| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
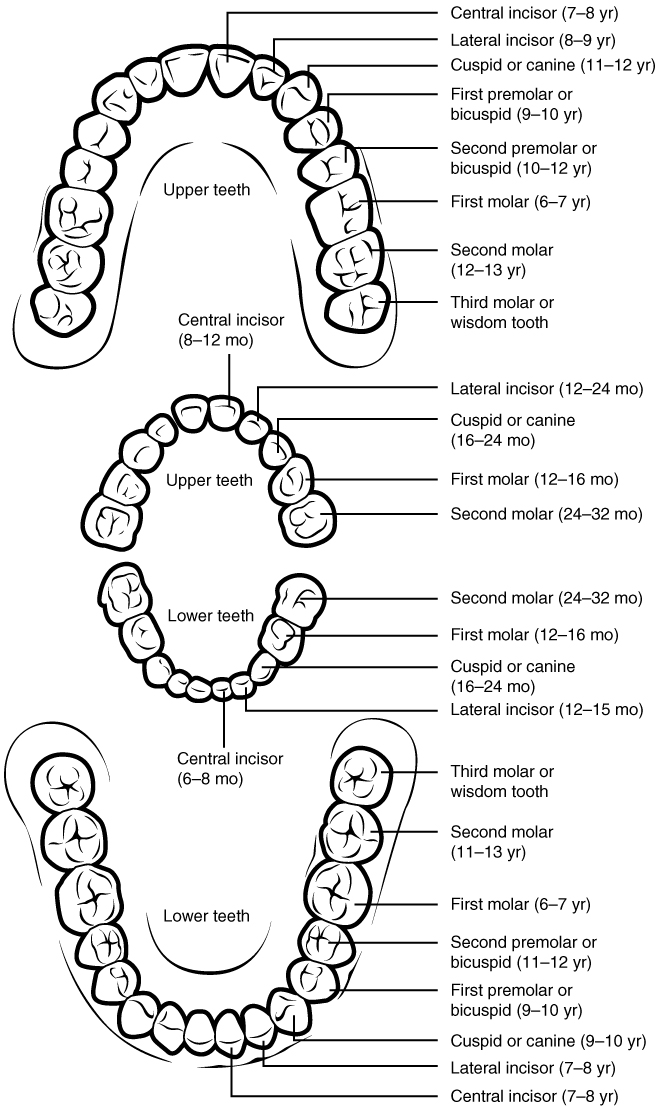
The teeth are secured in the alveolar processes (sockets) of the maxilla and the mandible. Gingivae (commonly called the gums) are soft tissues that line the alveolar processes and surround the necks of the teeth. Teeth are also held in their sockets by a connective tissue called the periodontal ligament.
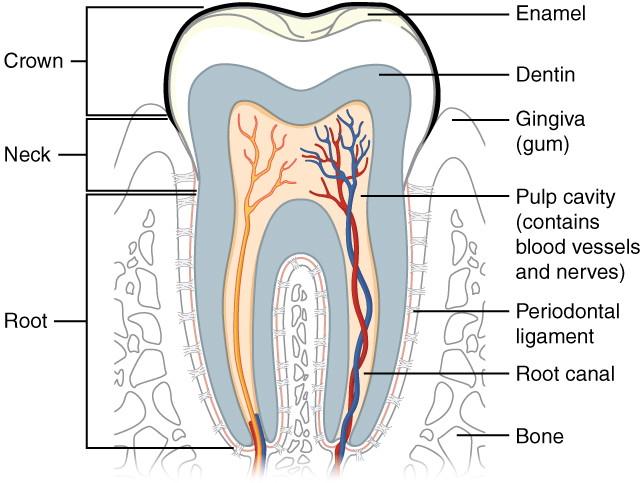
The two main parts of a tooth are the crown , which is the portion projecting above the gum line, and the root , which is embedded within the maxilla and mandible. Both parts contain an inner pulp cavity , containing loose connective tissue through which run nerves and blood vessels. The region of the pulp cavity that runs through the root of the tooth is called the root canal. Surrounding the pulp cavity is dentin , a bone-like tissue. In the root of each tooth, the dentin is covered by an even harder bone-like layer called cementum . In the crown of each tooth, the dentin is covered by an outer layer of enamel , the hardest substance in the body ( [link] ).
Although enamel protects the underlying dentin and pulp cavity, it is still nonetheless susceptible to mechanical and chemical erosion, or what is known as tooth decay. The most common form, dental caries (cavities) develops when colonies of bacteria feeding on sugars in the mouth release acids that cause soft tissue inflammation and degradation of the calcium crystals of the enamel. The digestive functions of the mouth are summarized in [link] .
| Digestive Functions of the Mouth | ||
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Action | Outcome |
| Lips and cheeks | Confine food between teeth |
|
| Salivary glands | Secrete saliva |
|
| Tongue’s extrinsic muscles | Move tongue sideways, and in and out |
|
| Tongue’s intrinsic muscles | Change tongue shape |
|
| Taste buds | Sense food in mouth and sense taste |
|
| Lingual glands | Secrete lingual lipase |
|
| Teeth | Shred and crush food |
|

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?