| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The female reproductive system functions to produce gametes and reproductive hormones, just like the male reproductive system; however, it also has the additional task of supporting the developing fetus and delivering it to the outside world. Unlike its male counterpart, the female reproductive system is located primarily inside the pelvic cavity ( [link] ). Recall that the ovaries are the female gonads. The gamete they produce is called an oocyte . We’ll discuss the production of oocytes in detail shortly. First, let’s look at some of the structures of the female reproductive system.
The external female reproductive structures are referred to collectively as the vulva ( [link] ). The mons pubis is a pad of fat that is located at the anterior, over the pubic bone. After puberty, it becomes covered in pubic hair. The labia majora (labia = “lips”; majora = “larger”) are folds of hair-covered skin that begin just posterior to the mons pubis. The thinner and more pigmented labia minora (labia = “lips”; minora = “smaller”) extend medial to the labia majora. Although they naturally vary in shape and size from woman to woman, the labia minora serve to protect the female urethra and the entrance to the female reproductive tract.
The superior, anterior portions of the labia minora come together to encircle the clitoris (or glans clitoris), an organ that originates from the same cells as the glans penis and has abundant nerves that make it important in sexual sensation and orgasm. The hymen is a thin membrane that sometimes partially covers the entrance to the vagina. An intact hymen cannot be used as an indication of “virginity”; even at birth, this is only a partial membrane, as menstrual fluid and other secretions must be able to exit the body, regardless of penile–vaginal intercourse. The vaginal opening is located between the opening of the urethra and the anus. It is flanked by outlets to the Bartholin’s glands (or greater vestibular glands).
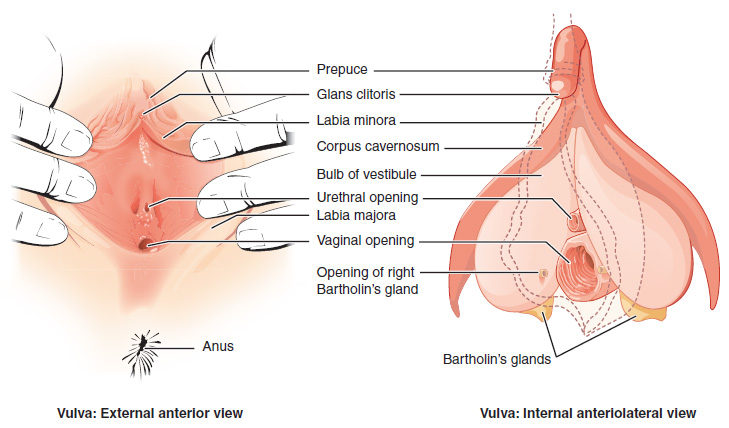
The vagina , shown at the bottom of [link] and [link] , is a muscular canal (approximately 10 cm long) that serves as the entrance to the reproductive tract. It also serves as the exit from the uterus during menses and childbirth. The outer walls of the anterior and posterior vagina are formed into longitudinal columns, or ridges, and the superior portion of the vagina—called the fornix—meets the protruding uterine cervix. The walls of the vagina are lined with an outer, fibrous adventitia; a middle layer of smooth muscle; and an inner mucous membrane with transverse folds called rugae . Together, the middle and inner layers allow the expansion of the vagina to accommodate intercourse and childbirth. The thin, perforated hymen can partially surround the opening to the vaginal orifice. The hymen can be ruptured with strenuous physical exercise, penile–vaginal intercourse, and childbirth. The Bartholin’s glands and the lesser vestibular glands (located near the clitoris) secrete mucus, which keeps the vestibular area moist.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?