| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When scientists first began to observe stained blood slides, it quickly became evident that leukocytes could be divided into two groups, according to whether their cytoplasm contained highly visible granules:
We will consider the granular leukocytes in order from most common to least common. All of these are produced in the red bone marrow and have a short lifespan of hours to days. They typically have a lobed nucleus and are classified according to which type of stain best highlights their granules ( [link] ).
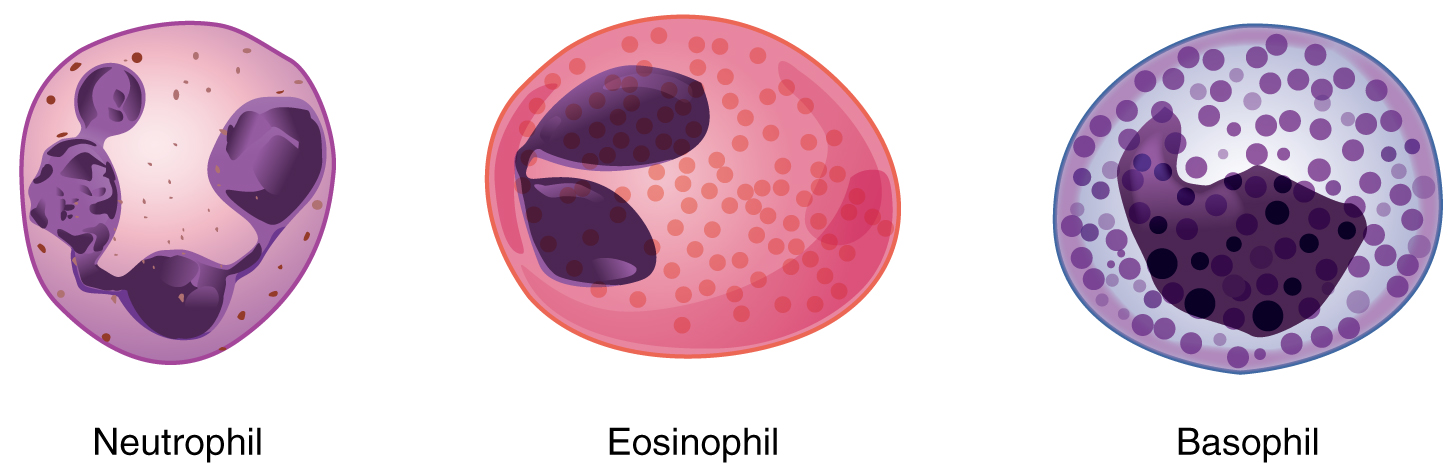
The most common of all the leukocytes, neutrophils will normally comprise 50–70 percent of total leukocyte count. They are 10–12 µ m in diameter, significantly larger than erythrocytes. They are called neutrophils because their granules show up most clearly with stains that are chemically neutral (neither acidic nor basic). The granules are numerous but quite fine and normally appear light lilac. The nucleus has a distinct lobed appearance and may have two to five lobes, the number increasing with the age of the cell. Older neutrophils have increasing numbers of lobes and are often referred to as polymorphonuclear (a nucleus with many forms), or simply “polys.” Younger and immature neutrophils begin to develop lobes and are known as “bands.”
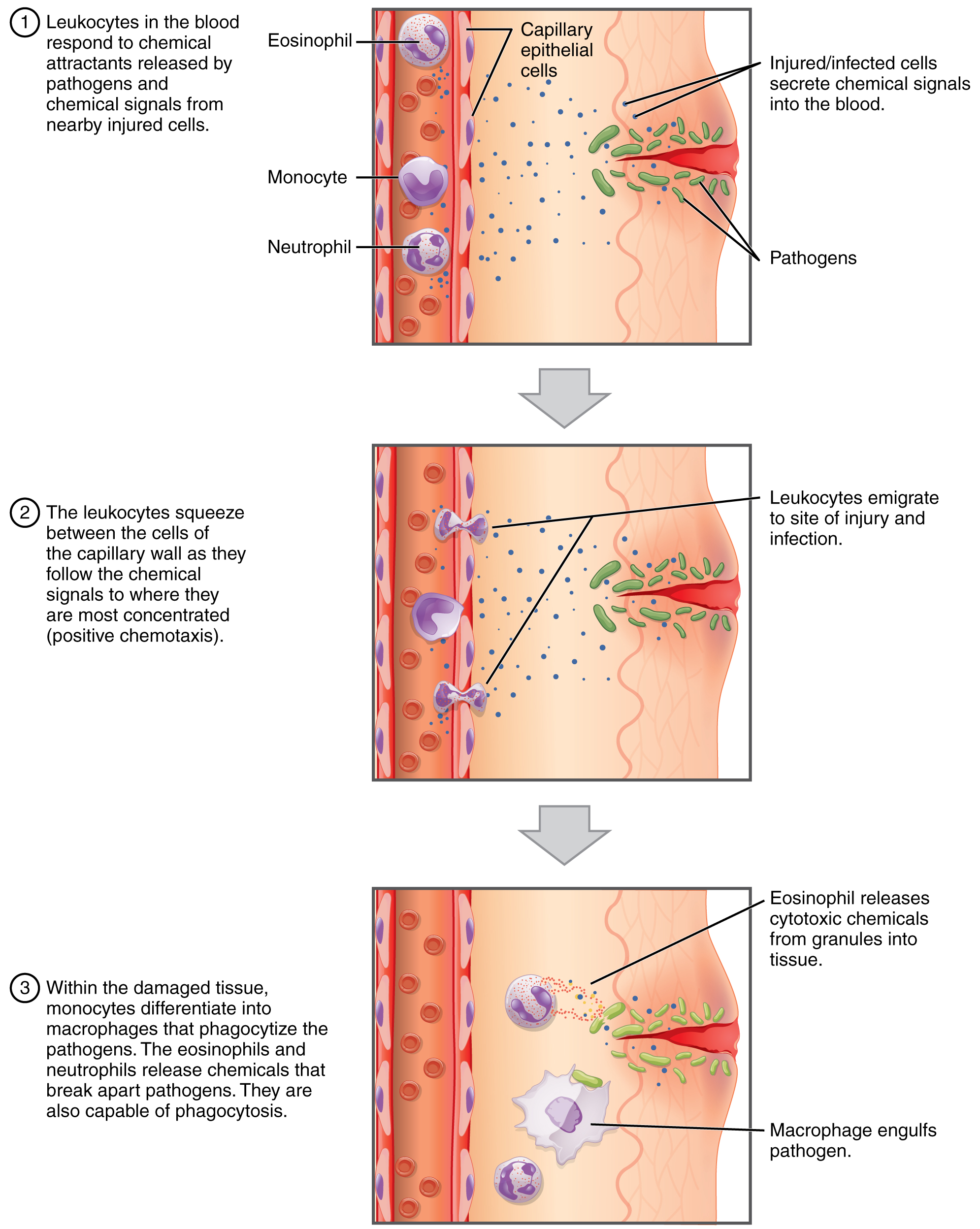
Neutrophils are rapid responders to the site of infection and are efficient phagocytes with a preference for bacteria. Their granules include lysozyme , an enzyme capable of lysing, or breaking down, bacterial cell walls; oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide; and defensins , proteins that bind to and puncture bacterial and fungal plasma membranes, so that the cell contents leak out. Abnormally high counts of neutrophils indicate infection and/or inflammation, particularly triggered by bacteria, but are also found in burn patients and others experiencing unusual stress. A burn injury increases the proliferation of neutrophils in order to fight off infection that can result from the destruction of the barrier of the skin. Low counts may be caused by drug toxicity and other disorders, and may increase an individual’s susceptibility to infection.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?