| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
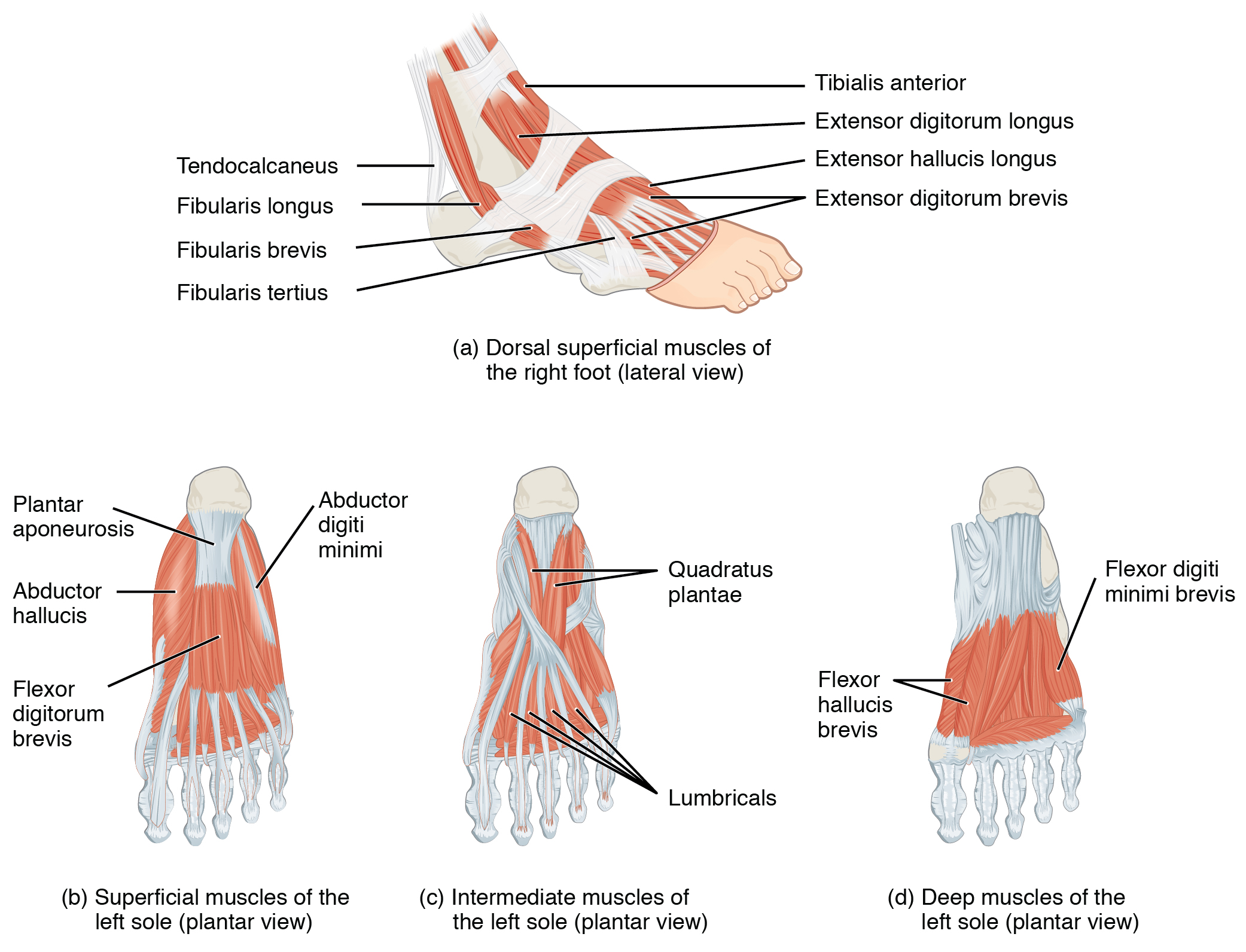
The lateral compartment of the leg includes two muscles: the fibularis longus (peroneus longus) and the fibularis brevis (peroneus brevis). The superficial muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg all insert onto the calcaneal tendon (Achilles tendon), a strong tendon that inserts into the calcaneal bone of the ankle. The muscles in this compartment are large and strong and keep humans upright. The most superficial and visible muscle of the calf is the gastrocnemius . Deep to the gastrocnemius is the wide, flat soleus . The plantaris runs obliquely between the two; some people may have two of these muscles, whereas no plantaris is observed in about seven percent of other cadaver dissections. The plantaris tendon is a desirable substitute for the fascia lata in hernia repair, tendon transplants, and repair of ligaments. There are four deep muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg as well: the popliteus , flexor digitorum longus , flexor hallucis longus , and tibialis posterior .
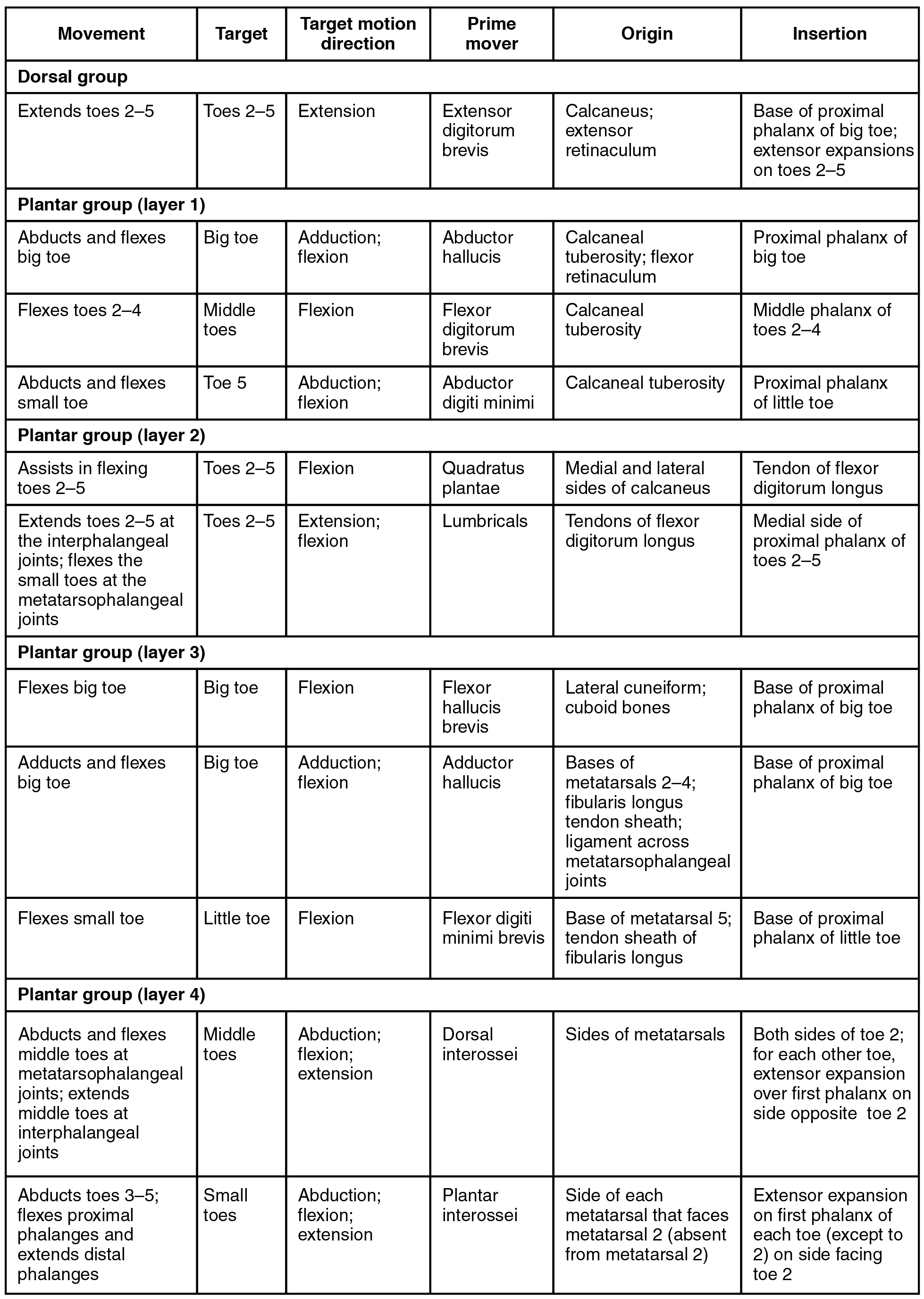
The foot also has intrinsic muscles, which originate and insert within it (similar to the intrinsic muscles of the hand). These muscles primarily provide support for the foot and its arch, and contribute to movements of the toes ( [link] and [link] ). The principal support for the longitudinal arch of the foot is a deep fascia called plantar aponeurosis , which runs from the calcaneus bone to the toes (inflammation of this tissue is the cause of “plantar fasciitis,” which can affect runners. The intrinsic muscles of the foot consist of two groups. The dorsal group includes only one muscle, the extensor digitorum brevis . The second group is the plantar group , which consists of four layers, starting with the most superficial.
The pelvic girdle attaches the legs to the axial skeleton. The hip joint is where the pelvic girdle and the leg come together. The hip is joined to the pelvic girdle by many muscles. In the gluteal region, the psoas major and iliacus form the iliopsoas. The large and strong gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus extend and abduct the femur. Along with the gluteus maximus, the tensor fascia lata muscle forms the iliotibial tract. The lateral rotators of the femur at the hip are the piriformis, obturator internus, obturator externus, superior gemellus, inferior gemellus, and quadratus femoris. On the medial part of the thigh, the adductor longus, adductor brevis, and adductor magnus adduct the thigh and medially rotate it. The pectineus muscle adducts and flexes the femur at the hip.
The thigh muscles that move the femur, tibia, and fibula are divided into medial, anterior, and posterior compartments. The medial compartment includes the adductors, pectineus, and the gracilis. The anterior compartment comprises the quadriceps femoris, quadriceps tendon, patellar ligament, and the sartorius. The quadriceps femoris is made of four muscles: the rectus femoris, the vastus lateralis, the vastus medius, and the vastus intermedius, which together extend the knee. The posterior compartment of the thigh includes the hamstrings: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and the semimembranosus, which all flex the knee.
The muscles of the leg that move the foot and toes are divided into anterior, lateral, superficial- and deep-posterior compartments. The anterior compartment includes the tibialis anterior, the extensor hallucis longus, the extensor digitorum longus, and the fibularis (peroneus) tertius. The lateral compartment houses the fibularis (peroneus) longus and the fibularis (peroneus) brevis. The superficial posterior compartment has the gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris; and the deep posterior compartment has the popliteus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?