this, ependymal cells can be considered a component of the BBB, or a place where the BBB breaks down. These glial cells appear similar to epithelial cells, making a single layer of cells with little intracellular space and tight connections between adjacent cells. They also have cilia on their apical surface to help move the CSF through the ventricular space. The relationship of these glial cells to the structure of the CNS is seen in [link] .
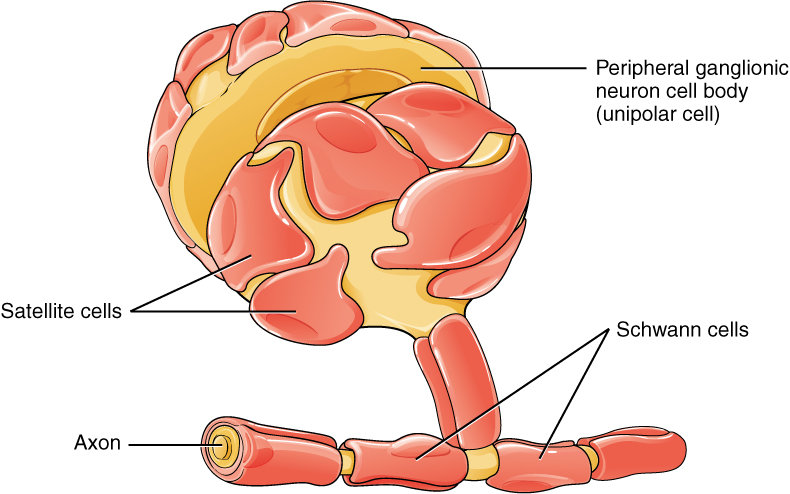
One of the two types of glial cells found in the PNS is the satellite cell . Satellite cells are found in sensory and autonomic ganglia, where they surround the cell bodies of neurons. This accounts for the name, based on their appearance under the microscope. They provide support, performing similar functions in the periphery as astrocytes do in the CNS—except, of course, for establishing the BBB.
The second type of glial cell is the Schwann cell , which insulate axons with myelin in the periphery. Schwann cells are different than oligodendrocytes, in that a Schwann cell wraps around a portion of only one axon segment and no others. Oligodendrocytes have processes that reach out to multiple axon segments, whereas the entire Schwann cell surrounds just one axon segment. The nucleus and cytoplasm of the Schwann cell are on the edge of the myelin sheath. The relationship of these two types of glial cells to ganglia and nerves in the PNS is seen in [link] .
The insulation for axons in the nervous system is provided by glial cells, oligodendrocytes in the CNS, and Schwann cells in the PNS. Whereas the manner in which either cell is associated with the axon segment, or segments, that it insulates is different, the means of myelinating an axon segment is mostly the same in the two situations. Myelin is a lipid-rich sheath that surrounds the axon and by doing so creates a myelin sheath that facilitates the transmission of electrical signals along the axon. The lipids are essentially the phospholipids of the glial cell membrane. Myelin, however, is more than just the membrane of the glial cell. It also includes important proteins that are integral to that membrane. Some of the proteins help to hold the layers of the glial cell membrane closely together.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?