| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
With up to 180 liters per day passing through the nephrons of the kidney, it is quite obvious that most of that fluid and its contents must be reabsorbed. That recovery occurs in the PCT, loop of Henle, DCT, and the collecting ducts ( [link] and [link] ). Various portions of the nephron differ in their capacity to reabsorb water and specific solutes. While much of the reabsorption and secretion occur passively based on concentration gradients, the amount of water that is reabsorbed or lost is tightly regulated. This control is exerted directly by ADH and aldosterone, and indirectly by renin. Most water is recovered in the PCT, loop of Henle, and DCT. About 10 percent (about 18 L) reaches the collecting ducts. The collecting ducts, under the influence of ADH, can recover almost all of the water passing through them, in cases of dehydration, or almost none of the water, in cases of over-hydration.
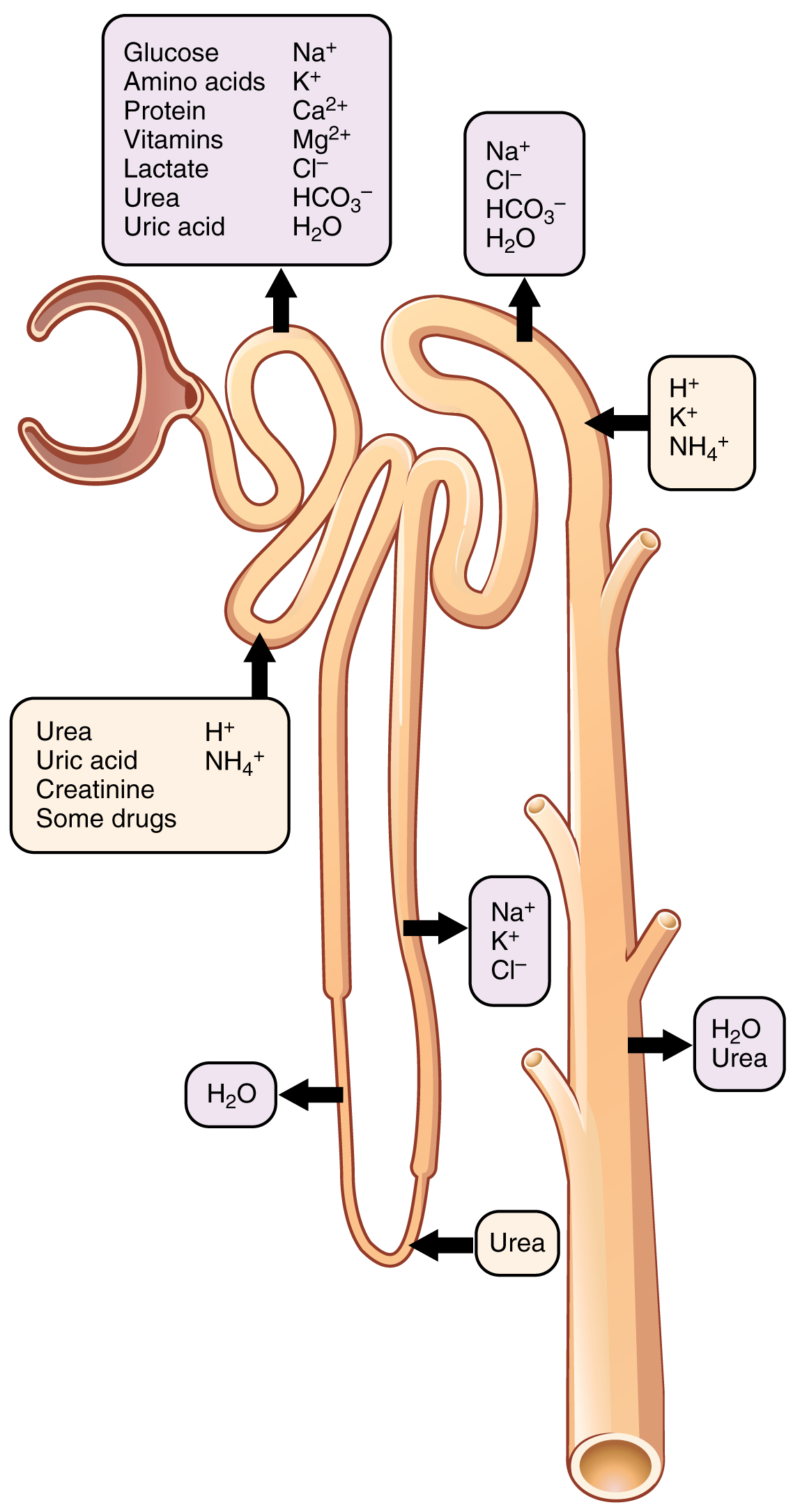
| Substances Secreted or Reabsorbed in the Nephron and Their Locations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substance | PCT | Loop of Henle | DCT | Collecting ducts |
| Glucose | Almost 100 percent reabsorbed; secondary active transport with Na + | |||
| Oligopeptides, proteins, amino acids | Almost 100 percent reabsorbed; symport with Na + | |||
| Vitamins | Reabsorbed | |||
| Lactate | Reabsorbed | |||
| Creatinine | Secreted | |||
| Urea | 50 percent reabsorbed by diffusion; also secreted | Secretion, diffusion in descending limb | Reabsorption in medullary collecting ducts; diffusion | |
| Sodium | 65 percent actively reabsorbed | 25 percent reabsorbed in thick ascending limb; active transport | 5 percent reabsorbed; active | 5 percent reabsorbed, stimulated by aldosterone; active |
| Chloride | Reabsorbed, symport with Na + , diffusion | Reabsorbed in thin and thick ascending limb; diffusion in ascending limb | Reabsorbed; diffusion | Reabsorbed; symport |
| Water | 67 percent reabsorbed osmotically with solutes | 15 percent reabsorbed in descending limb; osmosis | 8 percent reabsorbed if ADH; osmosis | Variable amounts reabsorbed, controlled by ADH, osmosis |
| Bicarbonate | 80–90 percent symport reabsorption with Na + | Reabsorbed, symport with Na + and antiport with Cl – ; in ascending limb | Reabsorbed antiport with Cl – | |
| H + | Secreted; diffusion | Secreted; active | Secreted; active | |
| NH 4 + | Secreted; diffusion | Secreted; diffusion | Secreted; diffusion | |
| HCO 3 – | Reabsorbed; diffusion | Reabsorbed; diffusion in ascending limb | Reabsorbed; diffusion | Reabsorbed; antiport with Na + |
| Some drugs | Secreted | Secreted; active | Secreted; active | |
| Potassium | 65 percent reabsorbed; diffusion | 20 percent reabsorbed in thick ascending limb; symport | Secreted; active | Secretion controlled by aldosterone; active |
| Calcium | Reabsorbed; diffusion | Reabsorbed in thick ascending limb; diffusion | Reabsorbed if parathyroid hormone present; active | |
| Magnesium | Reabsorbed; diffusion | Reabsorbed in thick ascending limb; diffusion | Reabsorbed | |
| Phosphate | 85 percent reabsorbed, inhibited by parathyroid hormone, diffusion | Reabsorbed; diffusion |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?