| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
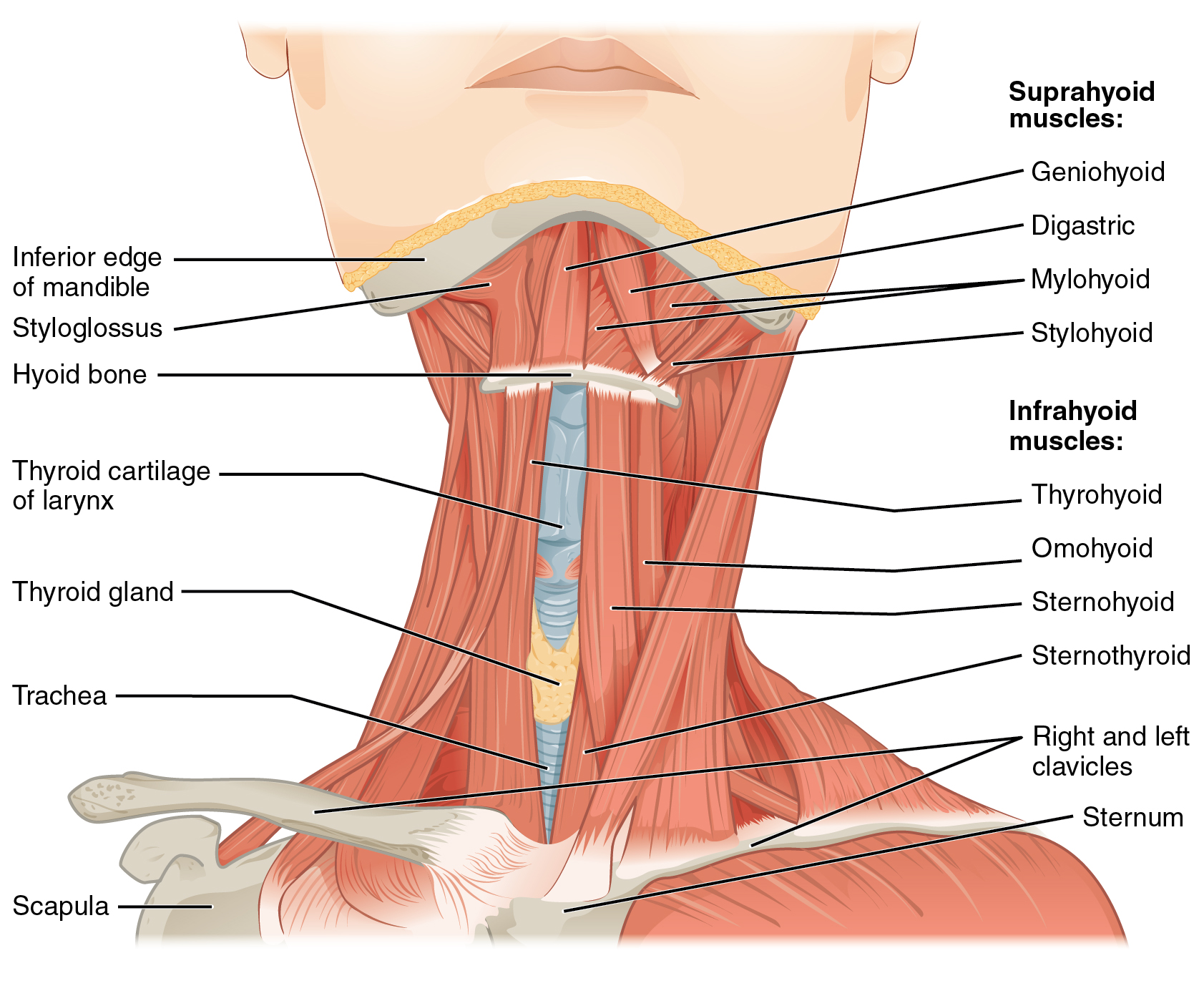
The suprahyoid muscles raise the hyoid bone, the floor of the mouth, and the larynx during deglutition. These include the digastric muscle, which has anterior and posterior bellies that work to elevate the hyoid bone and larynx when one swallows; it also depresses the mandible. The stylohyoid muscle moves the hyoid bone posteriorly, elevating the larynx, and the mylohyoid muscle lifts it and helps press the tongue to the top of the mouth. The geniohyoid depresses the mandible in addition to raising and pulling the hyoid bone anteriorly.
The strap-like infrahyoid muscles generally depress the hyoid bone and control the position of the larynx. The omohyoid muscle, which has superior and inferior bellies, depresses the hyoid bone in conjunction with the sternohyoid and thyrohyoid muscles. The thyrohyoid muscle also elevates the larynx’s thyroid cartilage, whereas the sternothyroid depresses it to create different tones of voice.
The head, attached to the top of the vertebral column, is balanced, moved, and rotated by the neck muscles ( [link] ). When these muscles act unilaterally, the head rotates. When they contract bilaterally, the head flexes or extends. The major muscle that laterally flexes and rotates the head is the sternocleidomastoid . In addition, both muscles working together are the flexors of the head. Place your fingers on both sides of the neck and turn your head to the left and to the right. You will feel the movement originate there. This muscle divides the neck into anterior and posterior triangles when viewed from the side ( [link] ).
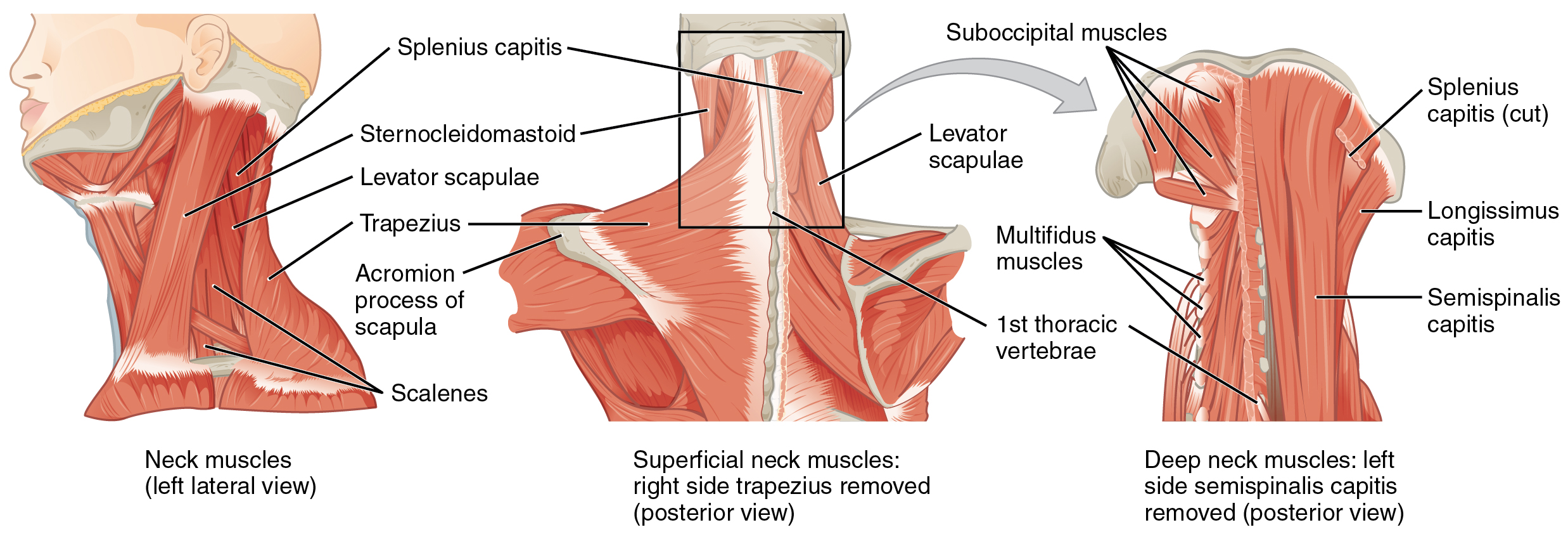
| Muscles That Move the Head | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Prime mover | Origin | Insertion |
| Rotates and tilts head to the side; tilts head forward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: rotates head to opposite side; bilaterally: flexion | Sternocleidomastoid | Sternum; clavicle | Temporal bone (mastoid process); occipital bone |
| Rotates and tilts head backward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: laterally flexes and rotates head to same side; bilaterally: extension | Semispinalis capitis | Transverse and articular processes of cervical and thoracic vertebra | Occipital bone |
| Rotates and tilts head to the side; tilts head backward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: laterally flexes and rotates head to same side; bilaterally: extension | Splenius capitis | Spinous processes of cervical and thoracic vertebra | Temporal bone (mastoid process); occipital bone |
| Rotates and tilts head to the side; tilts head backward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: laterally flexes and rotates head to same side; bilaterally: extension | Longissimus capitis | Transverse and articular processes of cervical and thoracic vertebra | Temporal bone (mastoid process) |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?