| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Despite differences in structure and function, all living cells in multicellular organisms have a surrounding cell membrane. As the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment. This cell membrane provides a protective barrier around the cell and regulates which materials can pass in or out.
The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of back-to-back phospholipids (a “bilayer”). Cholesterol is also present, which contributes to the fluidity of the membrane, and there are various proteins embedded within the membrane that have a variety of functions.
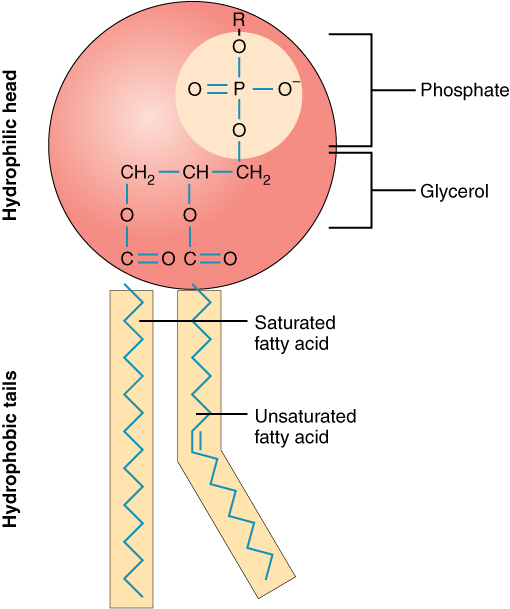
A single phospholipid molecule has a phosphate group on one end, called the “head,” and two side-by-side chains of fatty acids that make up the lipid tails ( [link] ). The phosphate group is negatively charged, making the head polar and hydrophilic—or “water loving.” A hydrophilic molecule (or region of a molecule) is one that is attracted to water. The phosphate heads are thus attracted to the water molecules of both the extracellular and intracellular environments. The lipid tails, on the other hand, are uncharged, or nonpolar, and are hydrophobic—or “water fearing.” A hydrophobic molecule (or region of a molecule) repels and is repelled by water. Some lipid tails consist of saturated fatty acids and some contain unsaturated fatty acids. This combination adds to the fluidity of the tails that are constantly in motion. Phospholipids are thus amphipathic molecules. An amphipathic molecule is one that contains both a hydrophilic and a hydrophobic region. In fact, soap works to remove oil and grease stains because it has amphipathic properties. The hydrophilic portion can dissolve in water while the hydrophobic portion can trap grease in micelles that then can be washed away.
The cell membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids. The lipid tails of one layer face the lipid tails of the other layer, meeting at the interface of the two layers. The phospholipid heads face outward, one layer exposed to the interior of the cell and one layer exposed to the exterior ( [link] ). Because the phosphate groups are polar and hydrophilic, they are attracted to water in the intracellular fluid. Intracellular fluid (ICF) is the fluid interior of the cell. The phosphate groups are also attracted to the extracellular fluid. Extracellular fluid (ECF) is the fluid environment outside the enclosure of the cell membrane. Interstitial fluid (IF) is the term given to extracellular fluid not contained within blood vessels. Because the lipid tails are hydrophobic, they meet in the inner region of the membrane, excluding watery intracellular and extracellular fluid from this space. The cell membrane has many proteins, as well as other lipids (such as cholesterol), that are associated with the phospholipid bilayer. An important feature of the membrane is that it remains fluid; the lipids and proteins in the cell membrane are not rigidly locked in place.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?