| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When a skeletal muscle fiber contracts, myosin heads attach to actin to form cross-bridges followed by the thin filaments sliding over the thick filaments as the heads pull the actin, and this results in sarcomere shortening, creating the tension of the muscle contraction. The cross-bridges can only form where thin and thick filaments already overlap, so that the length of the sarcomere has a direct influence on the force generated when the sarcomere shortens. This is called the length-tension relationship.
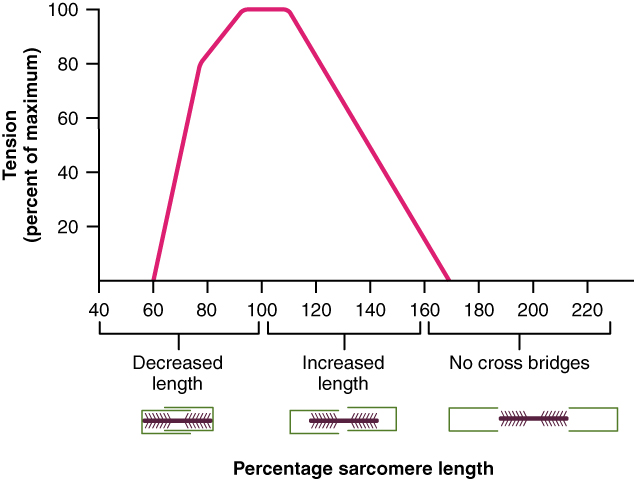
The ideal length of a sarcomere to produce maximal tension occurs at 80 percent to 120 percent of its resting length, with 100 percent being the state where the medial edges of the thin filaments are just at the most-medial myosin heads of the thick filaments ( [link] ). This length maximizes the overlap of actin-binding sites and myosin heads. If a sarcomere is stretched past this ideal length (beyond 120 percent), thick and thin filaments do not overlap sufficiently, which results in less tension produced. If a sarcomere is shortened beyond 80 percent, the zone of overlap is reduced with the thin filaments jutting beyond the last of the myosin heads and shrinks the H zone, which is normally composed of myosin tails. Eventually, there is nowhere else for the thin filaments to go and the amount of tension is diminished. If the muscle is stretched to the point where thick and thin filaments do not overlap at all, no cross-bridges can be formed, and no tension is produced in that sarcomere. This amount of stretching does not usually occur, as accessory proteins and connective tissue oppose extreme stretching.
A single action potential from a motor neuron will produce a single contraction in the muscle fibers of its motor unit. This isolated contraction is called a twitch . A twitch can last for a few milliseconds or 100 milliseconds, depending on the muscle type. The tension produced by a single twitch can be measured by a myogram , an instrument that measures the amount of tension produced over time ( [link] ). Each twitch undergoes three phases. The first phase is the latent period , during which the action potential is being propagated along the sarcolemma and Ca ++ ions are released from the SR. This is the phase during which excitation and contraction are being coupled but contraction has yet to occur. The contraction phase occurs next. The Ca ++ ions in the sarcoplasm have bound to troponin, tropomyosin has shifted away from actin-binding sites, cross-bridges formed, and sarcomeres are actively shortening to the point of peak tension. The last phase is the relaxation phase , when tension decreases as contraction stops. Ca ++ ions are pumped out of the sarcoplasm into the SR, and cross-bridge cycling stops, returning the muscle fibers to their resting state.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?