| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Vitamin K also supports bone mineralization and may have a synergistic role with vitamin D in the regulation of bone growth. Green leafy vegetables are a good source of vitamin K.
The minerals magnesium and fluoride may also play a role in supporting bone health. While magnesium is only found in trace amounts in the human body, more than 60 percent of it is in the skeleton, suggesting it plays a role in the structure of bone. Fluoride can displace the hydroxyl group in bone’s hydroxyapatite crystals and form fluorapatite. Similar to its effect on dental enamel, fluorapatite helps stabilize and strengthen bone mineral. Fluoride can also enter spaces within hydroxyapatite crystals, thus increasing their density.
Omega-3 fatty acids have long been known to reduce inflammation in various parts of the body. Inflammation can interfere with the function of osteoblasts, so consuming omega-3 fatty acids, in the diet or in supplements, may also help enhance production of new osseous tissue. [link] summarizes the role of nutrients in bone health.
| Nutrients and Bone Health | |
|---|---|
| Nutrient | Role in bone health |
| Calcium | Needed to make calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate, which form the hydroxyapatite crystals that give bone its hardness |
| Vitamin D | Needed for calcium absorption |
| Vitamin K | Supports bone mineralization; may have synergistic effect with vitamin D |
| Magnesium | Structural component of bone |
| Fluoride | Structural component of bone |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Reduces inflammation that may interfere with osteoblast function |
The endocrine system produces and secretes hormones, many of which interact with the skeletal system. These hormones are involved in controlling bone growth, maintaining bone once it is formed, and remodeling it.
Several hormones are necessary for controlling bone growth and maintaining the bone matrix. The pituitary gland secretes growth hormone (GH), which, as its name implies, controls bone growth in several ways. It triggers chondrocyte proliferation in epiphyseal plates, resulting in the increasing length of long bones. GH also increases calcium retention, which enhances mineralization, and stimulates osteoblastic activity, which improves bone density.
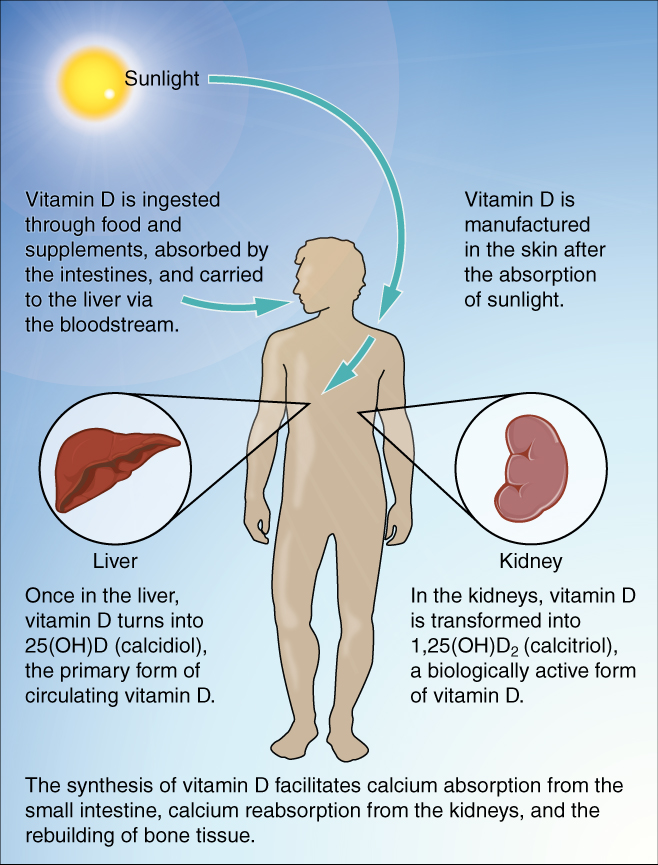
GH is not alone in stimulating bone growth and maintaining osseous tissue. Thyroxine, a hormone secreted by the thyroid gland promotes osteoblastic activity and the synthesis of bone matrix. During puberty, the sex hormones (estrogen in girls, testosterone in boys) also come into play. They too promote osteoblastic activity and production of bone matrix, and in addition, are responsible for the growth spurt that often occurs during adolescence. They also promote the conversion of the epiphyseal plate to the epiphyseal line (i.e., cartilage to its bony remnant), thus bringing an end to the longitudinal growth of bones. Additionally, calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, is produced by the kidneys and stimulates the absorption of calcium and phosphate from the digestive tract.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?