| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
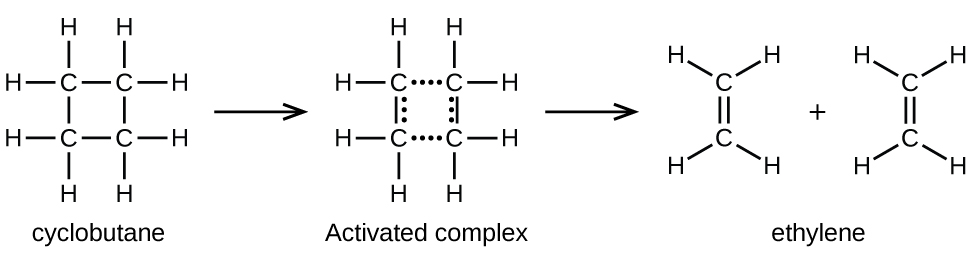
In a sample of C 4 H 8 , a few of the rapidly moving C 4 H 8 molecules collide with other rapidly moving molecules and pick up additional energy. When the C 4 H 8 molecules gain enough energy, they can transform into an activated complex, and the formation of ethylene molecules can occur. In effect, a particularly energetic collision knocks a C 4 H 8 molecule into the geometry of the activated complex. However, only a small fraction of gas molecules travel at sufficiently high speeds with large enough kinetic energies to accomplish this. Hence, at any given moment, only a few molecules pick up enough energy from collisions to react.
The rate of decomposition of C 4 H 8 is directly proportional to its concentration. Doubling the concentration of C 4 H 8 in a sample gives twice as many molecules per liter. Although the fraction of molecules with enough energy to react remains the same, the total number of such molecules is twice as great. Consequently, there is twice as much C 4 H 8 per liter, and the reaction rate is twice as fast:
A similar relationship applies to any unimolecular elementary reaction; the reaction rate is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant, and the reaction exhibits first-order behavior. The proportionality constant is the rate constant for the particular unimolecular reaction.
The collision and combination of two molecules or atoms to form an activated complex in an elementary reaction is called a bimolecular reaction . There are two types of bimolecular elementary reactions:
For the first type, in which the two reactant molecules are different, the rate law is first-order in A and first order in B :
For the second type, in which two identical molecules collide and react, the rate law is second order in A :
Some chemical reactions have mechanisms that consist of a single bimolecular elementary reaction. One example is the reaction of nitrogen dioxide with carbon monoxide:
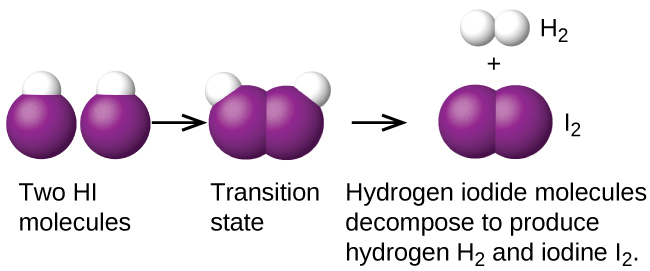
Another is the decomposition of two hydrogen iodide molecules to produce hydrogen, H 2 , and iodine, I 2 [link] :
Bimolecular elementary reactions may also be involved as steps in a multistep reaction mechanism. The reaction of atomic oxygen with ozone is one example:
An elementary termolecular reaction involves the simultaneous collision of three atoms, molecules, or ions. Termolecular elementary reactions are uncommon because the probability of three particles colliding simultaneously is less than one one-thousandth of the probability of two particles colliding. There are, however, a few established termolecular elementary reactions. The reaction of nitric oxide with oxygen appears to involve termolecular steps:
Likewise, the reaction of nitric oxide with chlorine appears to involve termolecular steps:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?