| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Classes of Antigen-presenting Cells | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| MHC | Cell type | Phagocytic? | Function |
| Class I | Many | No | Stimulates cytotoxic T cell immune response |
| Class II | Macrophage | Yes | Stimulates phagocytosis and presentation at primary infection site |
| Class II | Dendritic | Yes, in tissues | Brings antigens to regional lymph nodes |
| Class II | B cell | Yes, internalizes surface Ig and antigen | Stimulates antibody secretion by B cells |
The process of eliminating T cells that might attack the cells of one’s own body is referred to as T cell tolerance . While thymocytes are in the cortex of the thymus, they are referred to as “double negatives,” meaning that they do not bear the CD4 or CD8 molecules that you can use to follow their pathways of differentiation ( [link] ). In the cortex of the thymus, they are exposed to cortical epithelial cells. In a process known as positive selection , double-negative thymocytes bind to the MHC molecules they observe on the thymic epithelia, and the MHC molecules of “self” are selected. This mechanism kills many thymocytes during T cell differentiation. In fact, only two percent of the thymocytes that enter the thymus leave it as mature, functional T cells.
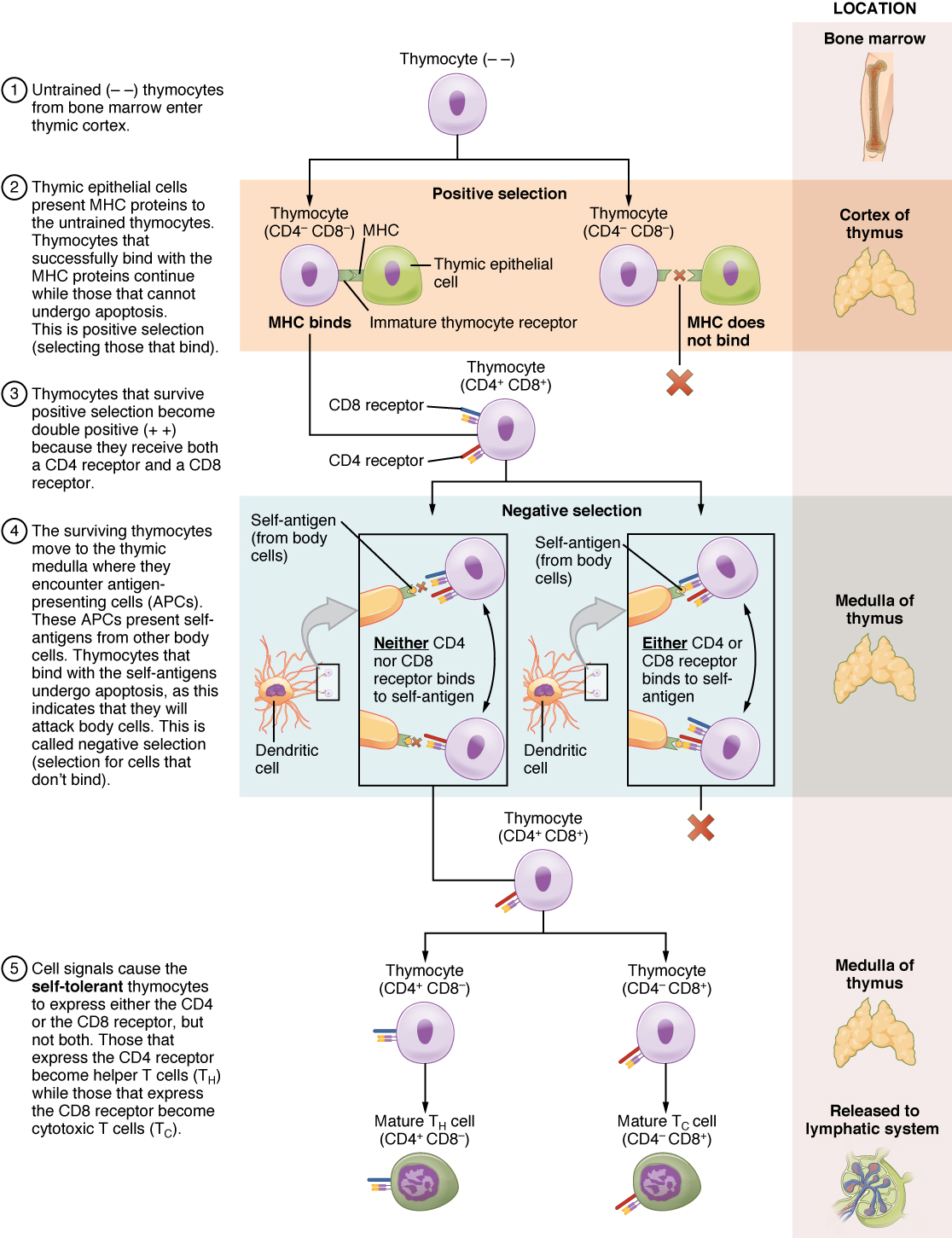
Later, the cells become double positives that express both CD4 and CD8 markers and move from the cortex to the junction between the cortex and medulla. It is here that negative selection takes place. In negative selection , self-antigens are brought into the thymus from other parts of the body by professional antigen-presenting cells. The T cells that bind to these self-antigens are selected for negatively and are killed by apoptosis. In summary, the only T cells left are those that can bind to MHC molecules of the body with foreign antigens presented on their binding clefts, preventing an attack on one’s own body tissues, at least under normal circumstances. Tolerance can be broken, however, by the development of an autoimmune response, to be discussed later in this chapter.
The cells that leave the thymus become single positives, expressing either CD4 or CD8, but not both (see [link] ). The CD4 + T cells will bind to class II MHC and the CD8 + cells will bind to class I MHC. The discussion that follows explains the functions of these molecules and how they can be used to differentiate between the different T cell functional types.
Mature T cells become activated by recognizing processed foreign antigen in association with a self-MHC molecule and begin dividing rapidly by mitosis. This proliferation of T cells is called clonal expansion and is necessary to make the immune response strong enough to effectively control a pathogen. How does the body select only those T cells that are needed against a specific pathogen? Again, the specificity of a T cell is based on the amino acid sequence and the three-dimensional shape of the antigen-binding site formed by the variable regions of the two chains of the T cell receptor ( [link] ). Clonal selection is the process of antigen binding only to those T cells that have receptors specific to that antigen. Each T cell that is activated has a specific receptor “hard-wired” into its DNA, and all of its progeny will have identical DNA and T cell receptors, forming clones of the original T cell.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?