| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In addition to their primary function of returning blood to the heart, veins may be considered blood reservoirs, since systemic veins contain approximately 64 percent of the blood volume at any given time ( [link] ). Their ability to hold this much blood is due to their high capacitance , that is, their capacity to distend (expand) readily to store a high volume of blood, even at a low pressure. The large lumens and relatively thin walls of veins make them far more distensible than arteries; thus, they are said to be capacitance vessels .
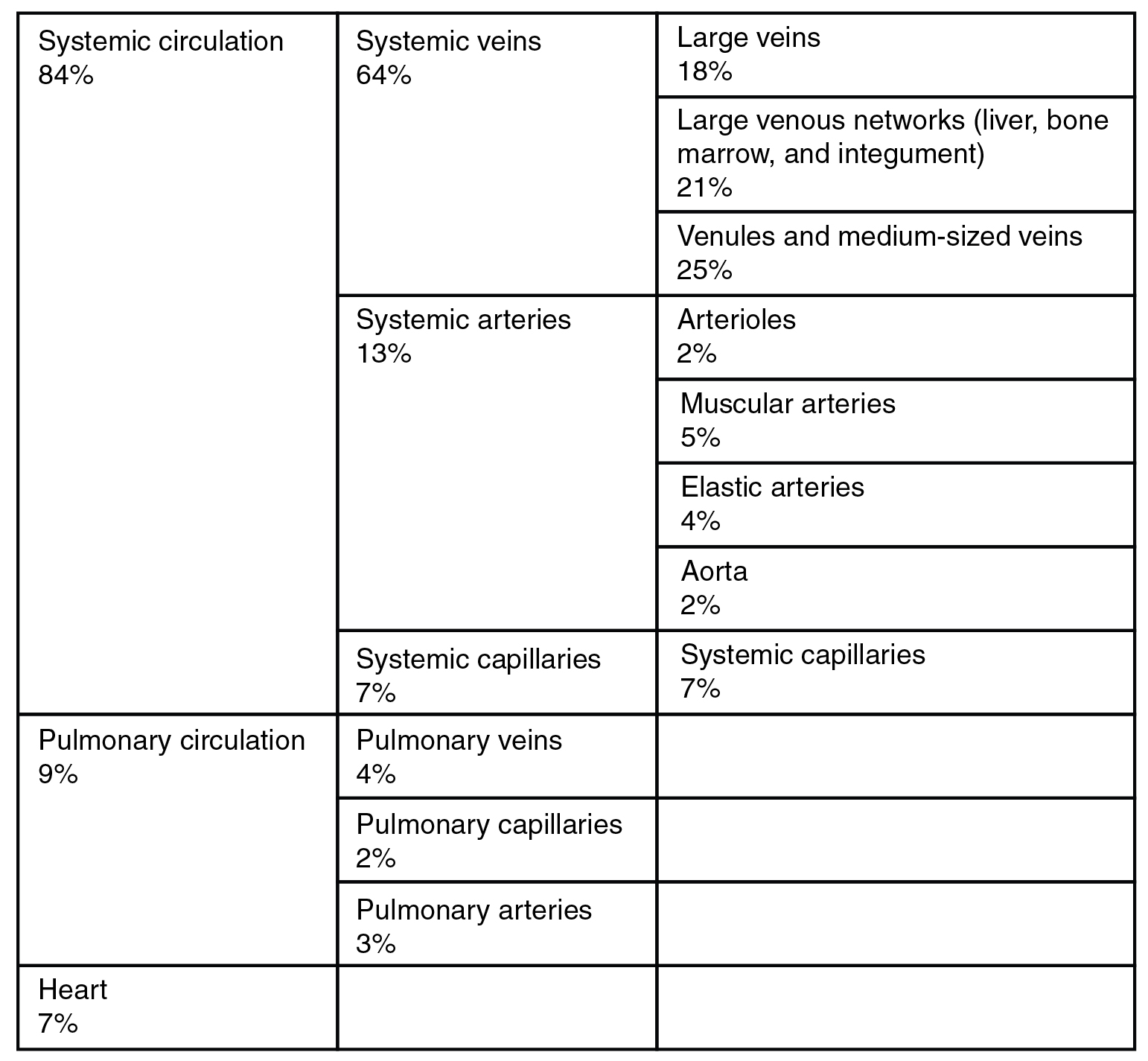
When blood flow needs to be redistributed to other portions of the body, the vasomotor center located in the medulla oblongata sends sympathetic stimulation to the smooth muscles in the walls of the veins, causing constriction—or in this case, venoconstriction. Less dramatic than the vasoconstriction seen in smaller arteries and arterioles, venoconstriction may be likened to a “stiffening” of the vessel wall. This increases pressure on the blood within the veins, speeding its return to the heart. As you will note in [link] , approximately 21 percent of the venous blood is located in venous networks within the liver, bone marrow, and integument. This volume of blood is referred to as venous reserve . Through venoconstriction, this “reserve” volume of blood can get back to the heart more quickly for redistribution to other parts of the circulation.
Vascular technicians are specialists in imaging technologies that provide information on the health of the vascular system. They may also assist physicians in treating disorders involving the arteries and veins. This profession often overlaps with cardiovascular technology, which would also include treatments involving the heart. Although recognized by the American Medical Association, there are currently no licensing requirements for vascular technicians, and licensing is voluntary. Vascular technicians typically have an Associate’s degree or certificate, involving 18 months to 2 years of training. The United States Bureau of Labor projects this profession to grow by 29 percent from 2010 to 2020.
Visit this site to learn more about vascular surgery.
Visit this site to learn more about vascular technicians.
Blood pumped by the heart flows through a series of vessels known as arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins before returning to the heart. Arteries transport blood away from the heart and branch into smaller vessels, forming arterioles. Arterioles distribute blood to capillary beds, the sites of exchange with the body tissues. Capillaries lead back to small vessels known as venules that flow into the larger veins and eventually back to the heart.
The arterial system is a relatively high-pressure system, so arteries have thick walls that appear round in cross section. The venous system is a lower-pressure system, containing veins that have larger lumens and thinner walls. They often appear flattened. Arteries, arterioles, venules, and veins are composed of three tunics known as the tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa. Capillaries have only a tunica intima layer. The tunica intima is a thin layer composed of a simple squamous epithelium known as endothelium and a small amount of connective tissue. The tunica media is a thicker area composed of variable amounts of smooth muscle and connective tissue. It is the thickest layer in all but the largest arteries. The tunica externa is primarily a layer of connective tissue, although in veins, it also contains some smooth muscle. Blood flow through vessels can be dramatically influenced by vasoconstriction and vasodilation in their walls.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?